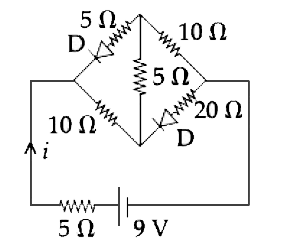
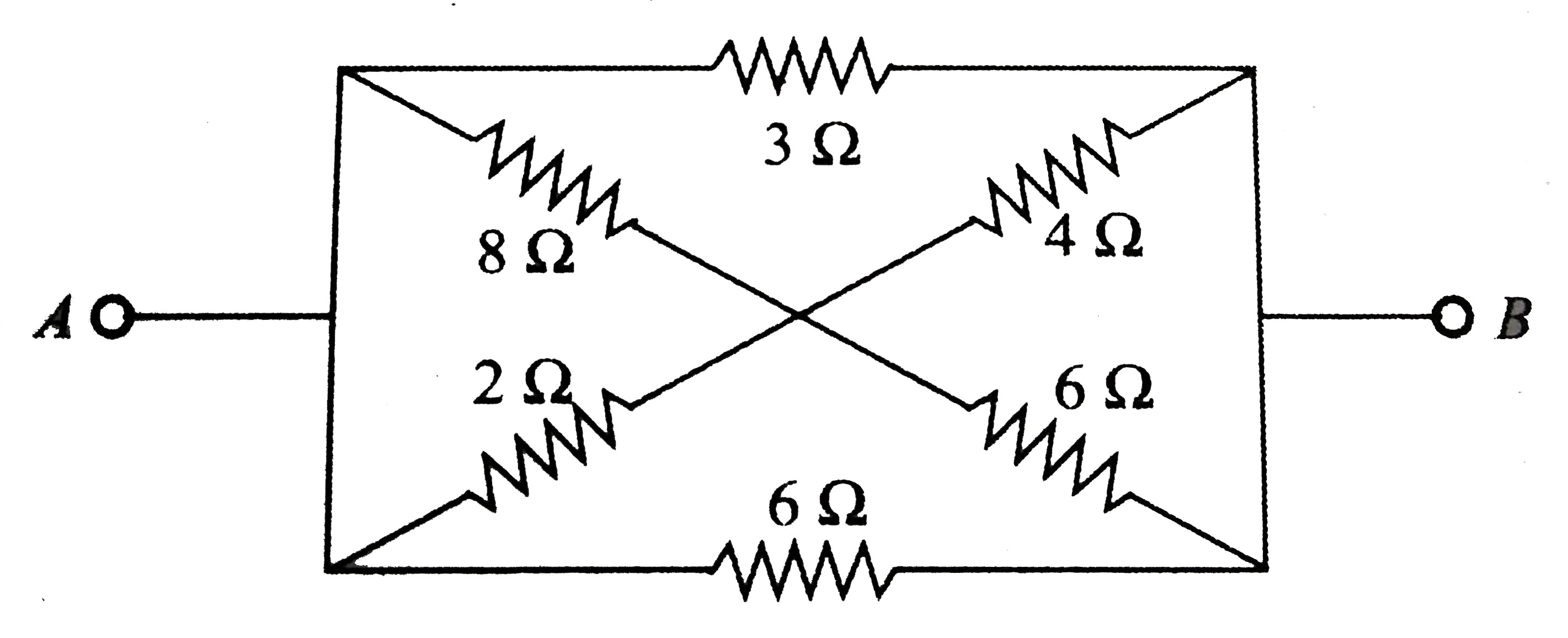
When some potential differece is maintained between A and B, current I enters the network at A and leaves at B
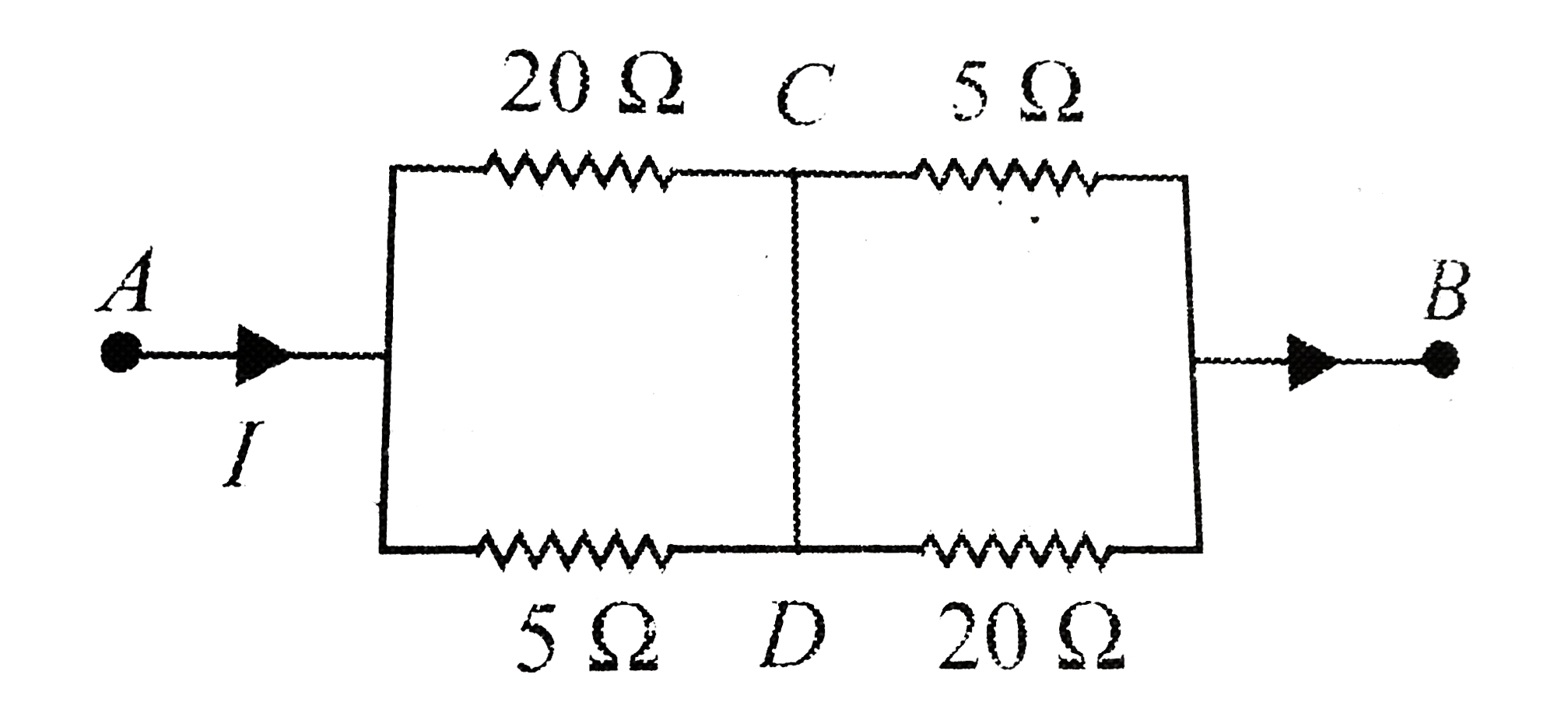
A
The equivalent resistance between A and B is 8Ω.
B
C and D are at the same potential.
C
No current flows between C and D.
D
Current 3I/5 flows from D to C.
Video Solution
Text Solution
The correct Answer is:A, B, D
As C and D are joined, they must be at the same potential and
may be treated as the same point. This gives the equivalent
resistance as 8Ω. We distribute current in the network using
symmetry.

