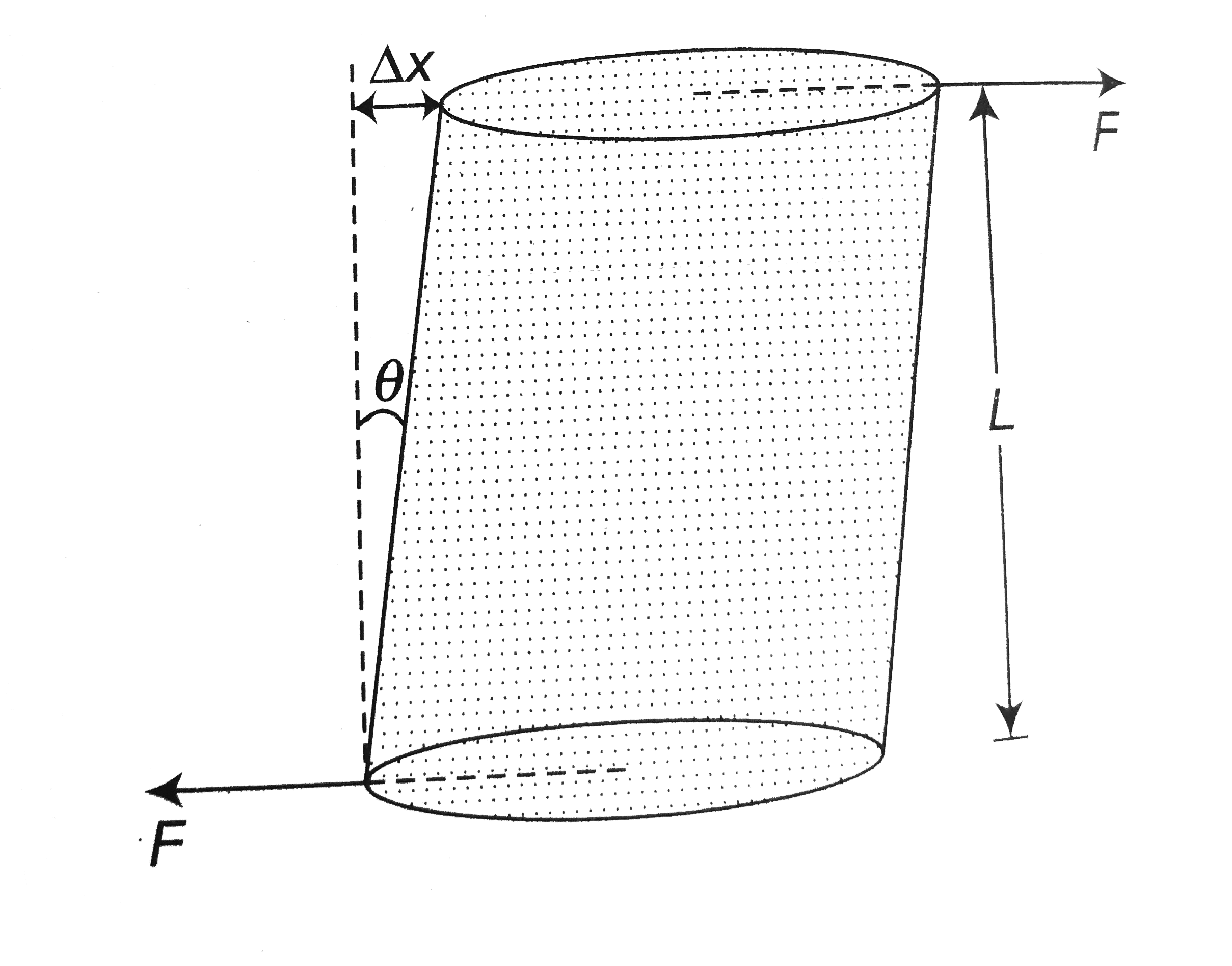
If two equal and opposite defirming forces are applied parallel to the cross sectional area of the cylinder as shown in the figure, there is a relative displacement between the oppsite faces of the cylinder. The ratio of Ax to L is known as
longitudinal strain
volumetric strain
shearing strain
Poisson's ratio
The correct Answer is:C
Shearing strain=△xL
Topper's Solved these Questions
- PROPERTIES OF MATTERBook:A2ZChapter:PROPERTIES OF MATTERExercise:Elasticity And Work Done In Stretching A Wire
Explore 25 Videos
- PROPERTIES OF MATTERBook:A2ZChapter:PROPERTIES OF MATTERExercise:Surface Tension And Surface Energy
Explore 29 Videos
- PROPERTIES OF MATTERBook:A2ZChapter:PROPERTIES OF MATTERExercise:Chapter Test
Explore 29 Videos
- OSCILLATION AND SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTIONBook:A2ZChapter:OSCILLATION AND SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTIONExercise:Chapter Test
