Determine the potential difference between the points C and D in figure. 
Text Solution
Since the capacitors are in series, charge on each capacitor is the same. At steady state, the charge on the capacitor is due to terminal patential differnee of cell ε.
When steady state is reached, no current flows throught the capaciotrs. The current in the circuit is,
I=121+3+6=1.2A
Terminal pot. diff. across A and B,
V=ε−Ir=12−1.2×1=10.8V
Capacitors are in series, their effective capacitance C=1×21+2=23μF
∴ Charge on each capacitor,
q=23×10−6×10.8=7.2×10−6C.
Pot. diff. between A and C
VA−VC=qC2=7.2×10−62×10−6=3.6V
po. diff. between A and D =VA−VD=IR2
=6×1.2=7.2V
Pot. diff. between C and D =VC−VD
(VA−VD)−(VA−VC)=7.2−3.6=3.6V
|
Similar Questions
Use Kirchhoff's rules to determine the potential difference between the points A and D when no current flows in the arm BE of the electric network shown in the Fig.
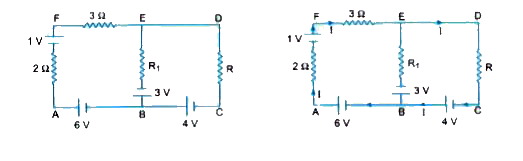
View Solution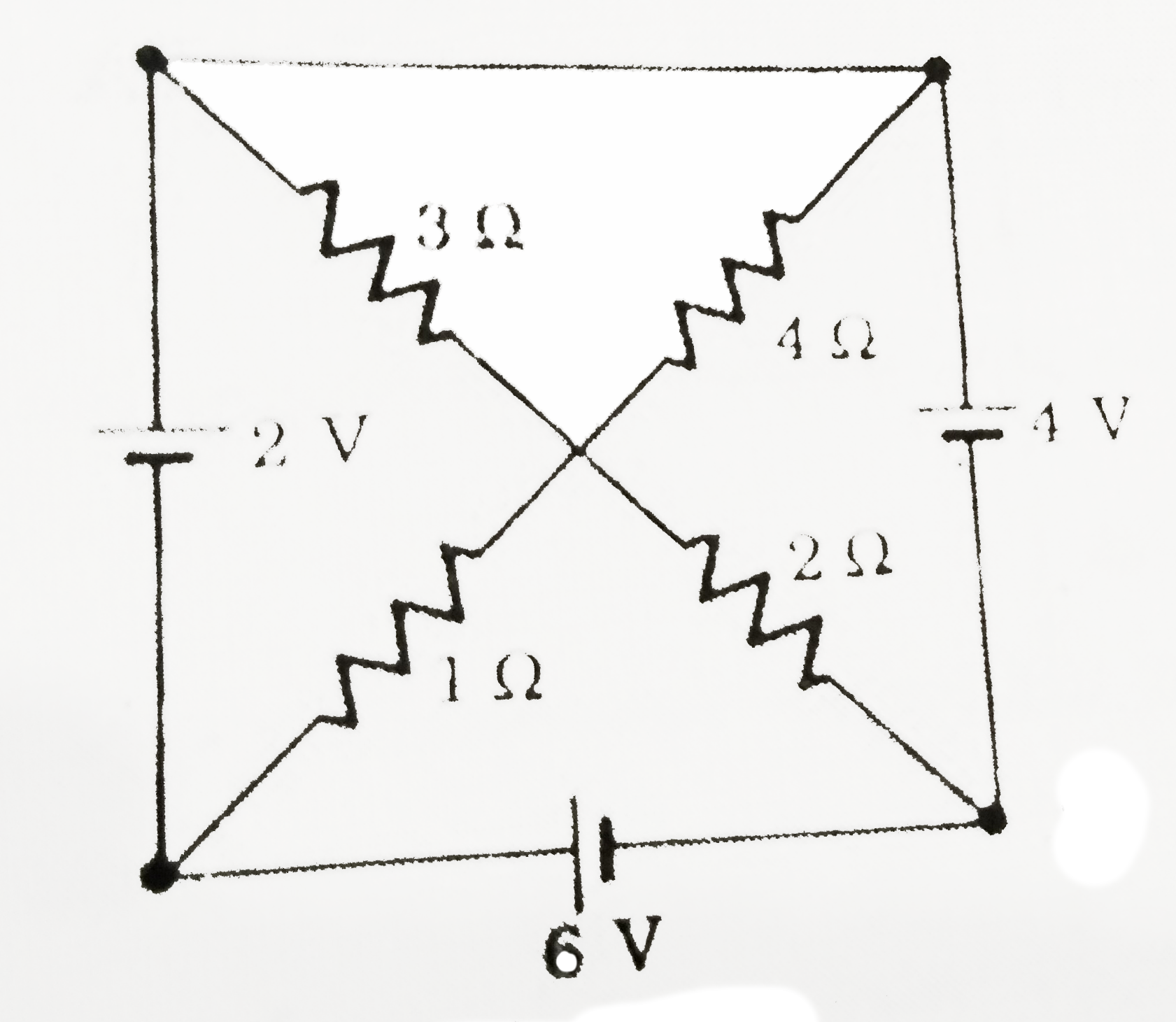
In the network shown in figure. (i) calculate the current of the 6V battery and (ii) determine the potential difference between the points A and B.