VA−VD=VA−VC
or 20i=5(I−i)
or i=I/5
I=2i=I−2I5=3I5= current flowing from D to C.
|
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
In the circuit shown in fig. some potential difference is applied between A and B. The equivalent resistance between A and B is R.
 ANo current flows through the 5Ω resistor.BR=15ΩCR=12.5ΩDR=185Ω
ANo current flows through the 5Ω resistor.BR=15ΩCR=12.5ΩDR=185ΩThe instantaneous potential differece between points A and B is :
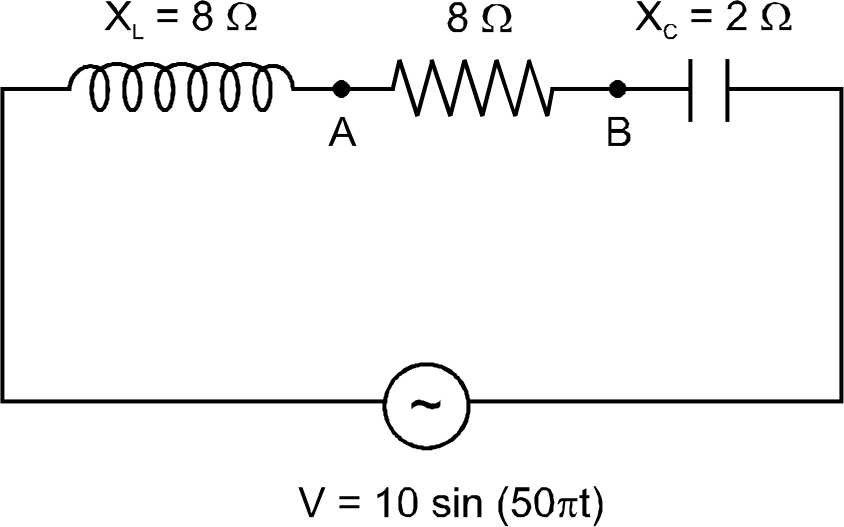 A8sin(50ωt+37π180)B8sin(50πt−37π180)C10sin(50πt)D10cos(50πt)
A8sin(50ωt+37π180)B8sin(50πt−37π180)C10sin(50πt)D10cos(50πt)Figure 7.37 shows a network of three resistances. When some potential difference is applied across the network , thermal powers dissipated by A,BandC are in the ratio
