On increasing the current drawn from a cell, the potential difference of its terminlas is lowered. Why?
This is due to internal resistance r of the cell. We know that terminal potential difference V=ε−Ir . If I is increased, V will be lowered.
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
As the current drawn from the cell increases, terminal potential difference of a cell is
AconstantBdecreasesCincreasesDnone of theseA cell of emf 6 V is being charged by 1 A current. If the internalresistance of the cell is 1 ohm, the potential difference across the terminals of the cell is
A5 VB7 VC6 VD8 VCurrent drawn from the cell is maximum when:
AR=0BR=rCR>rDR<r
Can the terminal potential difference of a cell exceed its e.m.f. ?
View SolutionIf the intensity of light falling on the emitting substance of a photoelectric cell be increased then what will be the effect on (i) current flowing from the cell, (ii) potential difference required to stop the current completely?
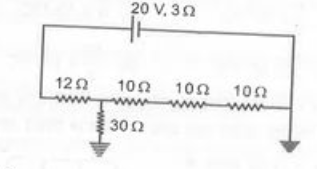
View Solution(a) Find the potential difference between A and B
(b) Calculate the current flowing in the circuit and the potential difference across terminals of each cell.
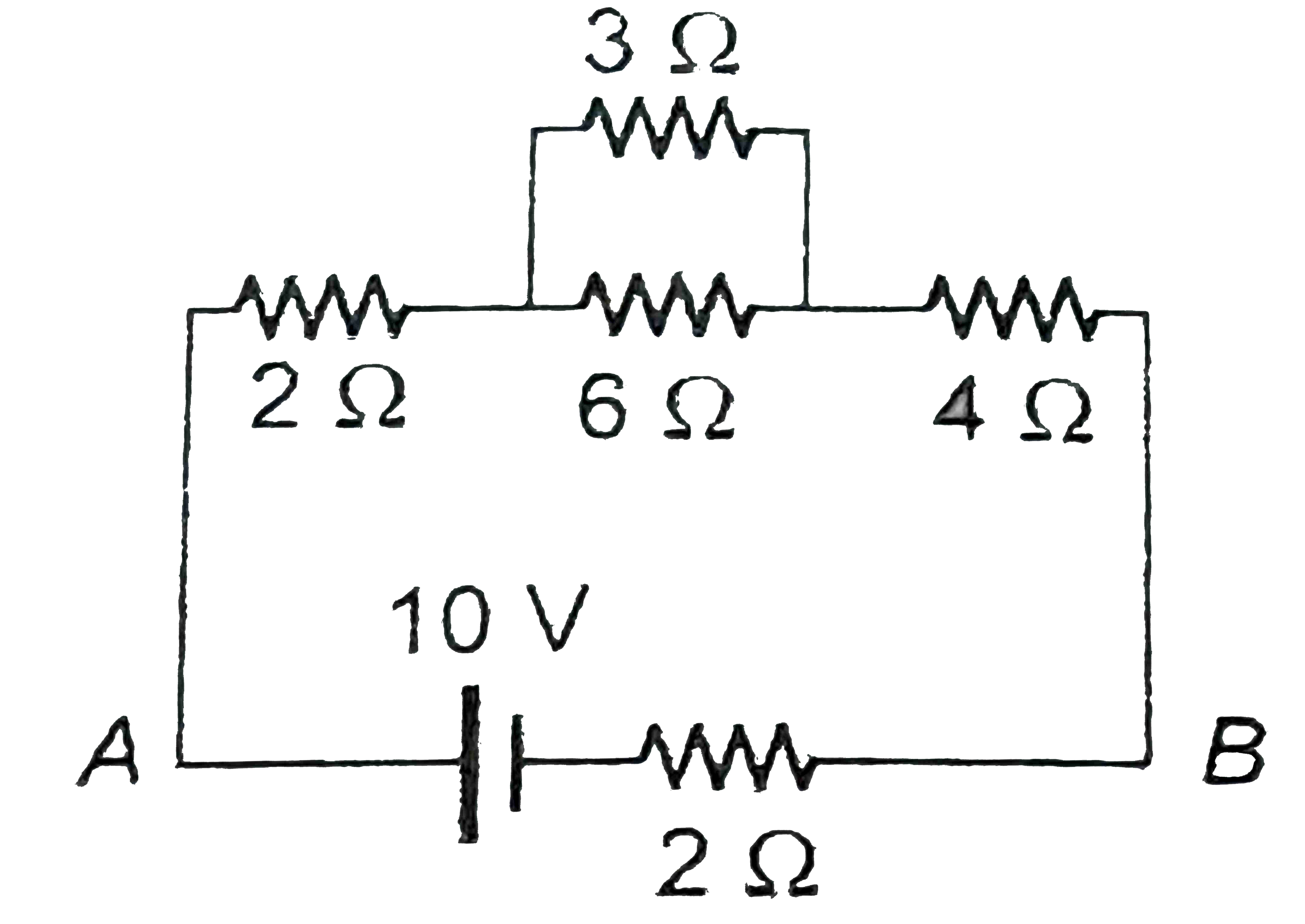
( c) Calculate the potential difference across terminals of each cell.