View Solution
Knowledge Check
The potential difference between the point A and B in figure will be
 A23VB89VC43VD2V
A23VB89VC43VD2V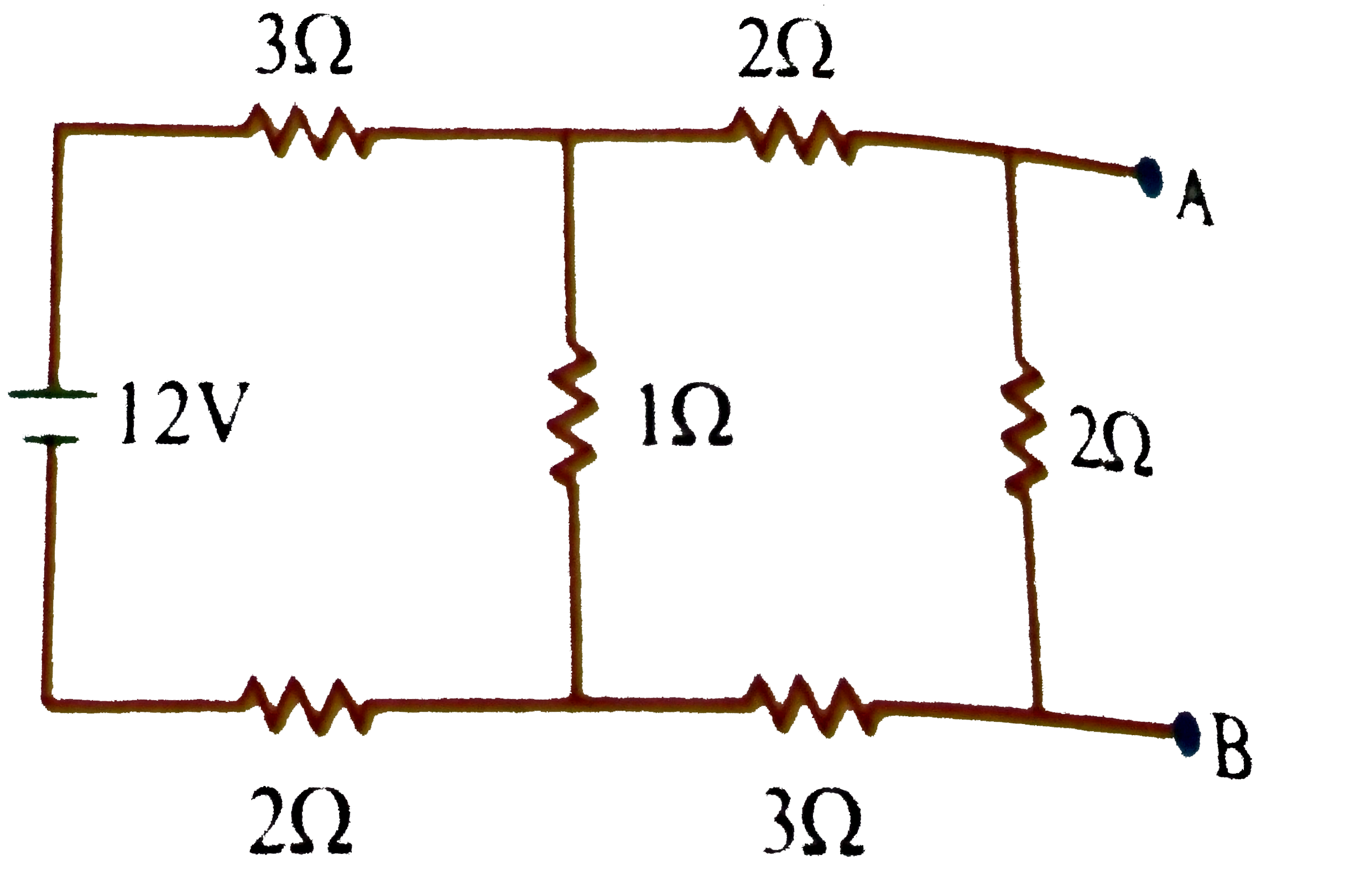
The potential difference between points A and B isA1.50VB2.50VC1.00VD0.50VThe