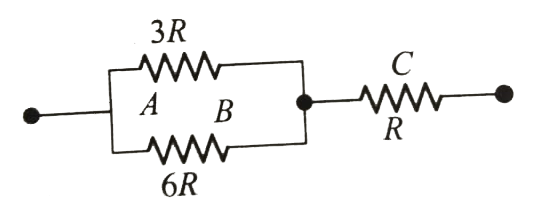 A2:3:4B2:4:3C4:2:3D3:2:4
A2:3:4B2:4:3C4:2:3D3:2:4
Find the potential difference between points A and B (VB−VA) in the network
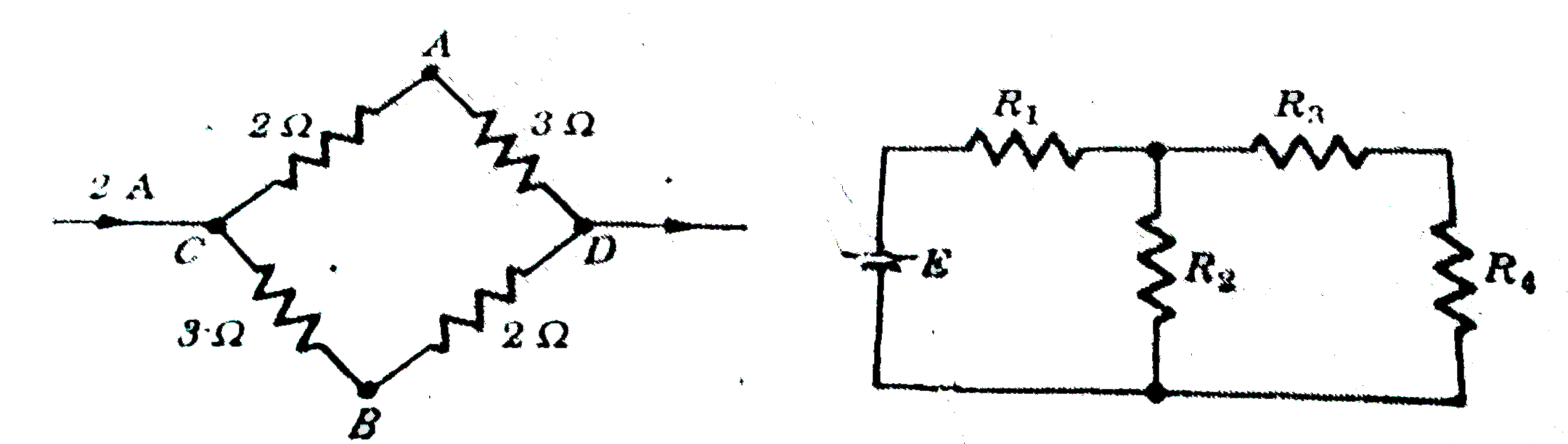
View SolutionFind the effective resistance between points A and B for the network
View SolutionThe effective resistance between A and B in the network shown is
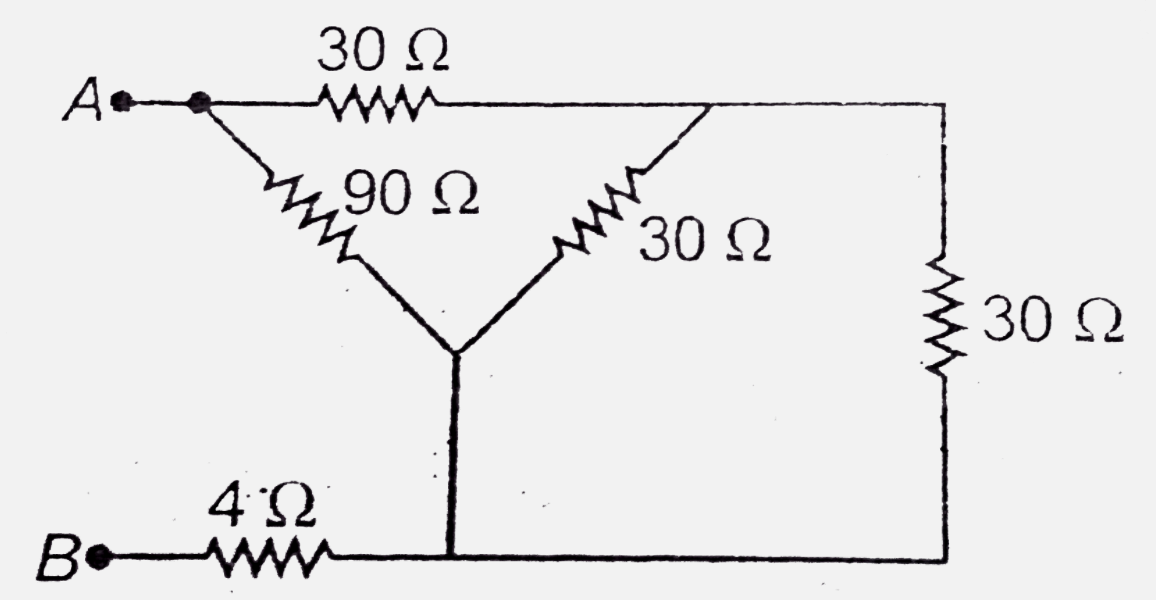
View SolutionFind the potential difference between the points A and B for the network shown in Fig. 4.52.

View SolutionThe equivalent resistance between A and B in the network in fig.,
View Solution