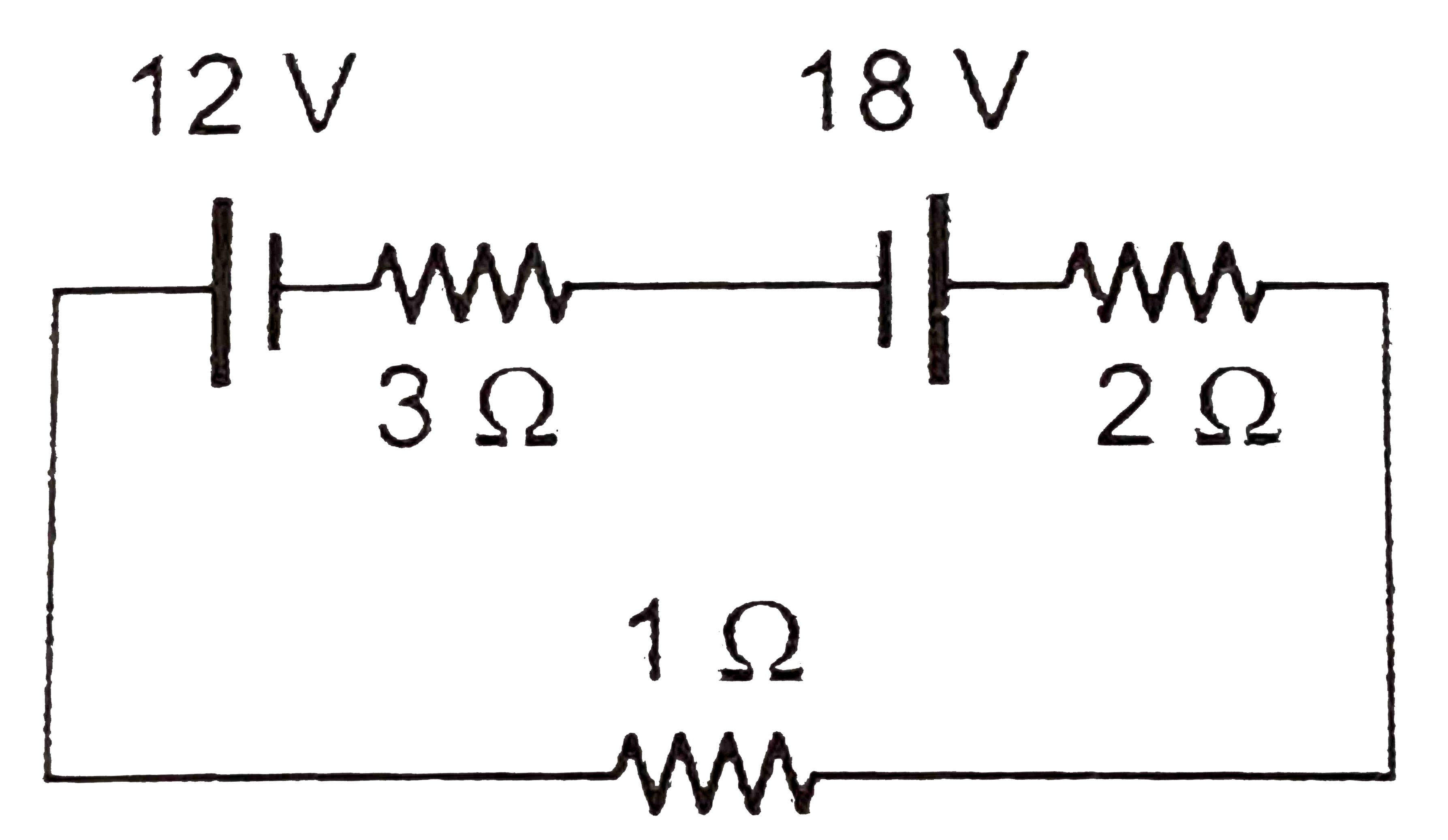
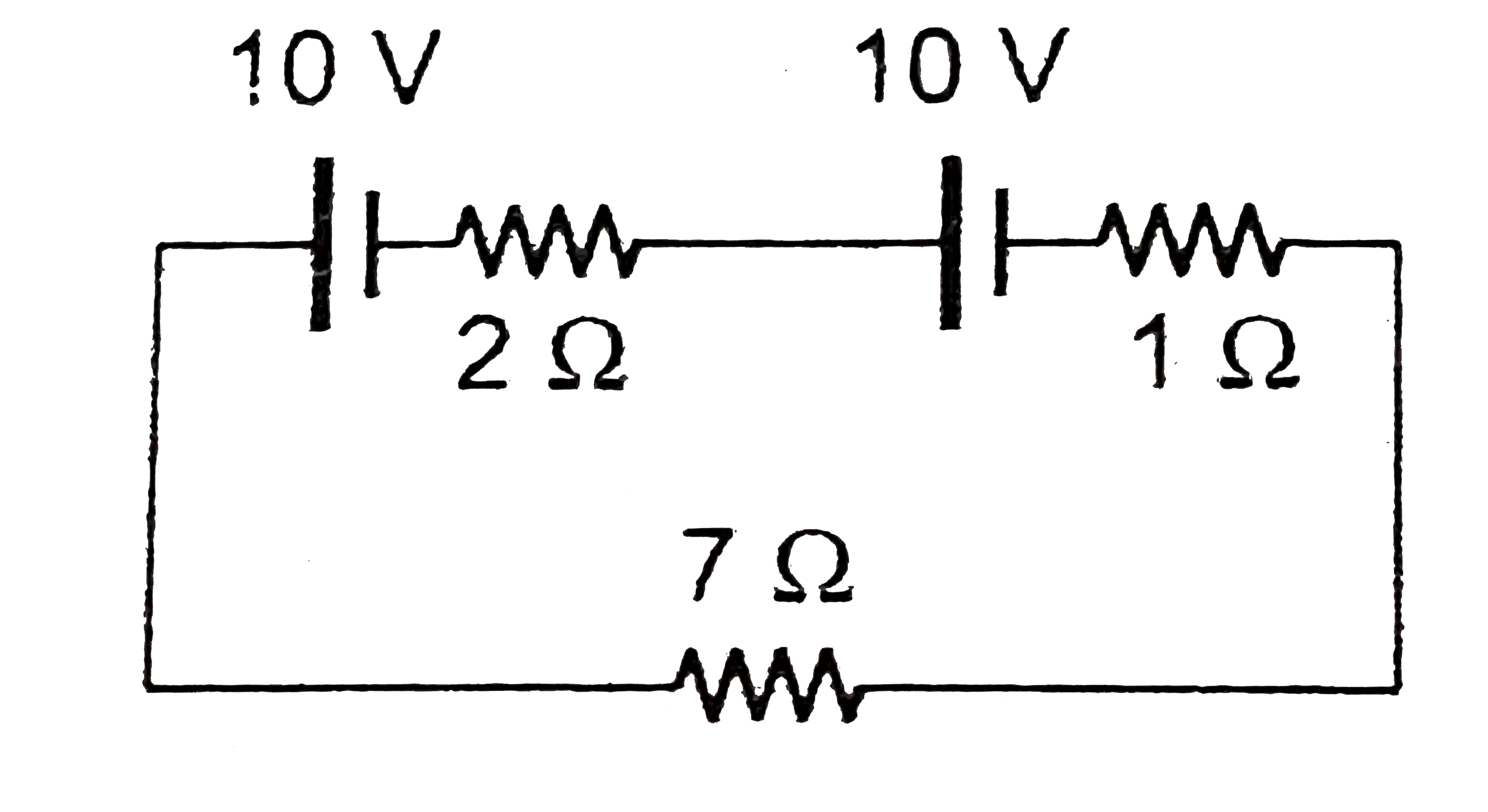