potential difference between points A and B is
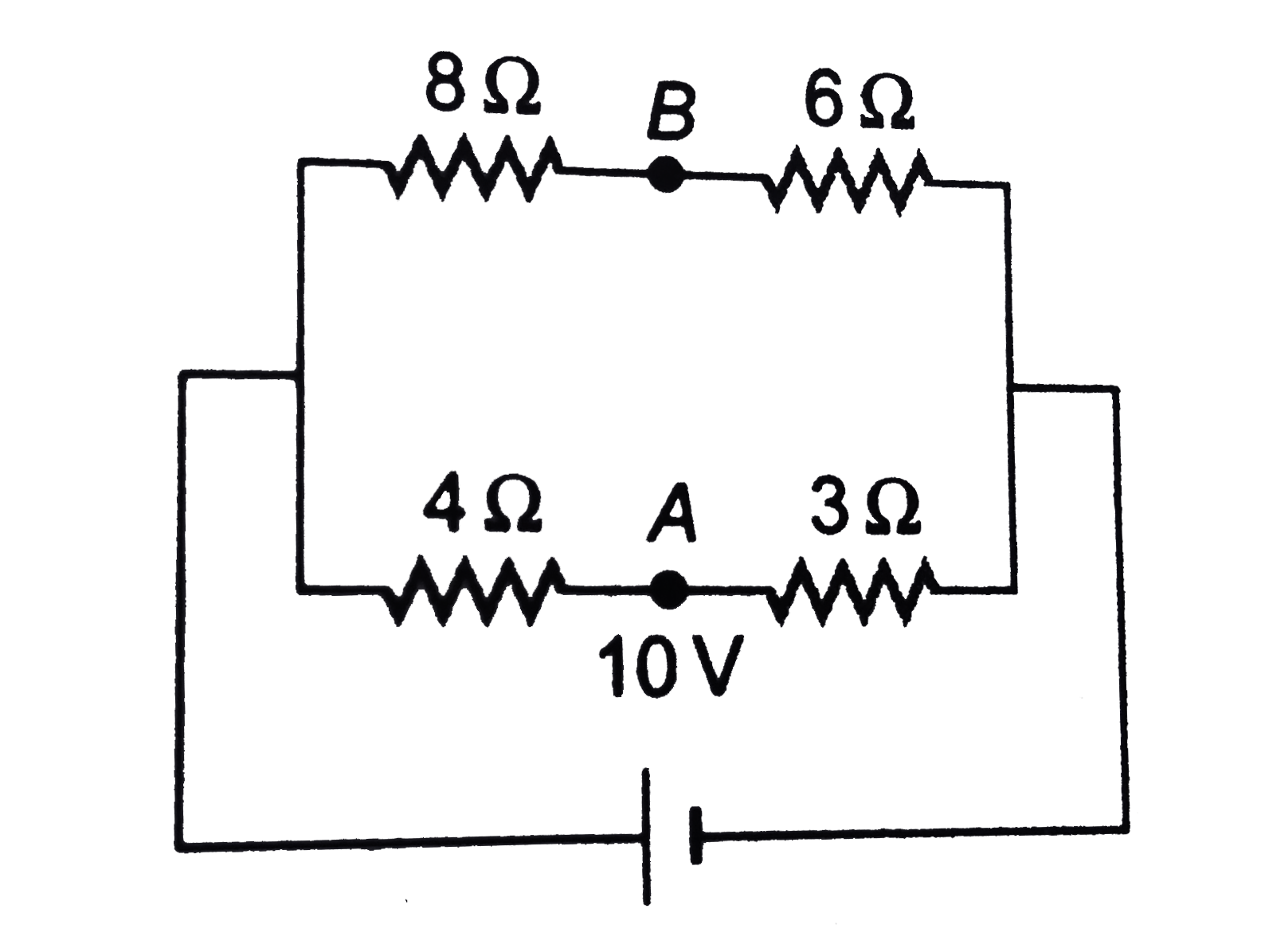 A207VB407VC107VDzero
A207VB407VC107VDzero
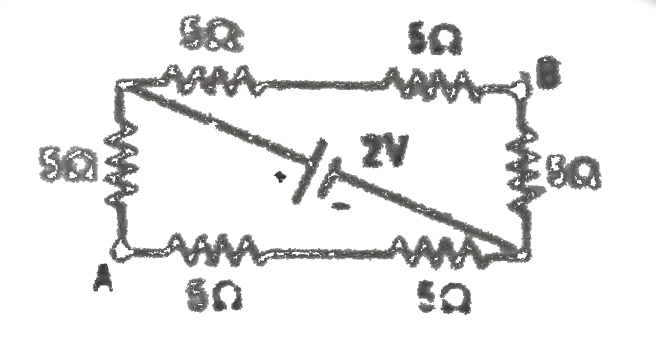
The potential difference between points A and B is -
