Ram ans Shyam purchased two electric tea kettles A and B of same size, same thickness, and same volume of 0.4L. They studied the specification of kettles as under
Ke≤A:
specific heat capacity =1680Jkg−1K−1
Mass = 200 g
Cost = Rs. 400
Kettle B:
Specific heat capacity = 2450Jkg−1K−1
Mass = 400 g
Cost = Rs. 400
When kettle A is switched on with constant potential source, the tea begins to boil in 6 min. When kettle B is switched on with the same source separately, then tea begins to boil in 8 min. The efficiengy of kettle is defined as
(Energy used for liquid heating)/(Total energy supplied)
They made discussion on specification and efficiency of kettles and subsequently prepared a list of questions to draw the conclusions. Some of them are as under (assume specific heat of tea liquid as 4200Jkg−1K−1 and density 1000kgm−3
Ratio of efficiency consumed charges for one time boiling of tea in kettle A to that in kettle B is
3:5
2:3
3:4
1:1
The correct Answer is:C
c. η=0.4×4200(θ−θ1)420×4.8(θ−θ1)×100=250/3=83.34%
η=0.4×4200(θ−θ1)420×6.4(θ−θ1)×100=62.5%
HA=0.2×1680(θ−θ1)+0.4×4200(θ−θ1)
=420×[0.8+4](θ−θ1)
HB=0.4×2450(θ−θ1)+0.4×4200(θ−θ1)
=420×(2.4+4)(θ−θ1) .
HAHB=4.86.4=34
HA=V2RA×6
HB=V2RB×8
HAHB=RBRA×34butHAHB=34
Then RB=RA
Topper's Solved these Questions
- MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3Book:CENGAGE PHYSICSChapter:MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3Exercise:Interger Answer type
Explore 20 Videos
- MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3Book:CENGAGE PHYSICSChapter:MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3Exercise:Fill in the blanks
Explore 10 Videos
- MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3Book:CENGAGE PHYSICSChapter:MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3Exercise:Assertion and Reason Type
