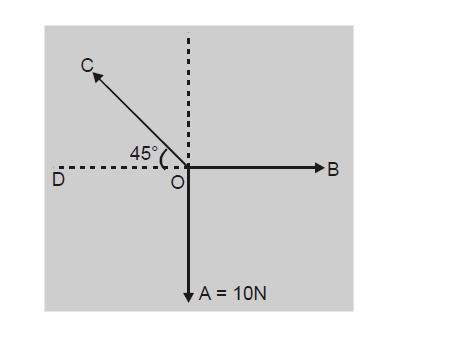
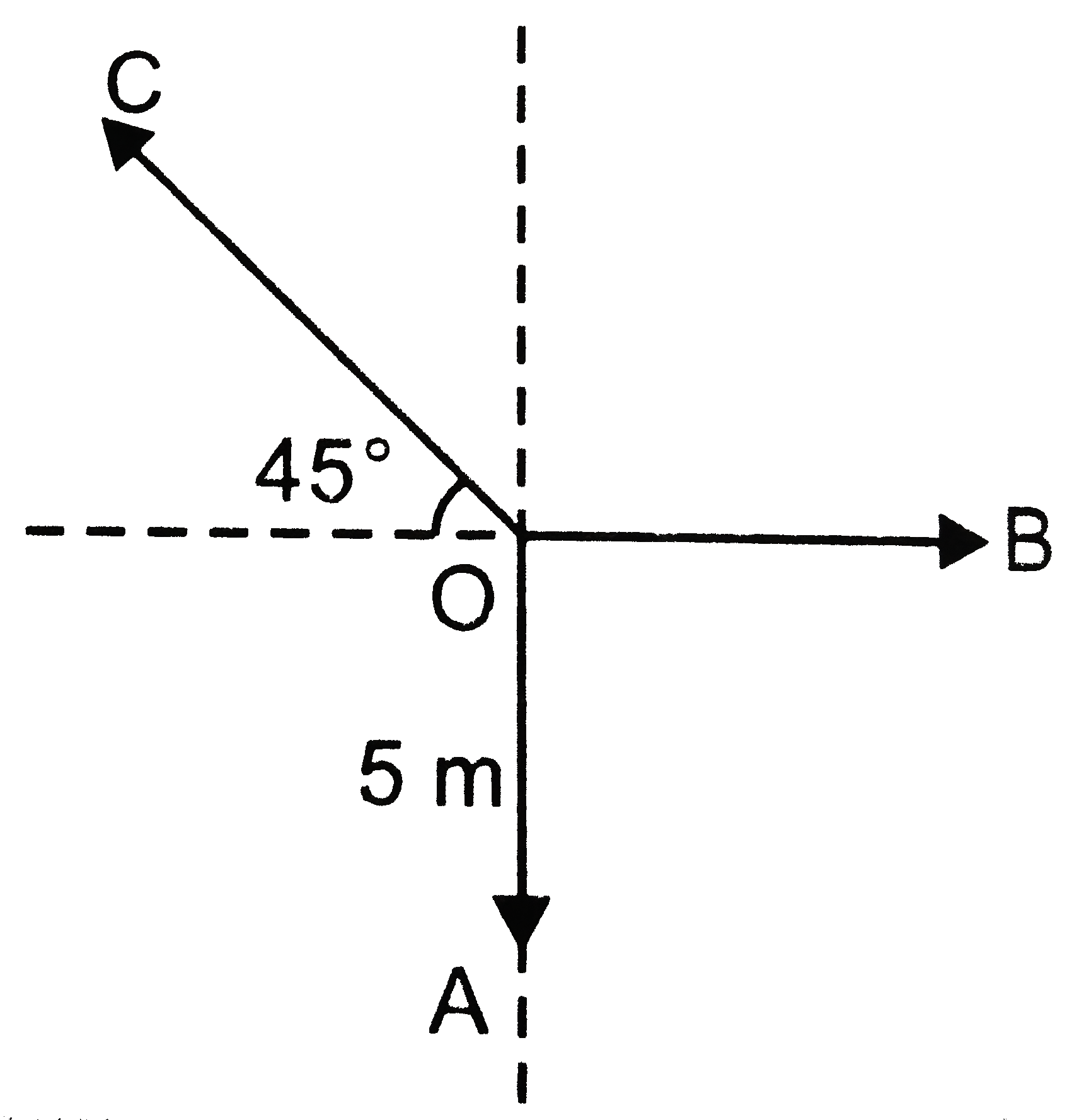
The sum of three vectors shown in Fig. 2 ( c) . 77. is zero .
 .
.
(a) What is the magnitude of the vector −−→OB?<br>(b)Wˆisthemagnitudeofthe→−−→r vec (OC) ?
Video Solution
Text Solution
 .
.
