The linear magnification of a concave mirror is.
always positive
always negative
sometimes positive and sometimes negative
cannot predict
The correct Answer is:A
To determine the linear magnification of a concave mirror, we can analyze the behavior of images formed by the mirror under different object placements.
1. Understanding the Concave Mirror:
- A concave mirror has a reflecting surface that curves inward. It has a focal point (F) and a center of curvature (C).
2. Object Placement:
- The position of the object relative to the focal point is crucial. There are two main cases to consider:
- Case 1: Object is placed beyond the focal length (|u| > |f|).
- Case 2: Object is placed between the focal length and the mirror (|u| < |f|).
3. Case 1: Object Beyond Focal Length:
- When the object is beyond the focal length, the image formed is real and inverted.
- In this case, the image distance (v) is negative according to the sign convention used in optics.
- The magnification (m) is given by the formula:
m=vu
- Since v is negative and u is negative (as per the sign convention), the magnification becomes:
m=−v−u=vu (positive)
- Therefore, the magnification is positive.
4. Case 2: Object Between Focal Length and Mirror:
- When the object is placed between the focal point and the mirror, the image formed is virtual and upright.
- In this case, the image distance (v) is positive.
- Using the same magnification formula:
m=vu
- Here, v is positive, and u is negative, so the magnification becomes:
m=v−u (negative)
- Therefore, the magnification is negative.
5. Conclusion:
- Based on the two cases analyzed, we conclude that the linear magnification of a concave mirror can be:
- Sometimes positive (when the object is beyond the focal length).
- Sometimes negative (when the object is between the focal length and the mirror).
Final Answer:
The linear magnification of a concave mirror is sometimes positive and sometimes negative.
---
- A concave mirror has a reflecting surface that curves inward. It has a focal point (F) and a center of curvature (C).
- The position of the object relative to the focal point is crucial. There are two main cases to consider:
- Case 1: Object is placed beyond the focal length (|u| > |f|).
- Case 2: Object is placed between the focal length and the mirror (|u| < |f|).
- When the object is beyond the focal length, the image formed is real and inverted.
- In this case, the image distance (v) is negative according to the sign convention used in optics.
- The magnification (m) is given by the formula:
m=vu
- Since v is negative and u is negative (as per the sign convention), the magnification becomes:
m=−v−u=vu (positive)
- Therefore, the magnification is positive.
- When the object is placed between the focal point and the mirror, the image formed is virtual and upright.
- In this case, the image distance (v) is positive.
- Using the same magnification formula:
m=vu
- Here, v is positive, and u is negative, so the magnification becomes:
m=v−u (negative)
- Therefore, the magnification is negative.
- Based on the two cases analyzed, we conclude that the linear magnification of a concave mirror can be:
- Sometimes positive (when the object is beyond the focal length).
- Sometimes negative (when the object is between the focal length and the mirror).
The linear magnification of a concave mirror is sometimes positive and sometimes negative.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- RAY OPTICSBOOK - PRADEEPCHAPTER - RAY OPTICSEXERCISE - (Test Your Grip)Multiple Choice(sec -A)
1 Video
- RAY OPTICSBOOK - PRADEEPCHAPTER - RAY OPTICSEXERCISE - (Test Your Grip)Fill in the blanks(a)
10 Videos
- RAY OPTICSBOOK - PRADEEPCHAPTER - RAY OPTICSEXERCISE - Assertion-Reason Question
17 Videos
- PROPERTIES OF BULK MATTERBOOK - PRADEEPCHAPTER - PROPERTIES OF BULK MATTEREXERCISE - Multiple choice questions
7 Videos
- SYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTIONBOOK - PRADEEPCHAPTER - SYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTIONEXERCISE - Assertion- Reason Type questions
20 Videos
Similar Questions
Light of wavelength 6000Å falls on a plane reflecting surface. The reflected wavelength is.
View SolutionReflection is the phenomenon of………without…….. .
View SolutionAssertion : The clouds in the sky generally appear to be whitish.
Reason : Diffraction due to clouds is efficient in equal measures its all wavelengths.