Explore 29 Videos
- ROTATIONAL DYNAMICSBook:A2ZChapter:ROTATIONAL DYNAMICSExercise:Chapter Test
Explore 29 Videos
Similar Questions
If the potential energy of a spring is V on stretching it by 2cm, then its potential energy when it is stretched by 10cm will be
View SolutionThe rain are in spherical shape due to
View Solution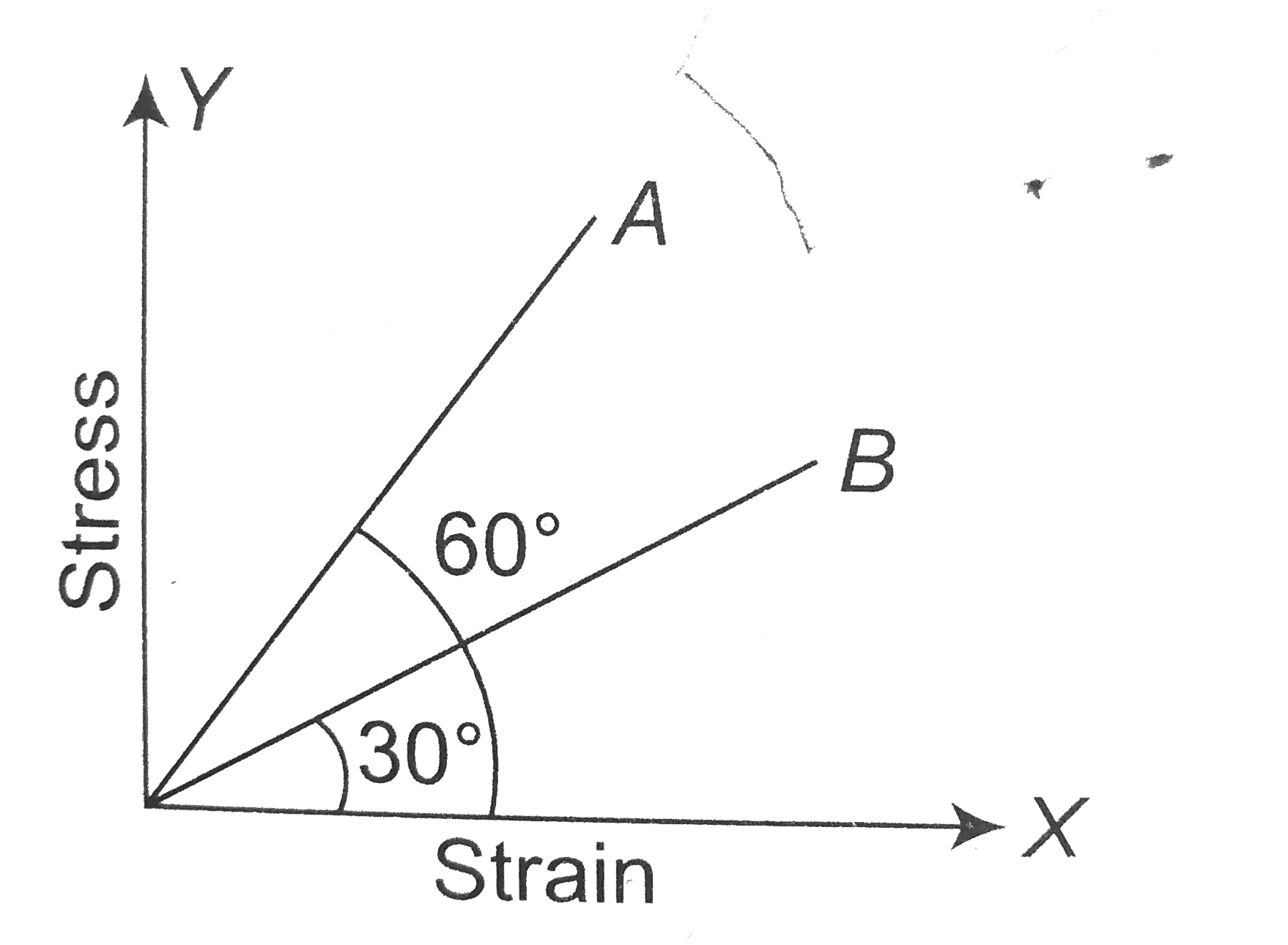
The stress versus strain graphs for wires of two materials A and B are as shown in the figure. If YA and YB are the Young's moduli of the materials then
View SolutionA chimpainzee swinging on a sitting position stands up suddenly the time period
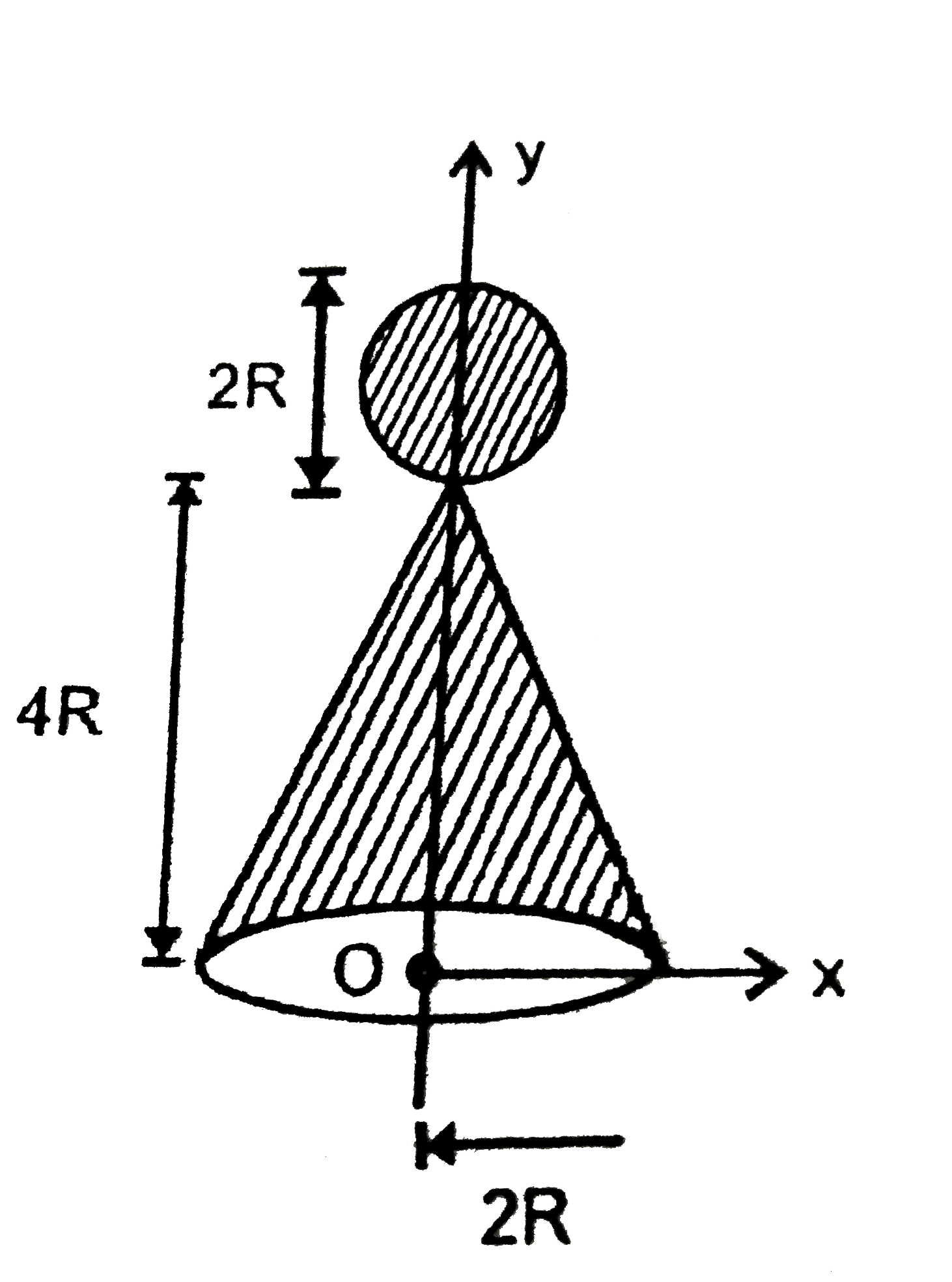
View SolutionA carpenter has constructed a toy as shown in figure. If the density of the material of the sphere is 12 tirnes that of cone, the y− coordinate of COM of toy point O
View SolutionA clockwise torque of 6N−m is applied to the circular cylinder as shown in the figure. There is no friction between the cylinder and the block.

View SolutionIn the figure shown, forces of equal magnitude are applied to the two ends of a uniform rod. Consider A as the cross-sectional area of the rod. For this situation, mark out the incorrect statements.
View SolutionA liquid of density rho is filled in a beaker of cross section A to a height H and then a cylinder of mass M and cross-section a is made to float in it as shown in If the atmospheric pressure is P_0 find the pressure (a) at the top face B of the cylinder (b) at the bottom face C of the cylinder and (c ) at the base D of the beaker. (d) Can ever these pressure be equal ?
View SolutionA cylinder is lying with axis parallel to uniform electric field vecE . What is the total flux through the cylinder with cross-section S and length L ?
