The rate constant for the first order decomposition of ethylene oxide into CH4andCO,
 to CH_4 +CO<span class=) ,isdescribedbylogk(s^(-1))=14.3-(12.5 xx 10^(4))/(T)K
,isdescribedbylogk(s^(-1))=14.3-(12.5 xx 10^(4))/(T)K
Then the activation of energy of the reaction is
2,39×105kJmol−1
2.39×103kJmol−1
4.78×105kJmol−1
4.78×102kJmol−1
The correct Answer is:B
logk=logA−Ea2.303RT
logk=14.34−12.5×104kT
From Eqs. (i) and (ii)
Ea2.303R=12.5×104k
Ea=(12.5×104k)×2.303×8.314Jk−1mol−1
=239×104Jmol−1=239×106Jmol−1
Ea=2.39×103kJmol−1
Topper's Solved these Questions
- CHEMICAL KINETICS Book:MHTCET PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS AND PRACTICE PAPERSChapter:CHEMICAL KINETICS Exercise:MHT CET CORNER
Explore 20 Videos
- CHEMICAL KINETICS Book:MHTCET PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS AND PRACTICE PAPERSChapter:CHEMICAL KINETICS Exercise:Exercise 1
Explore 63 Videos
- BIOMOLECULES Book:MHTCET PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS AND PRACTICE PAPERSChapter:BIOMOLECULES Exercise:MHT CET CORNER
Explore 24 Videos
- CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS AND ENERGETICBook:MHTCET PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS AND PRACTICE PAPERSChapter:CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS AND ENERGETICExercise:MHT CET Corner
Explore 40 Videos
Similar Questions
The rate constant and half - life of a first order reaction are related to each other as _____.
View SolutionRate of a reaction can be defined as
View SolutionGlucose on oxidation with bromine water yields gluconic acid. This reaction confirms the presence of
View SolutionIdentify an extensive property amongst the following:
View SolutionThe rate constant for the first order decomposition of ethylene oxide into CH4 and CO,
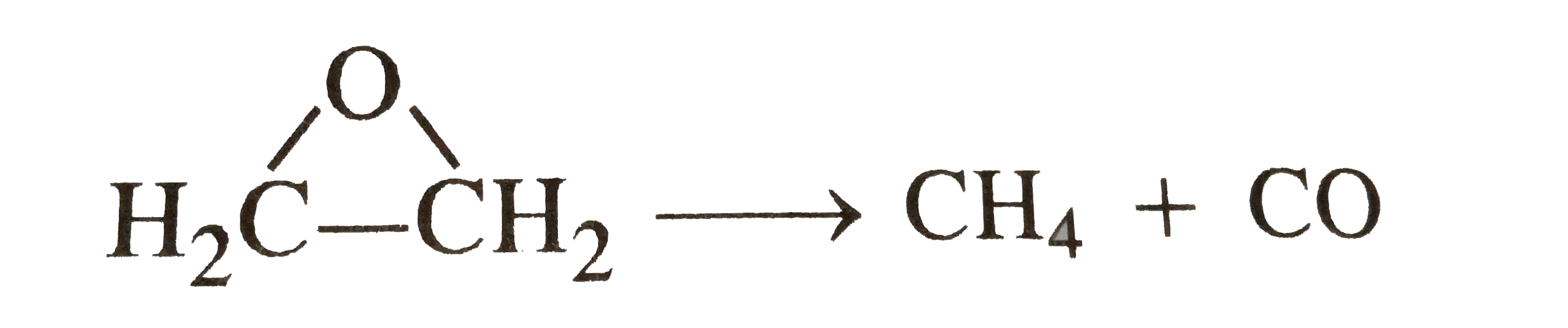
may be describe by
logk(ins−1)=14.34−1.25×104KT
The activation energy of the reaction is
View SolutionRate constant for the decomposition of ethylene oxide into CH_(4) and CO may be described be the equation. logk(s)^(-1)=14.34-(1.25xx10^(4))/(T) (a) What is the energy of activation of this reaction ? (b) What is the value of k at 670K ?
View SolutionFor a first order reaction the rate constant at 500 k is 8xx10^(-4)s^(-1) . Calculate the frequency, if the energy of activation for the reaction is 190 "kJ mol"^(-1) .
View SolutionThe rate constant of a first order reaction is 2.31×10−3s−1 Calculate the half-life period of the activation energy of the reaction.
View SolutionThe rate constant for a first order decomposition reaction is given by log K=10 - 1000/T .Then,what will be activation energy in kcal/mol?
View SolutionThe rate constant for a first order decomposition reaction is given by "log K=\(10-\frac{1000}{T}\) .Then,what will be activation energy in kcal/mol?
View SolutionRate constant for the decomposition of ethylene oxide into CH4 and CO may be described by the equation logl(s−1)=14.34−1.25×104T
(a) What is the energy of activation of this reaction ?
(b) What is the value of k at 670K ?
View SolutionIf the first order rate constants for the decomposition of enthy 1 iodide at 600 K and 700 K are 2.0xx10^(-5) s^(-1) and 2.0xx10^(-4) s^(-1) respectively, the activation energy for this reaction in kJ mol^(-1) is
View SolutionThe rate constant for the first order reaction is given by log_(10) k = 14.34-1.25xx10^4 T . Calculate activation energy of the reaction (239.3 kJ//mol)
View SolutionFor a first order reaction the rate constant for decomposition of N_(2)O is 6xx10^(-4)sec^(-1) . The half-life period for the decomposition in seconds is :
View SolutionThe rate constant of the first order reaction , that is decomposition of ethylene oxide into CH4 and CO, may be described by the following equation
logk(s−1)=14.34−1.25×104TK
Find (a) energy of activation ,
View SolutionThe rate constant of the first order reaction , that is decomposition of ethylene oxide into CH4 and CO, may be described by the following equation
logk(s−1)=14.34−1.25×104TK
rate constant at 397∘C
View Solution