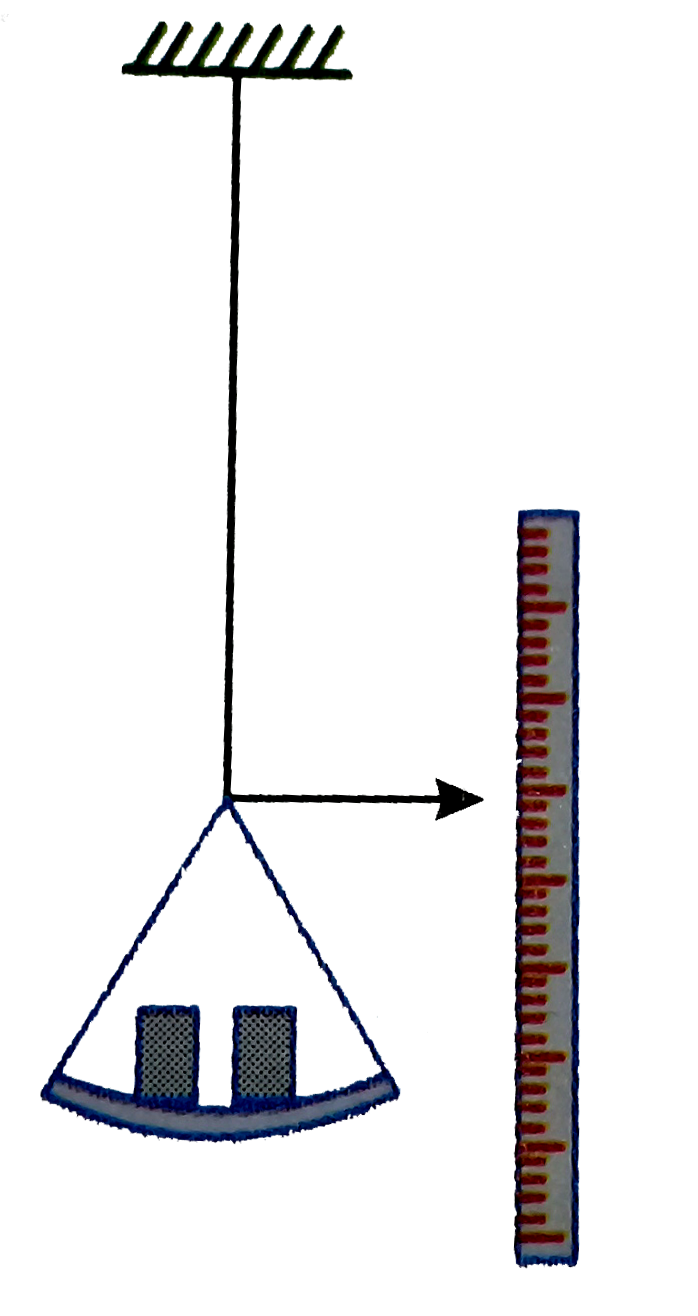
View SolutionIn the experiment to determine Young's modulus of the material of a wire under tension
used in the arrangement as shown. The percentage error in the measurement
of length is a in the measurement of the radius of the wire is b and in the
measurement of the change in length of the wire is c. Percentage error in the measurement
of Young's modulus for a given load is
View SolutionAssertion : In rolling, all points of a rigid body have the same linear velocity.
Reason : The rotational motion does not affect the linear velocity.
View Solution(a) The magnification of a concave mirror is - 1. What is the position of the object? (b) The magnification of a spherical mirror is ±2. What kind of mirror can it be?
View SolutionWhat is meant by linear magnification of a concave mirror?
View SolutionThe linear magnification of a concave mirror can be positive or negative. Why?
View SolutionThe linear magnification of a concave mirror is.
View Solutionसमतल दर्पण के लिए रैखिक आवर्धन का मान ____ होता है।
View Solutionअवतल लेंस में रैखिक आवर्धन सदैव ____ होता है।
View Solutionरेखीय आवर्धन से क्या तात्पर्य है ? गोलीय दर्पण के लिए रेखीय आवर्धन के सूत्र लिखिए।
View Solutionअवतल लेंस के लिए रेखीय आवर्धन होता है :
View Solutionअवतल दर्पण द्वारा बने प्रतिबिंब का रैखिक आवर्धन होता है-
View SolutionThe magnification produced by a concave mirror
View Solution

