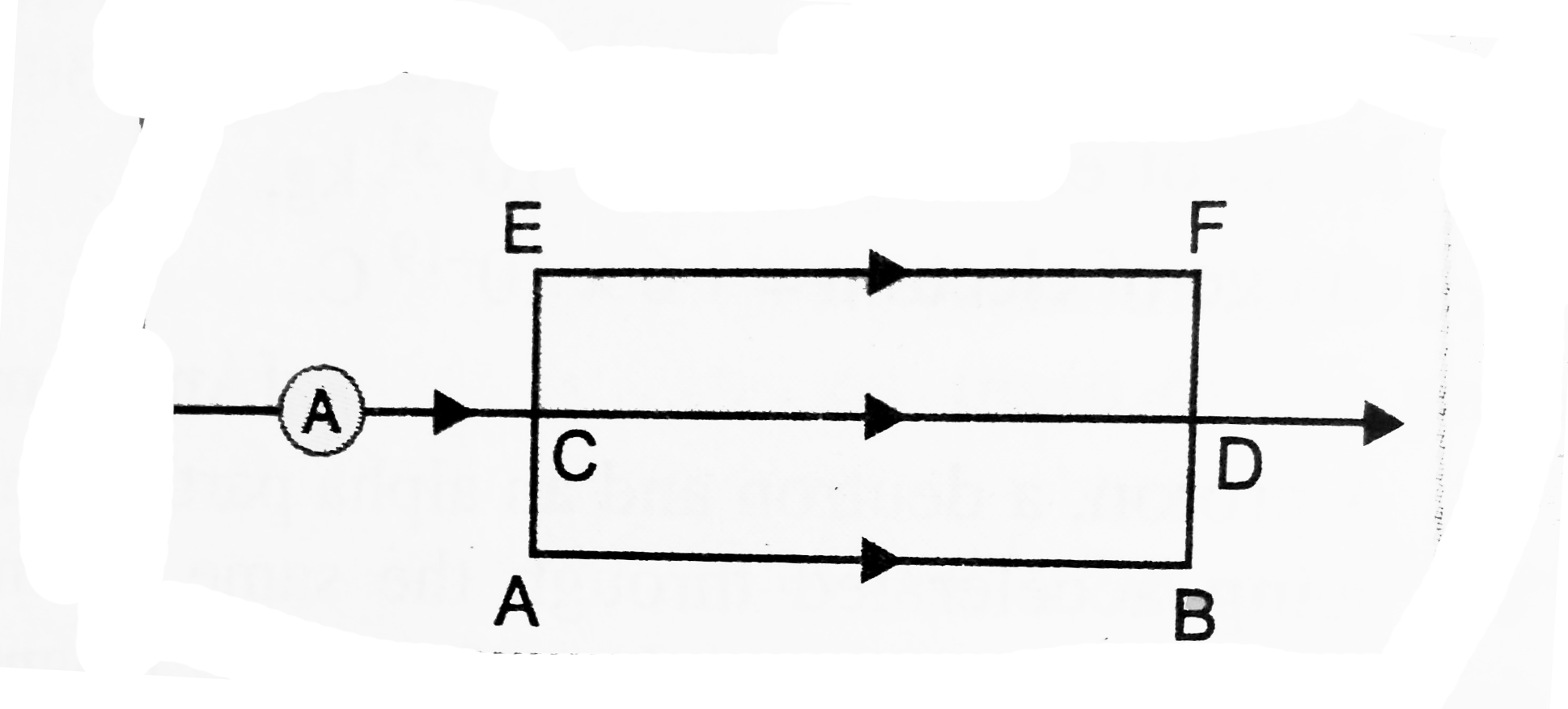
Three long parallel wires AB, CD and EF of equal resistance are connected as shown in figure. The separation between the neighbouring wires is 2⋅0cm and wires AE and BF supplied to the wires and ammeter reads 12A.
(a) or wire AB (b) of wire CD.
The correct Answer is:(a) 2⋅4×10−4Nm−1 directed upwards (b) Zero
As three parallel wires are of equal resistance and the total current supplied is 12A, so current through each wire is 4A.