(d) Calculate the potential difference between A and B
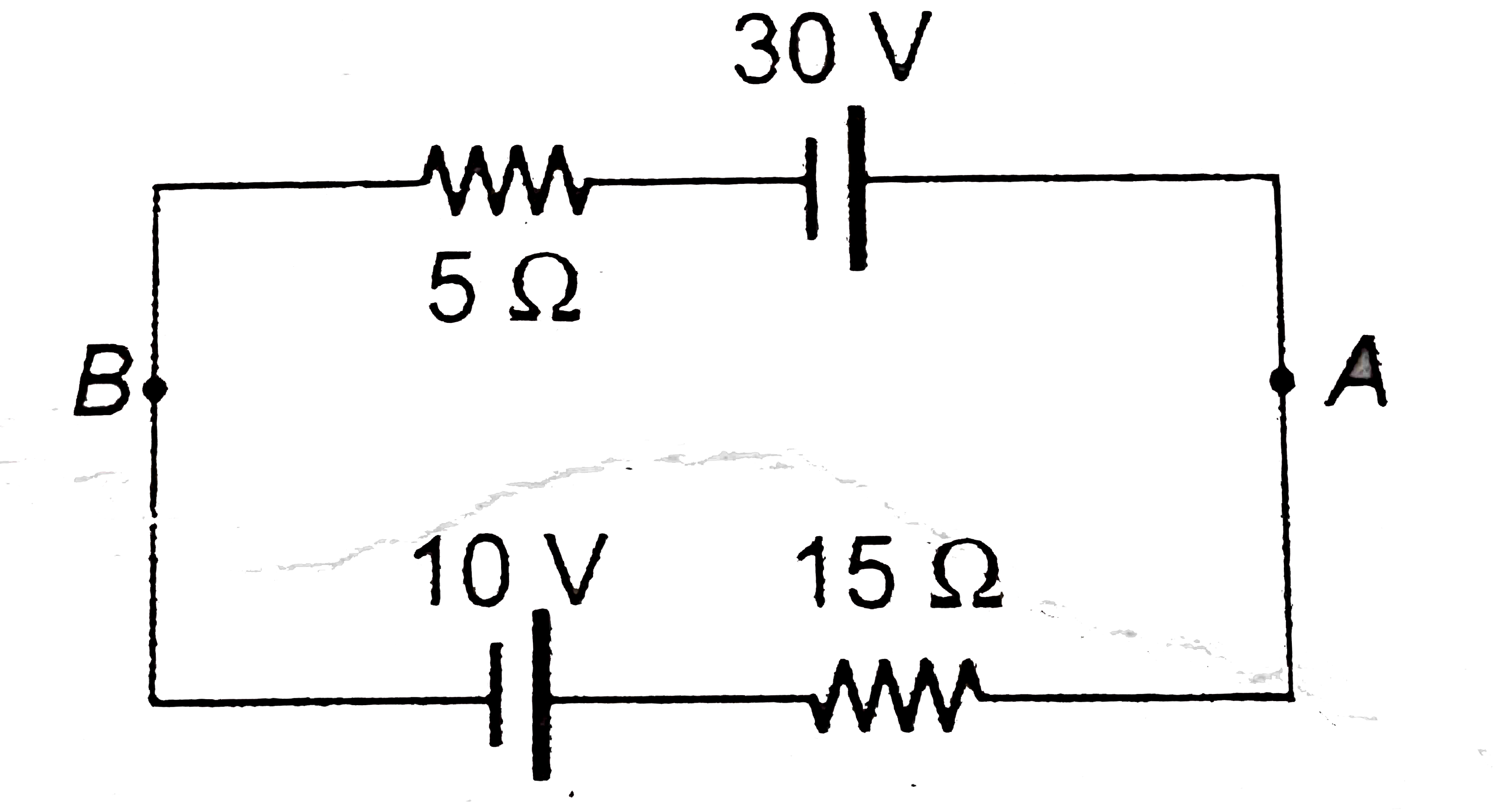
( e) Calculate the current in each resistor and terminal potential difference across each cell.