Explore 8 Videos
- MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDSBook:CENGAGE PHYSICSChapter:MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDSExercise:Question Bank
Explore 4 Videos
- MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 5Book:CENGAGE PHYSICSChapter:MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 5Exercise:Integer
Explore 12 Videos
Similar Questions
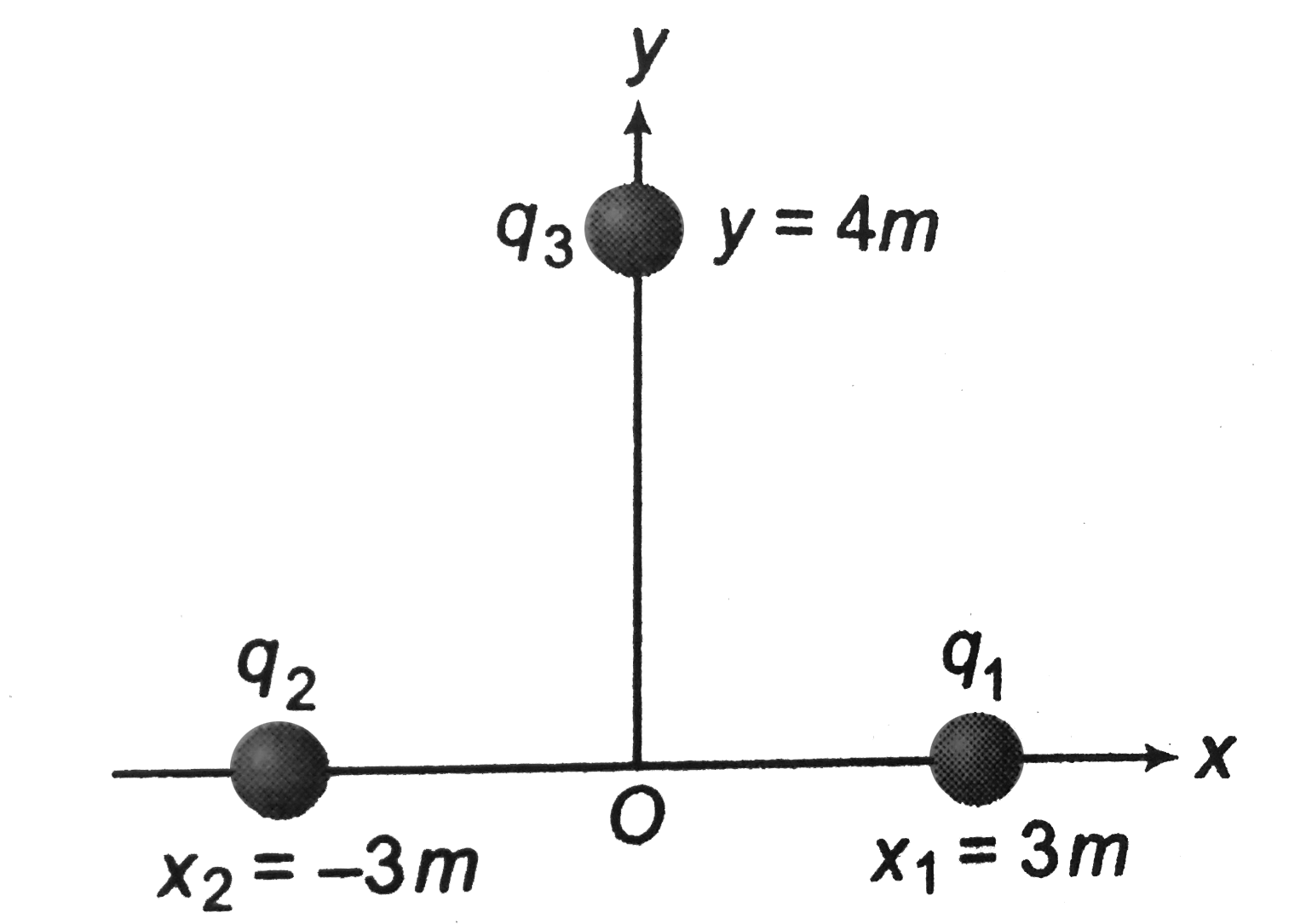
Two point charges q1=q2=2μC are fixed at x1=+3m and x2=−3m as shown in figure. A third particle of mass 1 g and charge q3=−4μC are released from rest at y=4.0m.Find the speed of the particle as it reaches the origin.
View SolutionFive identical capacitor paltes, each of area A, are arranged such that adjacent plates are at a distance d apart, the plates are connected to a source of emf V as shown in the figure
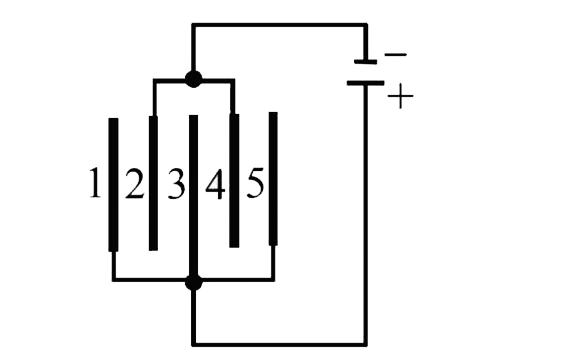
The charge on plate 1 is ………..and on plate 4 is.............
View SolutionStatement I: When air between the plates of a parallel plate condenser is replaced by an insulating dielectric medium, its capacity decreases.
Statement II: Electric field intensity between the plates with dielectric in between is reduced.
View SolutionThe diameter of a brass rod is 4 mm and Young's modulus of brass is 9×1010N/m2. The force required to stretch by 0.1 % of its length is
View SolutionA charged particle enters a uniform magnetic field with velocity v0=4m/s perpendicular to it, the length of magnetic field is x=(√32)R, where R is the radius of the circular path of the particle in the field. Find the magnitude of charge in velocity (in m/s) of the particle when it comes out of the field.
