Can one consider the temperature 20and30K as low for to 0.226 and 0.760J/(mol.K)?
At low temperature C∝T3. This is also a test of the "lowness" of the temperature We see that
(C1C2)1/3=1.4982≈1.5=T1T2=3020
Thus T3 law is obeyed and T1,T2 can we regarded low.
Similar Questions
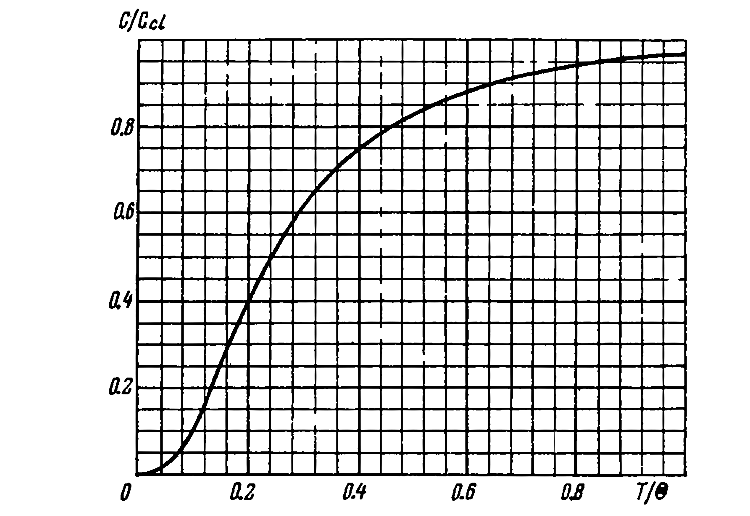
Figure. 6.10 shows heat capacity of a crystal vs temperatue in terms of the Debye theory. Here Ccl is classical heat capacity Θ is the Debye temperature. Using this plot, find:
(a0 The Debye temperature for silver if at a temperature T=65K its molar heat capacity is equal to 15J(mol.K),
(b) the molar heat capacity of aluminum at T=80K if at T=250K it is equal to 22.4J(mol.K)
(c )the maximum vibration frequency for copper whose heat capacity at T=125K differs form the classical value by 25%.
View Solution0.32g of exygen is kept in a rigid container and is heated. Find the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature from 250C→350C. The molar heat capacity of oxygen at constant volume is 20JK−1mol−1.
View Solution
Knowledge Check
What is the activation energy (KJ/mol) for a reaction if its rate constant doubles when the temperature is raised from 300 K to 400 K ? (R=8.314 J mol−1K−1)
A68.8B6.88C34.4D3.44Two moles of ideal helium gas are in a rubber balloon at 30∘C. The balloon is fully expandable and can be assumed to require no energy in its expansion. The temperature of the gas in the balloon is slowly changed to 35∘C. The amount of heat required in raising the temperature is nearly (take R
=8.31J/mol.K)A62JB104JC124JD208JHeat of combustion of ethanol at constant pressure and at temperature T K(=298 K) is found to be -qJ mol−1. Hence , heat of combustion (in J mol−1) of ehtanol at the same temperature at constant volume will be:
ART-qB−(q+RT)Cq-RTDq+RT
The kinetic energy of one gram molecule of a gas at normal temperature and pressure is (R=8.31J/mol−K)
View SolutionFind the amount of work done to increase the temperature of one mole of ideal gas by 30∘C .if its is expanding under the condition V∝R2/3(R=8.31J/mol−K):
View SolutionMolar heat capacity of aluminium is 25JK−1mol−1.The heat necessary to raise the temperature of 54 g of aluminium (Atomic mass 27 g mol−1) from 30∘C to 50∘C is
View SolutionThe rate of a reaction doubles when its temperature changes form 300K to 310K. Activation energy of such a reaction will be:
(R=8.314JK−1mol−1andlog2=0.301)
View SolutionAt a temperature of 0∘K, the germanium behaves as
View Solution