(f) Calculate potential difference across each cell.
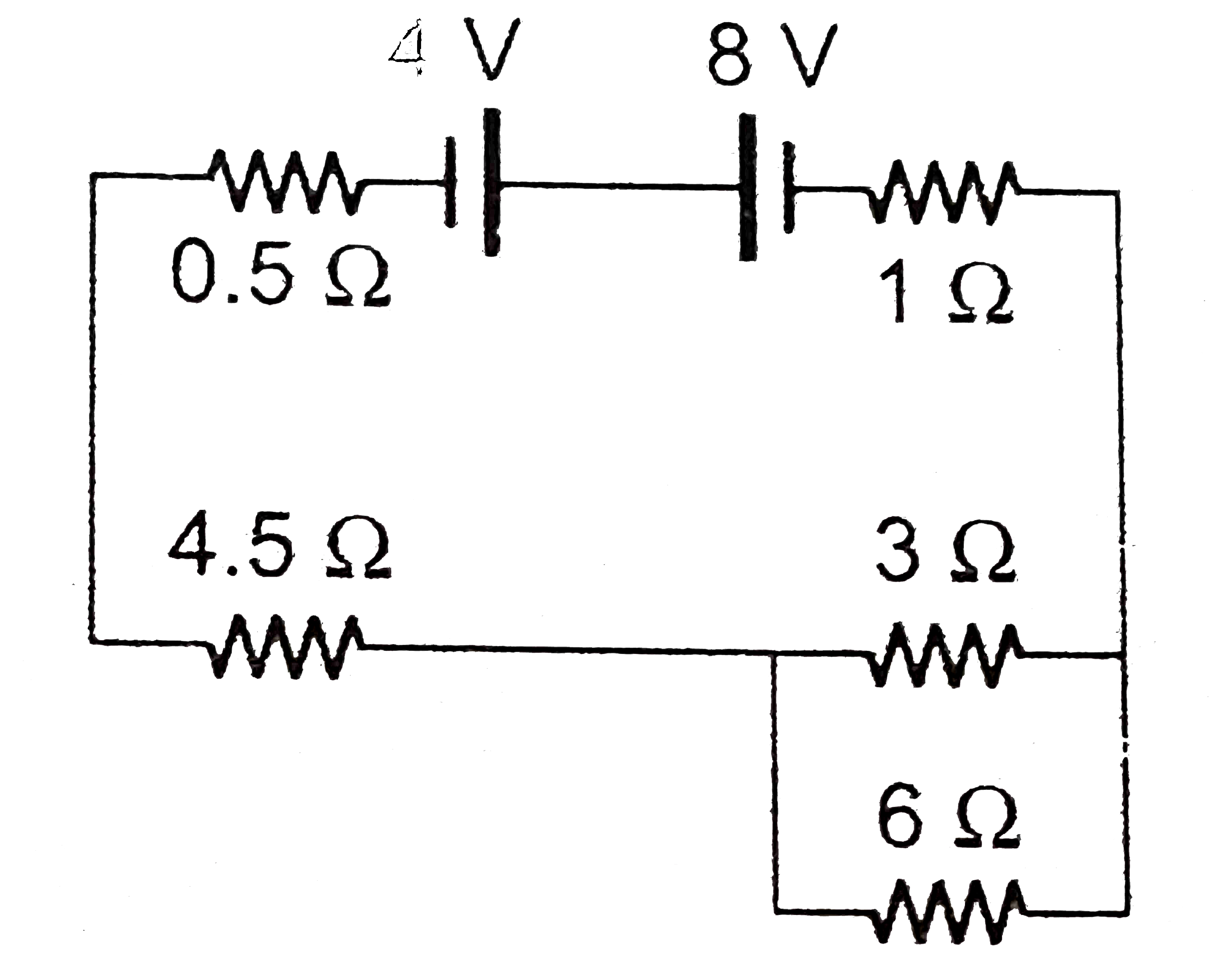
(g) A battery of 6 cells each of emf 2V and internal resistance 0.5Ω is being changed by DC mains of emf 220V by using an external resistance of 10Ω. Calculate.
