Two parallel plane-polarized beams of light of equal intesity whose oscillation planes N1 and N2 from a small angle φ between them (Fig.) fall on a Nicol prism. To equalize the intensities of the beams emerging behind the prism, its principle direction N must be aligned along the bisecting line A or B. find the value of the angle φ at which the rotation of the Nicol prism through a small angle δφ<<φ from the position A results in the fractional change of intensities of the beams ΔI/I by the value η=100 times exceeding that resulting due to rotation through the same angle from the position B.
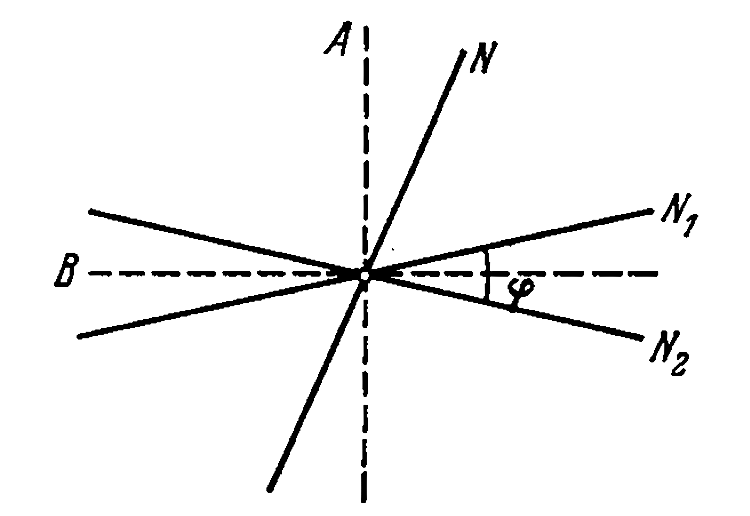
If the principle direction N of the Nicol is along A or B, the intensity o flight transmitted is the same whether the light incident is one with oscillation plane N1 or one with N2. If N makes an angle δφ with A as shown then the fractional difference in intensity transmitted (when the light incident is N1 or N2) is
(ΔII)A=cos2(90∘−φ2−δφ)−cos2(90∘+φ2−δφ)cos2(90∘−φ2)
=sin2(φ2+δφ)−sin2(φ2−δφ)sin2(φ2)
=2sin(φ2).2cos(φ2)δφsin2(φ2)=4cot(φ2)δφ
If N makes an angle δφ(<<φ) with B then
(ΔII)B=cos2(φ/2−δφ)−cos2(φ/2+δφ)cos∘φ/2=2cos(φ2).2sinφ/2δϕcos∘φ/2=4tanφ/2δφ
Thus η=(ΔII)A/(ΔII)B=cot2φ/2
or φ=2tan−1(1)√η
This given φ=11.4∘ for η=100.

Topper's Solved these Questions
- OPTICSBook:IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOVChapter:OPTICSExercise:Dispersion And Absorption Of Light
Explore 24 Videos
- OPTICSBook:IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOVChapter:OPTICSExercise:Optics Of Moving Sources
Explore 22 Videos
- OPTICSBook:IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOVChapter:OPTICSExercise:Diffraction Of Light
Explore 60 Videos
- MECHANICSBook:IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOVChapter:MECHANICSExercise:Mechanics Problems
Explore 92 Videos
- OSCILLATIONS AND WAVESBook:IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOVChapter:OSCILLATIONS AND WAVESExercise:Electromagnetic Waves, Radiation
Explore 36 Videos
Similar Questions
A free electron is located in the field of a monochromatic light wave. The intensity of light is I=150W/m2, its frequency is ω=3.4.1015s−1. Find:
(a) the electron's oscillation amplitude and its velocity amplitude,
(b) the ratio Fm/Fe, where Fm and Fe are the amplitudes of forces with which the magnetic and electric components of the ligth wave field act on the electron, demonstrate that the ratio is equal to 12v/c, where v is the electron's velocity amplitude and c is the velocity of light.
Instruction. The action of the magnetic field component can be disregarded in the equation of motion of the electron since the calculations shown it to be negligible.
View SolutionIn the Fizeau experiment on measurement of the velocity of light the distance between the gear wheel and the mirror is l=7.0km, the number of teeth is z=720. Two successive disappearances of light are observed at the folllowing rotation velocities of the wheel: n1=283rps and n2=313 rps. Find the velocity of light.
View SolutionA plane light wave falls normally on a diaphragm with round aperature opening the first N Fresnel zones for a point P on a screen located at a distance b form the diaphragm. The wavelength of light is equal to λ. Find the intensity of light I0 in front of the diaphragm if the distribution of intensity of light I(r) on the screen is knows. Here r is the distance from the point P.
View Solutionbody with zero initial velocity moves down an inclined plane from a height hand then ascends along the same plane with an initial velocity such that it stops at the ame height h. In which case is the time of motion longer?
View SolutionAn electromagnetic wave of frequency v=3.0MHz passes from vacuum into a dielectric medium with permittivity ε=4.0. Then
View SolutionAssertion: Nicol prism is used to produce and analyse plane polarised light. Reason: Nicol prism reduces the intensity of light to zero.
View SolutionA Nicol prism is placed in the way of partially polarized beam of light. When the prism is turned from the position of maximum transmission through an angle φ=60∘, the intensity of transmitted light decreased by a factor of η=3.0. Find the degree of polarization of incident light.
View SolutionA narrow beam of natural light with wavelength λ=589nm falls normally on the surface of a Wollaston polarizing prism made of Iceland spar as shown in Fig. The optical axes of the two parts of the prism are mutually perpendicualr. Find the angle δ between the directions of the beams behind the prism if the angle θ is equal to 30∘.

View SolutionA beam of light AO is incident a glass slab (μ=1.54) in the direction show. The reflected ray OB is passed through a Nicol prism. On viewing through a Nicol prism, we find on rotating the prism that

View SolutionIf the light waves pass through a nicol prism then all the oscillations occur only in one plane, such beam of light is called as
View SolutionAn unpolarised light of intensity I_(0) falls on a pair of Nicol prism. Angle between the two prisms is 60^(@) . Intensity of the light emitted from the prism will be
View SolutionAssertion : Nicol prism is used to produce and analyse plane polarised light.
Reason : Nicol prism reduces the intensity of light to zero.
View Solutionदो निकोल प्रिज्म इस प्रकार विन्यस्त है कि उनके मुख्य तलों के मध्य कोण 60∘है तो निकाय से आपतित अध्रुवित प्रकाश का कितना प्रतिशत गुजरेगा -
View SolutionUnpolarised light of intensity I_(0) falls on a Nicol prism. The light emerging from this Nicol Prism falls on another Nicol whose polarising axis is inclined to that of first by an angle 30^(@) . The light emerging from the second Nicol has the intensity :
View SolutionA : Nicol prism is used to produce and analyse plane polarised light. R : Nicol prism reduces the intensity of light to zero.
View Solution