View SolutionRam ans Shyam purchased two electric tea kettles A and B of same size, same thickness, and same volume of 0.4L. They studied the specification of kettles as under
Ke≤A:
specific heat capacity =1680Jkg−1K−1
Mass = 200 g
Cost = Rs. 400
Kettle B:
Specific heat capacity = 2450Jkg−1K−1
Mass = 400 g
Cost = Rs. 400
When kettle A is switched on with constant potential source, the tea begins to boil in 6 min. When kettle B is switched on with the same source separately, then tea begins to boil in 8 min. The efficiengy of kettle is defined as
(Energy used for liquid heating)/(Total energy supplied)
They made discussion on specification and efficiency of kettles and subsequently prepared a list of questions to draw the conclusions. Some of them are as under (assume specific heat of tea liquid as 4200Jkg−1K−1 and density 1000kgm−3
Efficiency of kettle A is
View SolutionRam ans Shyam purchased two electric tea kettles A and B of same size, same thickness, and same volume of 0.4L. They studied the specification of kettles as under
Ke≤A:
specific heat capacity =1680Jkg−1K−1
Mass = 200 g
Cost = Rs. 400
Kettle B:
Specific heat capacity = 2450Jkg−1K−1
Mass = 400 g
Cost = Rs. 400
When kettle A is switched on with constant potential source, the tea begins to boil in 6 min. When kettle B is switched on with the same source separately, then tea begins to boil in 8 min. The efficiengy of kettle is defined as
(Energy used for liquid heating)/(Total energy supplied)
They made discussion on specification and efficiency of kettles and subsequently prepared a list of questions to draw the conclusions. Some of them are as under (assume specific heat of tea liquid as 4200Jkg−1K−1 and density 1000kgm−3
Efficiency of kettle B is .
View SolutionRam ans Shyam purchased two electric tea kettles A and B of same size, same thickness, and same volume of 0.4L. They studied the specification of kettles as under Kettle A: specific heat capacity = 1680 Jkg^(-1)K^(-1) Mass = 200 g Cost = Rs. 400 Kettle B: Specific heat capacity = 2450 Jkg^(-1) K^(-1) Mass = 400 g Cost = Rs. 400 When kettle A is switched on with constant potential source, the tea begins to boil in 6 min. When kettle B is switched on with the same source separately, then tea begins to boil in 8 min. The efficiengy of kettle is defined as (Energy used for liquid heating)/(Total energy supplied) They made discussion on specification and efficiency of kettles and subsequently prepared a list of questions to draw the conclusions. Some of them are as under (assume specific heat of tea liquid as 4200J kg^(-1)K^(-1) and density 1000 kgm^(-3) If resistances of coil of kettles A and B are R_(A) and R_(B) , respectively, then we can say
View SolutionRam ans Shyam purchased two electric tea kettles A and B of same size, same thickness, and same volume of 0.4L. They studied the specification of kettles as under Kettle A: specific heat capacity = 1680 Jkg^(-1)K^(-1) Mass = 200 g Cost = Rs. 400 Kettle B: Specific heat capacity = 2450 Jkg^(-1) K^(-1) Mass = 400 g Cost = Rs. 400 When kettle A is switched on with constant potential source, the tea begins to boil in 6 min. When kettle B is switched on with the same source separately, then tea begins to boil in 8 min. The efficiengy of kettle is defined as (Energy used for liquid heating)/(Total energy supplied) They made discussion on specification and efficiency of kettles and subsequently prepared a list of questions to draw the conclusions. Some of them are as under (assume specific heat of tea liquid as 4200J kg^(-1)K^(-1) and density 1000 kgm^(-3) If both the kettles are joined with the same source in series one after the other, then boiling starts in kettle A and kettle B after
View SolutionAn electric kettle of 1200W has 1 kg water at 20^@C . The water equivalent of the kettle is 500g . The time required to heat water from 20^(@) to 100^(@)C will be (specific heat of water = 4200 J//kg^(@)C) .
View SolutionWhat will be the result of mixing 2kg of cooper at 100^(@)C with 0.75 kg of ice at 0^(@)C (Specific heat capacity of cooper =378J kg^(-1)K^(-1) specific heat capacity of water =4200 J kg^(-1)K^(-1) and specific latent heat of fusion of ice =336xx10^(3)Jkg^(-1) )
View SolutionA 500-W-200V electric kettle is used to prepare 4cups of tea How long will it take? Assume that a cup contains 250cc of water. Specific heat capacity of water 4200Jkf−1K−1 and the initial temeprature of water 250∘C. Also calcuate the cost of prepare tea if 1 B.O.T. costs 35 paise.
View SolutionObtain the value of specific heat of water in terms of Jkg^(-1)K^(-1) .
View SolutionThe specific heat capacities of an ideal gas at the constant pressure and at constant volume are 620 Jkg^(-1) K^(-1) and 420 Jkg^(-1) K^(-1) respectively. The density of the gas at STP is approximately,
View Solution50 g of copper is heated to increase its temperature by 10∘C. If the same quantity of heat is given to 10 gm of water, the rise in temperdture is (specific heat of copper= 420 JKg−1K−1, specific heat of water = 4200 jkg−1k−1)
View Solution