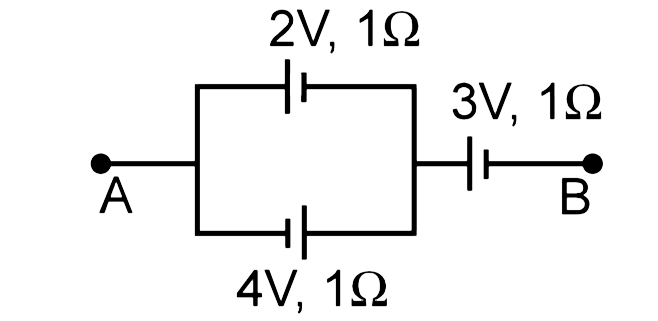
View SolutionThe potential difference between point A and B is
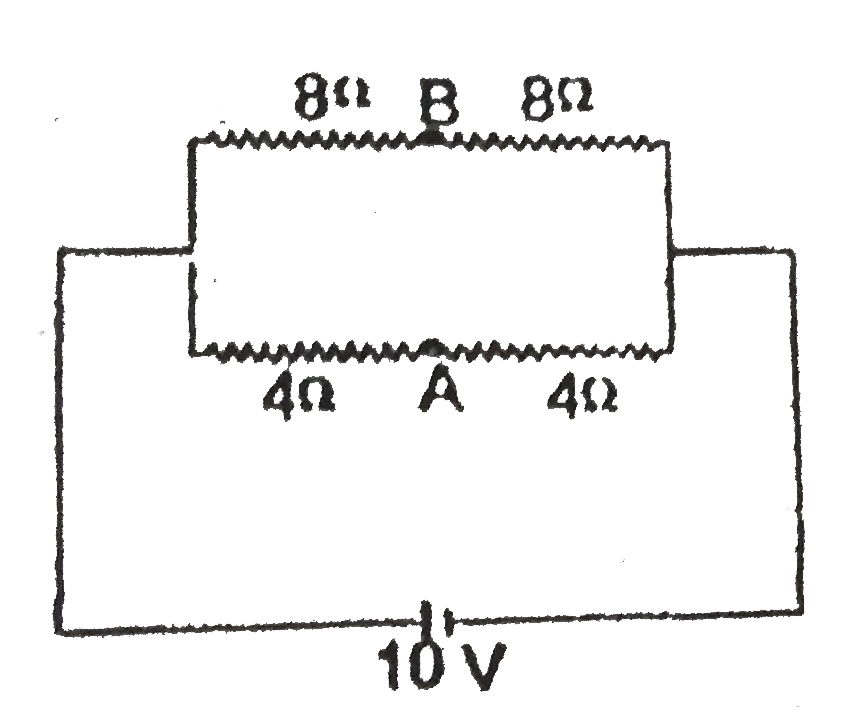
View SolutionThe potential difference between points A and B is:
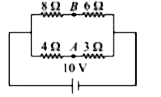
