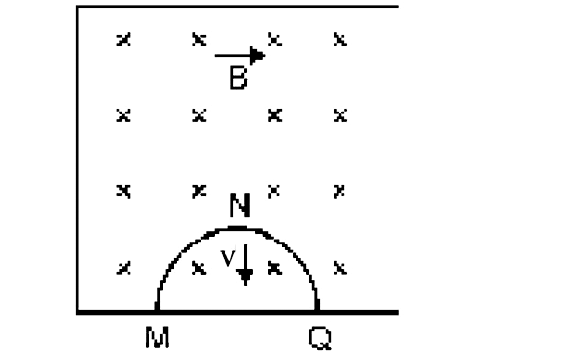
A thin semicircular conducting ring of radius R is falling with its plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic induction B. At the position MNQ, the speed of the ring is V and the potential difference developed across the ring is

Zero
BvπR2/2 and M is at higer potential
πRBV and Q is at higer potential
2RBV and Q is at higer potential
The correct Answer is:D
Rate of decrease of area of the semicircular ring dAdt=(2R)V
According to Faraday's law of induction induced emf e=−dφdt=−BdAdt=−B(2RV)
The induced current in the must generate magnetic field in the upward direction. thus Q is at higer potential
Similar Questions
A thin circular -conducting ring having N turns of radius R is falling with its plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic field B . At the position MNQ the speed of ring is v the induced e.m.f developed across the ring is
View SolutionA thin semicircular conductor ring with R diameter, horizontal magnetic field as shown in Fig. IV.13 vec B Is falling while its bottom is vertical. The velocity of the ring in position MNQ is v. The potential generated at the ends of the ring is
View Solutionत्रिज्या R की एक पतली अर्द्धवृत्ताकार धात्विक वलय क्षैतिज चुम्बकीय प्रेरण B में इस प्रकार गिर रही है कि इसका तल ऊर्ध्वाधर रहता है। जब यह वलय MNQ की स्थिति में पहुँचती है तब इसका वेग । है। इस समय अर्द्धवृत्ताकार वलय में उत्पन्न विभवान्तर होगा

View SolutionA thin semicircular conducting ring of radius R is falling with its plane verticle in a horizontal magnetic inducting B . At the position MNQ , the speed of the ring is V and the potential difference developed across the ring is (1.) zero (2.) BcpiR^(2)//2 (3.) piRBV (4.) 2RBV
View SolutionA thin semi-circular conducting ring of radius R is falling with its plane verticle in horizontal magnetic induction (→B). At the position MNQ the speed of the ring is v, and the potential difference developed across the ring is
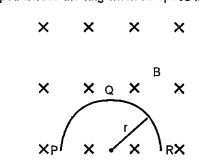
View SolutionA thin semicircular conducting ring (PQR) of radius 'r' is falling with its plane vertical in horizontal magnetic field B as shown in figure the potential diffrence developed across the ring when its speed is v is
View Solutionr त्रिज्या की. एक पतली अर्द्धवृत्ताकार चालक रिंग (वलय) PQR, किसी क्षैतिज चुम्बकीय क्षेत्र B में गिर रही है। गिरते समय इसका समतल, आरेख में दर्शाये गये अनुसार, ऊर्ध्वाधर रहता है। जब गिरती हुई रिंग की चाल v है तो, इसके दो सिरों के बीच विकसित विभवान्तर होगा
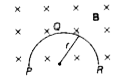
View Solutionr त्रिज्या की एक पतली अर्द्ध वृत्ताकार चालक रिंग (वलय) (PQR) किसी क्षैतिज चुंबकीय क्षेत्र B में गिर रही है। गिरते समय इसका समतल, आरेख में दर्शाये गए अनुसार, ऊर्ध्वाधर रहता है। जब गिरती हुई रिंग की चाल v है तो, इसके दो सिरों के बीच विकसित विभवांतर होगा
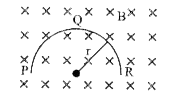
View Solution