(i) the charging current
(ii) the potential difference across the battery.
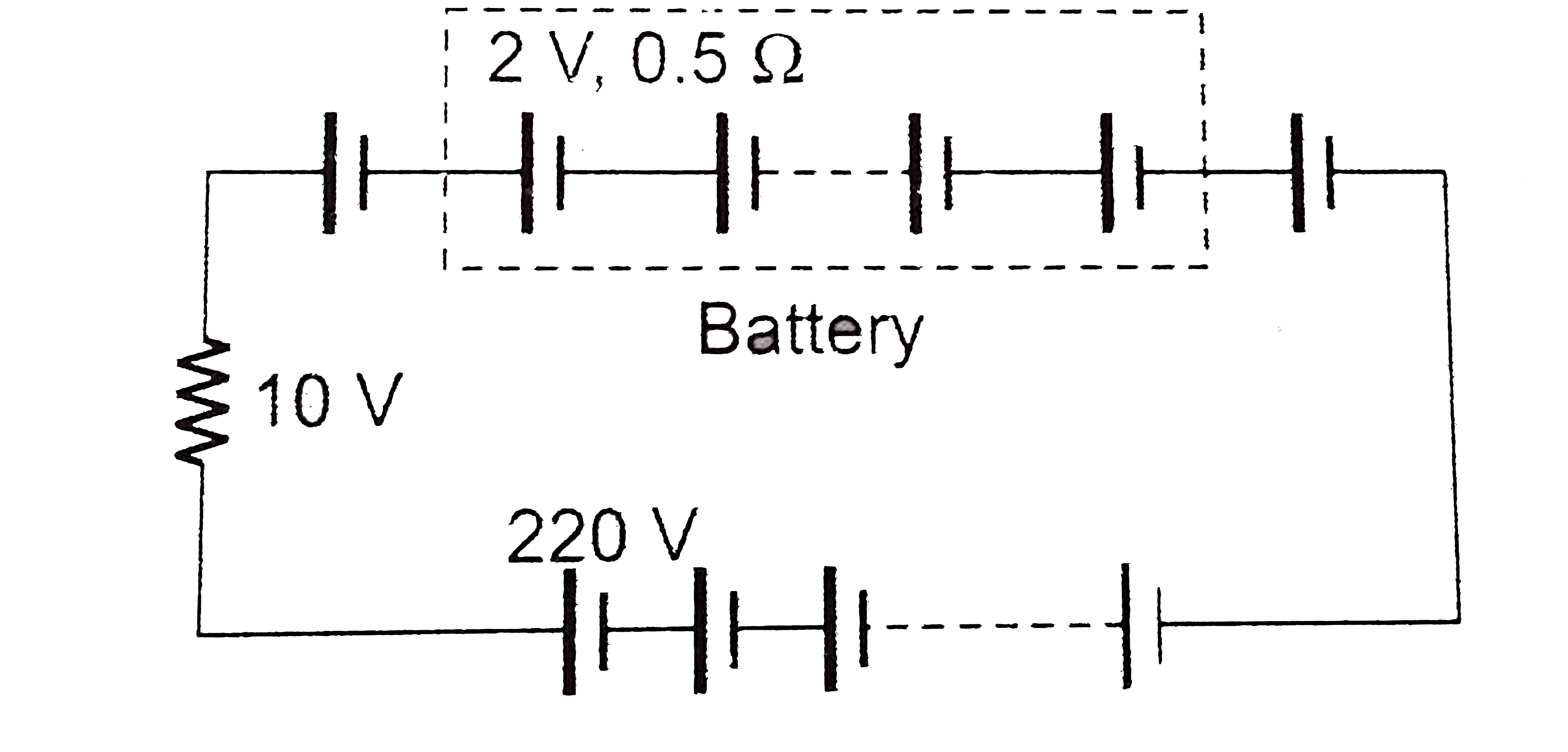 .
.
View SolutionDraw a. current versus load and b. current versus potential difference (across its two terminals) graph for a cell.
View SolutionWhen a current drawn from a battery is 0.5 A its terminal potential difference is 20 V. And when current drawn from it is 2.0 A, the terminal voltage reduces to 16 V. Find out. e.m.f and internal resistance of the bettery.
View Solution