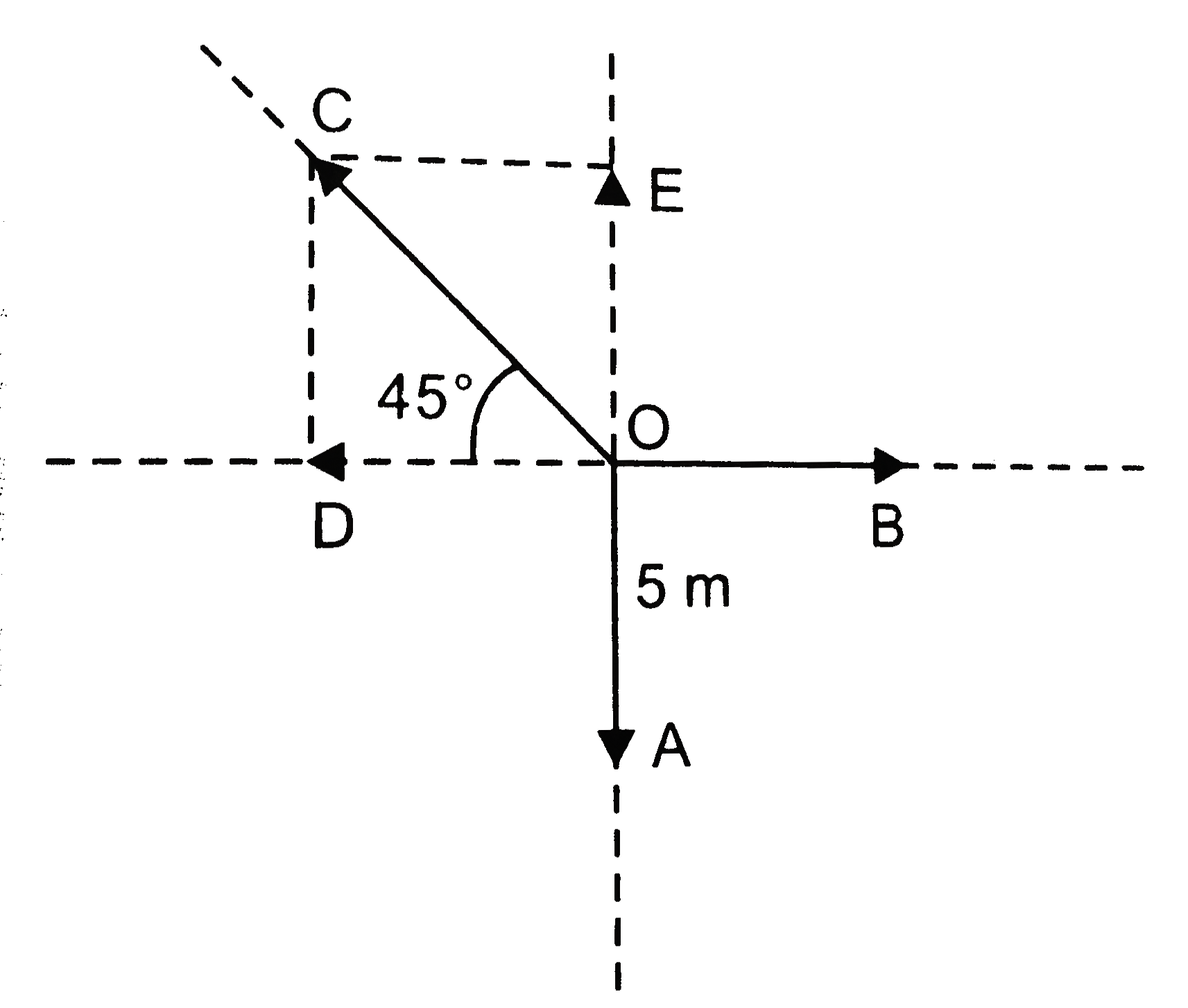
Resolving −−→OC into two rectangular components, we have OCcos45∘ aling OD and (OC sin 45^@along OE.Sincethe∑ofthethree→−−→rsiszero,sothepartic≤∈equilibriumundertheeffectofappliedforces.<br>Hence, OB=OC cos 45^@...(i)<BR>and OA =OC sin 45^@<bR>or OC = (OA)/( sin 45^@) = 5/( 1 //sqrt 2) = 5 sqrt 2 m<bR>From(i), OB= OC cos 45^2 = 5 sqrt 2 xx 1/( sqrt 2) = 5 sm.
|
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
What is the magnitude of the sum of the vectors →P=3ˆIand→Q=4ˆj ?
A3B4C5D7What is the angle between the vector →A and →B as shown in figure ?
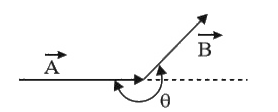 AθBπ−θCθ−πD2π−θ
AθBπ−θCθ−πD2π−θThe magnitude of the x-component of vector →A is 3 and the magnitude of vector →A is 5. What is the magnitude of the y-component of vector →A ?
A3B4C5D8
When two vector →a and →b are added, the magnitude of the resultant vector is always
View Solution→A is a vector of magnitude 2.7 units due east . What is the magnitude and direction of vector 4 →A ?
View SolutionIf →A is a vector of magnitude 3 units due east. What is the magnitude and direction of a vector −4→A ?
View SolutionIf →A is a vector of magnitudes 5units due east. What is the magnitude and direction of a vector −5→A?
View SolutionThe resultant of two vectors →Aand→B is perpendicular to the vector →A and its magnitude is equal to half the magnitude of vector →B. What is the angle between →Aand→B ?
View Solution