View SolutionThe potential difference between points A nd B is
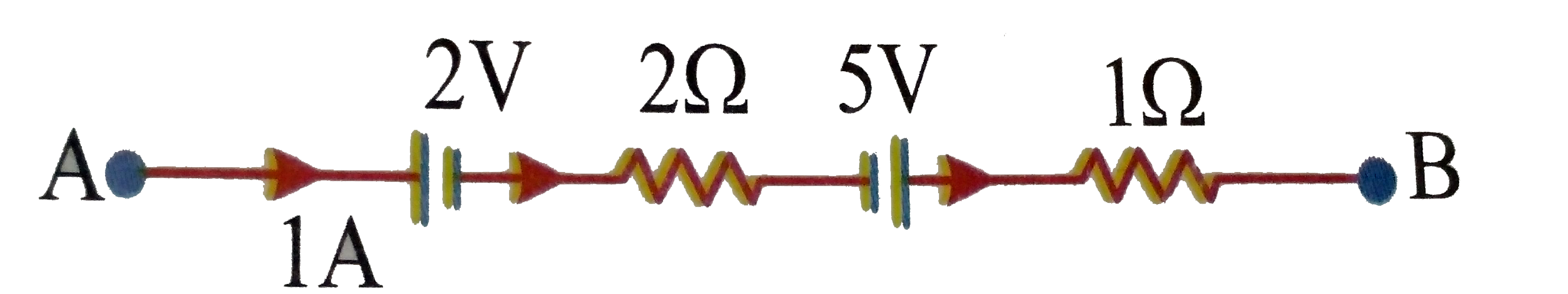
View SolutionThe potential difference between points A and B adjoining figure is
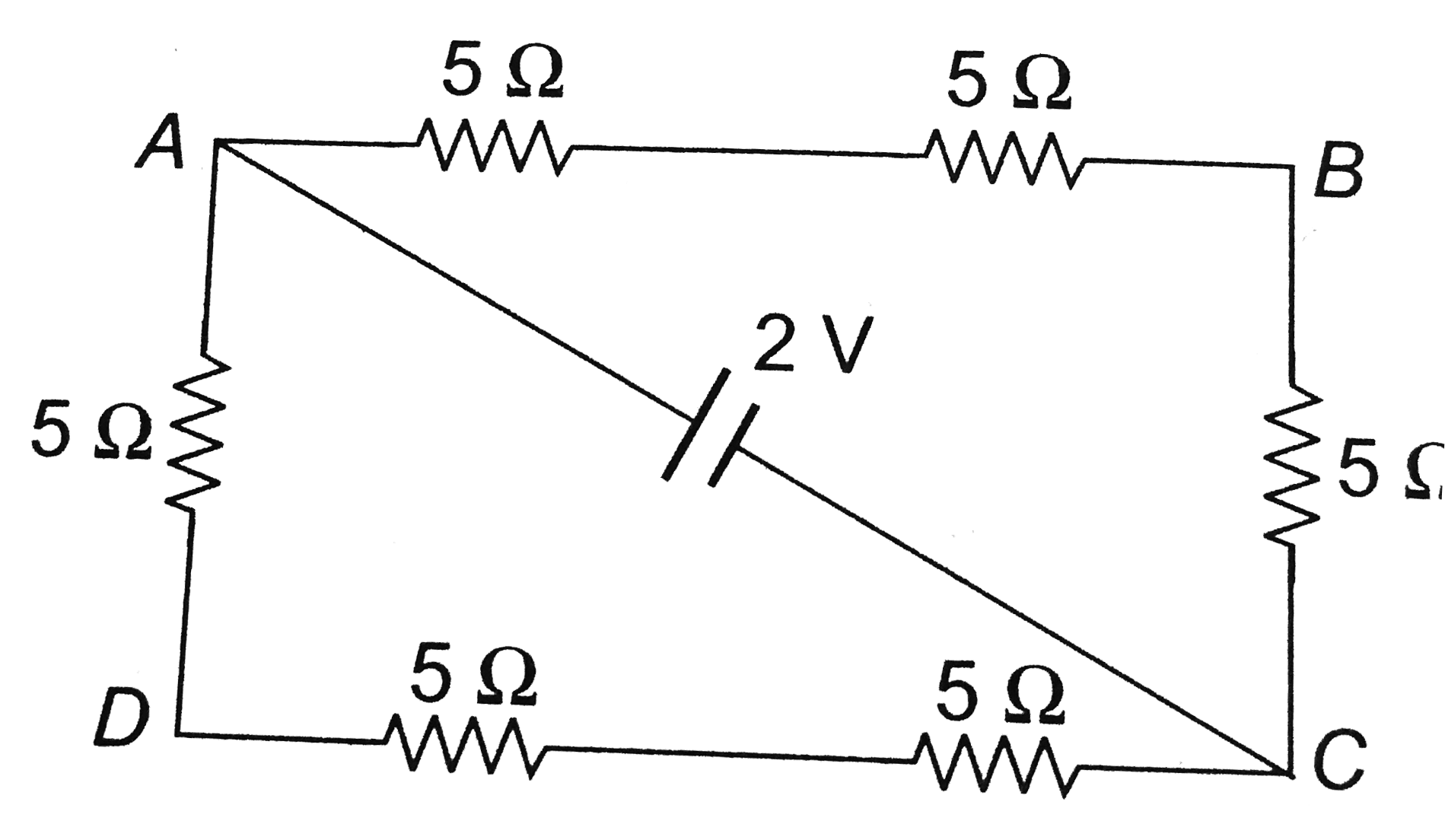
View Solution

