CH3−C≡CH40%H2SO4−−−−−−→1%HgSO4AIsomerisation−−−−−−−→CH3−C||O−CH3
Structure of 'A' and type of isomerism in the above reaction are respectively
prop-1-en-2-ol, metamerism
prop-1-en-1-ol, tautomerism
prop-2-en-2-ol, geometrical isomerism
prop-1-en-2-ol, tautomerism.
The correct Answer is:D
CH3−C≡CH40%H2SO4−−−−−−→1%HgSO4CH3−OH∣C=CH2Prop-1-en-2-ol(A) ⏐⏐↓ Tautomerisation O||CH3−C−CH3Acetone
Topper's Solved these Questions
- ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDSBook:NCERT FINGERTIPSChapter:ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDSExercise:Assertion And Reason
Explore 15 Videos
- ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDSBook:NCERT FINGERTIPSChapter:ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDSExercise:Higher Order Thinking Skills
Explore 6 Videos
- ALCOHOLS,PHENOLS AND ETHERSBook:NCERT FINGERTIPSChapter:ALCOHOLS,PHENOLS AND ETHERSExercise:Assertion And Reason
Explore 14 Videos
- AMINES Book:NCERT FINGERTIPSChapter:AMINES Exercise:NCERT EXEMPLER PROBLEMS
Explore 1 Video
Similar Questions
Assertion : In formaldehyde all the four atoms lie in one plane.
Reason : Carbonyl carbon forms a π-bond with oxygen by overlapping of p -orbitals.
View SolutionAn alcohol (A ) on dehydration gives (B) which adds bromine molecule to give (C ), (C ) on heating with sodamide gives (D) which on hydration in the presence of Hg++/H2SO4 gives (E ). E on reduction by lithium aluminium hydride gives (A). (E ) is also obtained on dry distillation of calcium salt of acetic acid. How many enolisable proton present in the product (E ) ?
View SolutionAssertion : Catalytic reduction of butanal gives butanol.
Reason: Aldehydes on reduction give corresponding primary alcohols.
View SolutionThe correct increasing order of basic stregth for the following compounds is ________________ .
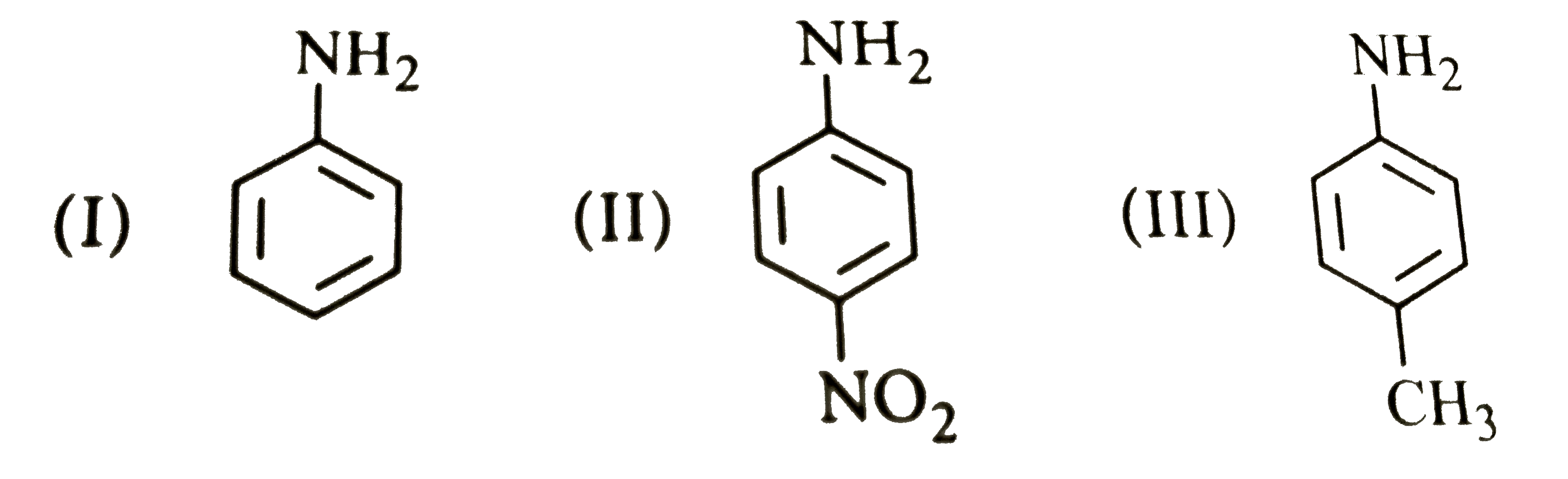
View SolutionWrite the IUPAc name of the following compound :
(a) CH3−CH2−CH3∣CH−CH=CH−CH2−CH3
(b) CH3−CH2−CH3∣CH−CH2−CH3∣CH−CH∣CH2∣CH2∣CH−CH3∣CH3−CH=CH3∣C−CH3
View SolutionCH_(3) - C -= CHoverset(40%H_(2)SO_(4))underset(1%HgSO_(4))rarrAoverset("isomerisation")rarr Structure of A and type of isomerism in the above reaction respectively are
View SolutionCH_(3)-underset(CH_(3))underset(|)(CH)-CH=CH-CH_(2)-overset(O)overset(||)(C)-OH
View SolutionCH_(3)-underset(CH_(3))underset(|)overset(CH_(3))overset(|)(CH)-overset(KMnO_(4))to (A) overset(H^(+))underset(Delta)to (B) overset(HBr) underset(RO OR) to (C) Product (C) in the above reaction is:
View SolutionCH3C≡CH40%H2SO4−−−−−−→1%HgSO4AIsomeristion−−−−−−→CH3−C−CH3∣∣O
Structure of A and type of isomerism in the above reaction respectively are
View SolutionCH_(3)-C-=CH underset(1%HgSO_(4))overset(40%H_(2)SO_(4))toA overset("Isomerisation")to CH_(3)-underset(O)underset(||)(C)-CH_(3) Structure of 'A' and type of isomerism in the above reaction are respectively.
View SolutionCH3−CH3| CH−C∣O−O−CH3| C | CH3−CH3 The common name of given ester is -
View SolutionCH_(3)-CH_(2)-C-=CH overset(40%H_2SO_(4))underset(1%HgSO_(4))toA overset ("isomerism")to CH_(3)-underset(O)underset(||)C-CH_(3) . Structure of ‘A’ and type of isomerism in the above reaction are respectively.
View SolutionCH3−C≡CH40%H2SO4−−−−−−→1%HgSO4Aisomerisation−−−−−−−→
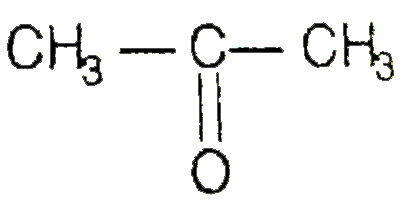
Structure of A and type of isomerism in the above reaction respectively are
View SolutionCH3−C≡CH40%H2SO4−−−−−−→1%HgSO4AIsomerisation−−−−−−−→CH3−C||O−CH3
Structure of 'A' and type of isomerism in the above reaction are respectively
View SolutionCH3−C≡CH40%H2SO4−−−−−−→1%HgSO4Aसमावयवन्−−−−→CH3−C∣∣O−CH3
उपरोक्त अभिक्रिया में 'A' का नाम और समावयता का प्रकार क्रमशः है-
View Solution