(a) Force per unit length of AB due to current in CD is
F1=μ04π2I1I2r=10−7×2×4×4(2×10−2)
Force per unit length of AB due to current in EF is
F2=μ04π2I1I3r1=10−7×2×4×4(4×10−2)
=0⋅8×10−4Nm−1, directed upward
Total force per unit length of AB is
F=F1+F2=1⋅6×10−4+0⋅8×10−4
=2⋅4×10−4Nm−1 directed upwards
(b) Force per unit length of CD due to current in AB is
F′1=μ04π2I1I2r=10−7×2×4×4(2×10−2)
=1⋅6×10−4Nm−1 directed downwards
Force per unit length of CD due to current in EF is
F′2=μ04π2I1I3r=10−7×2×4×42×10−2
=1⋅6×10−4Nm−1 directed upwards
=−1⋅6×10−4Nm−1 directed downwards
Total force per unit length of CD is
F′=F′1+F′2=(1⋅6×10−4)+(−1⋅6×10−4)=0
Similar Questions
In the figure shown a current I_(1) is established in the long straight wire AB. Another wire CD carrying currrent I_(2) is placed in the plane of the paper. The line joining the ends of this wire is perpendicular to the wire AB. The resultant force on the wire CD is :
View Solutionएक तार AB से होकर 10A की स्थिर (अपरिवर्ती) विद्युत धारा प्रवाहित हो रही है । यह तार एक मेज पर क्षैतिज रखा है। एक अन्य तार CD इस तार AB के ठीक ऊपर 2mm की ऊंचाई स्थित है। तार CD से 6A की विद्युत धारा प्रवाहित हो रही है। तार CD की प्रति एकांक लम्बाई का द्रव्यमान कितना हो ताकि मुक्त अवस्था में यह अपनी स्थिति में ही लटका रहे? तार AB के सापेक्ष तार में CD प्रवाहित विद्युत धारा की दिशा क्या होगी? (g का मान =10ms2 लीजिए)
View SolutionA steady (unchanging) electrical current of 6A is flowing through a wire AB. This wire is placed horizontally on a table. Another wire CD is located at a height of 1mm just above this wire AB. The electrical current from 4A to wire CD is getting progressed. What is the mass per unit length of the wire CD so that it hangs in its position in the free state? What will be the direction of current flowing in wire CD relative to wire AB? (value of g =10m//s^(2) Take)
View SolutionFigure shows a part of an electric circuit. The wires AB, CD, and EF are long and have identical resistances. The separation between the neighbouring wires is 1.0 cm. The wires AE and BF have negligible resistances and the ammeter reads 30 A . Calculate the magnetic force per unit length of AB and CD.

View SolutionA steady (irreversible) current of 12A is flowing through a wire AB. This wire is laid horizontally on a table. Another wire CD is located at the height of Imm, just above this wire AB. An electrical current of 5A is flowing through the wire CD. What is the mass per unit length of the wire CD so that it hangs in its position in the free state? What will be the direction of current flowing in wire CD relative to wire AB? [g value = 10 ms^(-2) Take]
View SolutionThere are two wires ab and cd in a vertical plane as shown in figure. Direction of current in wire a is rightwards. Choose the correct options.

View SolutionIn the figure shown a current I1 is established in the long straight wire AB. Another wire CD carrying currrent I2 is placed in the plane of the paper. The line joining the ends of this wire is perpendicular to the wire AB. The resultant force on the wire CD is :
View SolutionA long, horizontal wire AB rests on the surface of a table and carries a current I. Horizontal wire CD is vertically above wire AB, and is free to slide up and down on the two vetical mental guides C and D (as shown in Fig) Wire CD is connected through the sliding contacts to another wire that also carries a current I, opposite in direction to the current in wire AB. The mass per unit length of the wire CD is lambda . To what euqilibrium heigth h will the wire CD rise, assuming that magnetic force on it is wholly due to the current in wire AB?
View Solution
