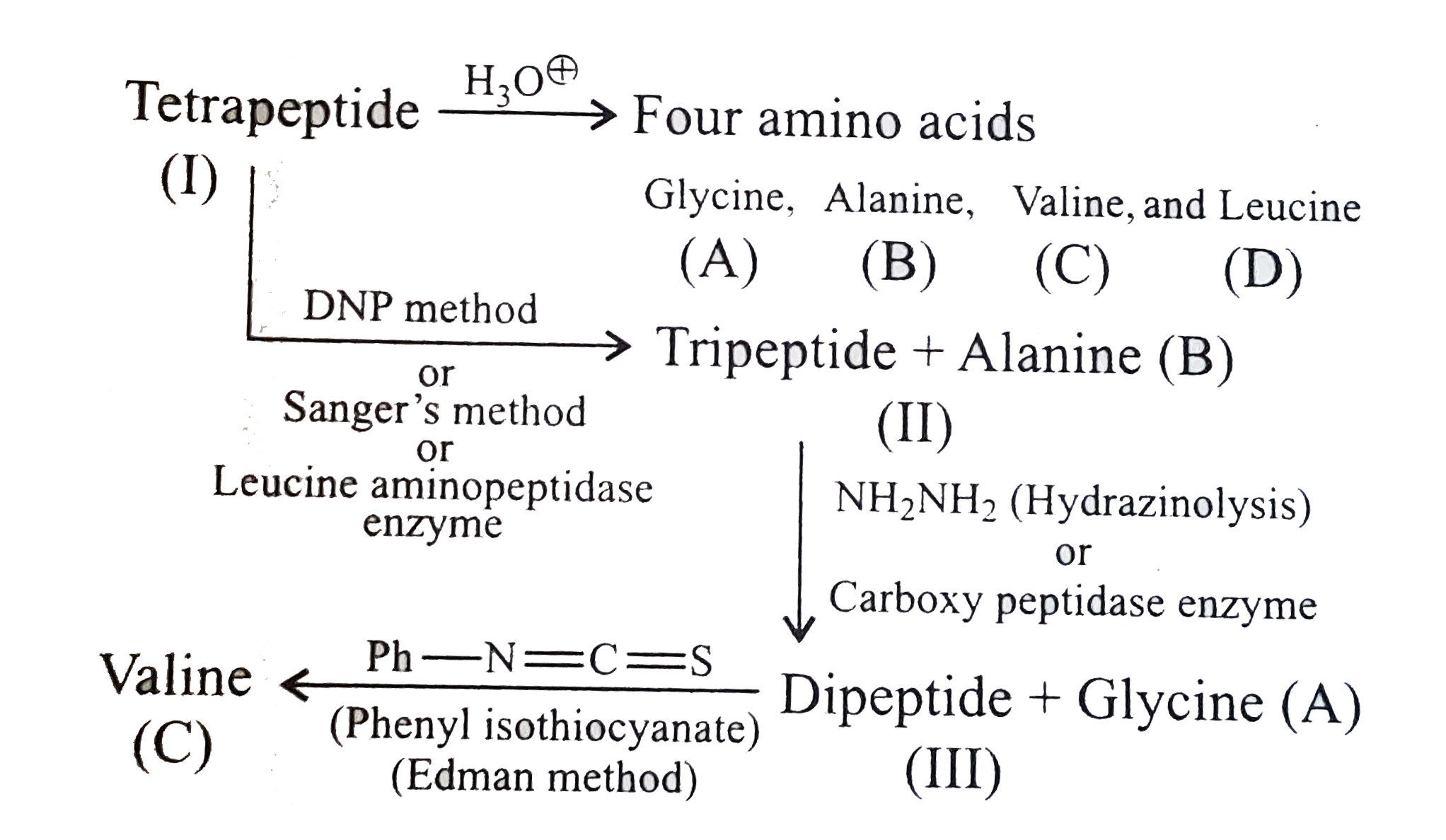
The tetrapeptide (I) is:
Gly → Leu → Val → Ala
Ala → Val → Gly → Leu
Gly → Val → Leu → Ala
Ala → Val → Leu → Gly
The correct Answer is:D
(1) DNP method or Leucine aminopeptidase enzyme releasess N−terminal amino acid.
Tetrapeptide(I)→Alanine(N-terminal)+Tripeptide
Ala(N-terminal)→Tripeptide
(2) Hydrazinolysis or carboxypeptidase enzyme releases C−terminal amino acid.
Tripetide(II)→Dipeptide+Glycine(C-terminal)
Ala(N-terminal)→Dipeptide→Gly(C-terminal)
(3) Dipeptide (III) now contains only two amino acids, valine and Leucine. Edman method releases N−terminal amino acid.

Similar Questions
A tetrapeptide is made of naturally occurring alanine, serine, glycine and valine. How many total numbers of possible sequences of the tetrapeptide is possible if the ECterminal amino acid is alanine?
View Solution(a) Write the Haworth structure of maltose.
(b) What is peptide linkages? How many peptide bonds are present in a tetrapeptide?
(c) Name the hormone which regulates blood sugar level in the body.
View Solution
Knowledge Check
Tetrapeptide is made of naturally occuring alanine , serine, glycine and valine . If the C-terminal amino acid is alanine and the N-terminal amino acid is chiral , the number of possible sequences of the tetrapeptide is
A12B8C6D4The number of peptide bonds present in an acyclic tetrapeptide is
A3B1C4D2The number of amino acids and number of peptide bonds in a linear tetrapeptide (made of different amino acids) are respectively.
A4 and 4B5 and 5C5 and 4D4 and 3
Atetrapeptide on complete hydrolysis gave Alanine, Glycine, Leucine and valine . It never gave Ala-Gly and Val-Ala on partial hydrolysis. How many such tetrapeptides are possible ?
View SolutionA tetrapeptide has −COOH group on alanine. This produces glycine (Gly), valine (Val), phenyl alanine (Phe) and alanine (Ala), on complete hydrolysis. For this tetrapeptide, the number of possible sequences (primary structures) with −NH2 group attached to a chiral centre is :
View SolutionA tetrapeptide has −COOH group on alanine. This produces glycine (Gly), valine (Val), phenyl alanine (Phe) and alanine (Ala), on complete hydrolysis. For this tetrapeptide, the number of possible sequences (primary structures) with −NH2 group attached to a chiral centre is :
View SolutionA tetrapeptide has −COOH group on alanine. This produces glycine (Gly), valine (Val), phenyl alanine (Phe) and alanine (Ala), on complete hydrolyses. For this tetrapeptide, the number of possible sequences (primary structures) with −NH2 group attached to a chiral centre is
View SolutionA tetrapeptide has −COOH group on alanine. This produces glycine (Gly), valine (Val), phenyl alanine (Phe) and alanine (Ala), on complete hydrolyses. For this tetrapeptide, the number of possible sequences (primary structures) with −NH2 group attached to a chiral centre is
View Solution