View SolutionA force F is applied horizontally on a cylinder in the line of centre as shown in the figure. The cylinder is on a rough surface of coefficient of fricition mu . The direction of the friction force acting on the cylinder will be
View SolutionA cylinder with a diameter of 0.240 m is placed between the plates of a hydraulic press as illustrated in the figure. A force equal to 4.45×105 N is applied to the cylinder. What is the pressure on the end of the cylinder due to the applied force ?
View Solutionयदि दो समान एवं विपरीत विरूपक बल चित्र में दिखाए गए अनुसार बेलन के अनुप्रस्थ-काट क्षेत्रफल के समानान्तर आरोपित किये जाते हैं, तो बेलन के विपरीत फलकों के मध्य आपेक्षिक विस्थापन होता है।
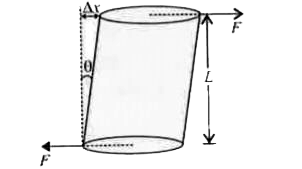
Δx से L का अनुपात कहलाता है-
View Solution
If two equal and opposite defirming forces are applied parallel to the cross sectional area of the cylinder as shown in the figure, there is a relative displacement between the oppsite faces of the cylinder. The ratio of Ax to L is known as
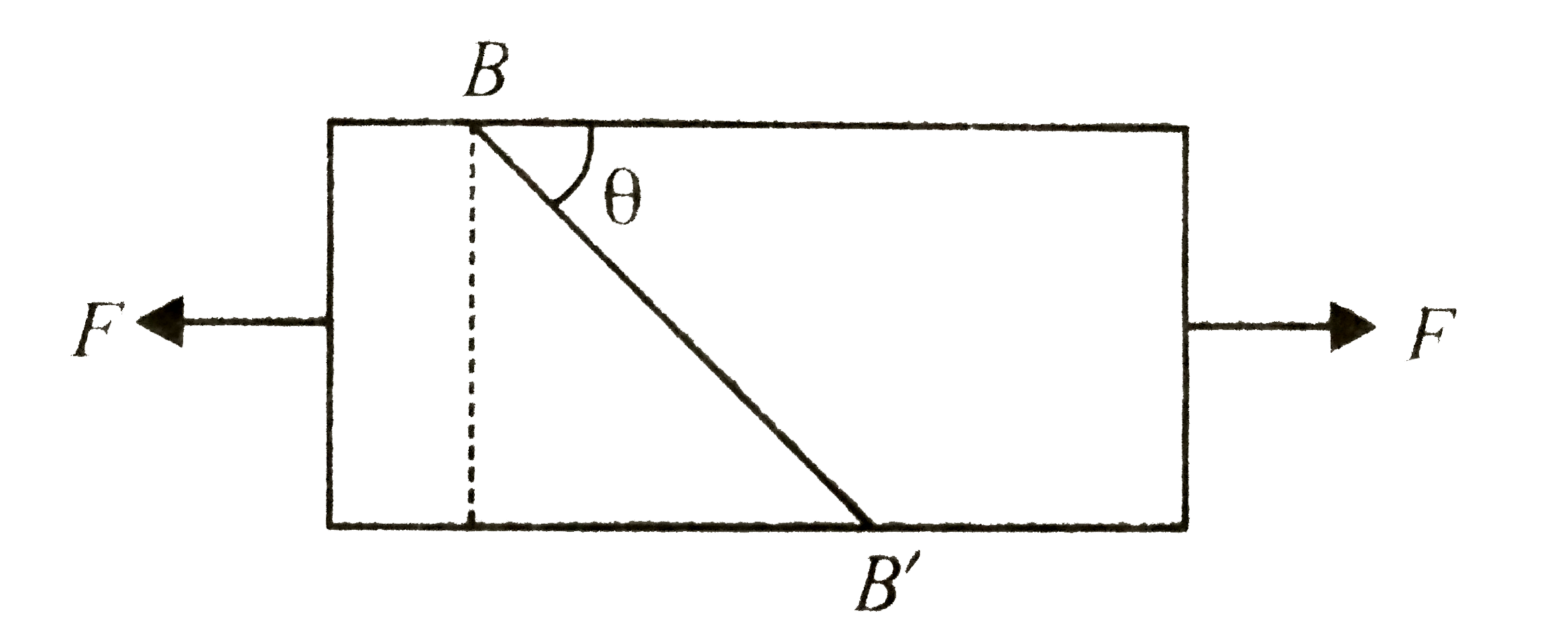
View SolutionA bar of cross- sectional area A is is subjected two equal and opposite tensile forces at its ends as shown in figure. Consider a plane BB' making an angle θ with length. The ratio of tensile stress to the shearing stress on the plane BB' is
View SolutionA cylinder is sandwiched between two planks. Two constant horizontal forces F and 2F are applied on the planks as shown Masses of planks and cylinder are indicated in the figure Radius of the cylinder is as shown. Then
View Solution
