AΣ+ hyperon with kinetic energy TΣ=320MeV distingrated during its flight into a neutrral particle and a positive pion outgoing with kinetic energy Tπ=42MeV at right angles to the hyperon's motion direction. Find the rest mass of the neutral particle (in MeV units).

By energy conservation
√m2Σc4+c2+P2Σ=√m2πc4+c2P2π+√m2nc4+c2p2π+c2P2Σ
or (√mΣc4+c2P2Σ−√m2πc4+c2p2π)2=m2nc4+c2p2π+c2P2Σ
or m2Σc4+c2P2Σ+m2πc4+c2p2π−2√m2πc4+c2P2Σ√m2πc2+c2p2π
=m2nc2+c2p2π+c2P2Σ
or using the K.E o f Σ&π
m2n=m2Σ+m2p−2(mΣ+TΣc2)(mπ+Tπc2)
and mn√m2Σ+m2π−2(mπ+TΣc2)(mπ+Tπc2)=0.949GeVc2
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
An alpha-particle with kinetic energy Tα=7.0MeV is scattered elastically by an initially stationary Li6 nucleus. Find the kinetic energy of the recoil nucleus if the angle of divergence of the two particle is Θ=60∘.
View SolutionHow will the rending of the ammeter change if the key K is closed?
View SolutionThe velocity of a particle at which the kinetic energy is eqyal to its rest mass energy is
View SolutionFind the velocity at which the kinetic energy of a particle equals its rest energy.
View SolutionAn alpha-particle with kinetic energy Tα=7.0MeV is scattered elastically by an initially stationary Li6 nucleus. Find the kinetic energy of the recoil nucleus if the angle of divergence of the two particle is Θ=60∘.
View SolutionFind the enrgy of the reaction N^(14)(alpha,p)O^(17) if the kinetic enrgy of the incoming alpha-pariticle is T_(alpha)=40MeV and the proton outgoing at an angle theta=60^(@) to the motion direction of the alpha-particle has a kinetic energy T_(P)= 2.09 MeV .
View SolutionAn alpha particles kinetic energy T=5.3MeV initiates a nuclear reaction Be9(α,n)C12 with energy yield Q=+5.7MeV. Find the kinetic energy of the nerutron outgoing at right angle to the motion direction of the alpha-particles.
View SolutionA neutron with kinetic energy T= 10MeV activates a nuclear reaction C^(12)(n,alpha)Be^(9) whose threshold is T_(th)= 6.17MeV . Find the kinetic energy of the alpha-particles outgoing at right angles to the incoming neutrons' direction.
View SolutionFind the kinetic energy of a neutron emerging as a result of the decay of a stationary Σ−hyperon(Σ−→n+π−).
View SolutionA stationary neutral particle disintegrated into a proton with kinetic energy T= 5.3MeV and a negative pion. Find the mass of that particle. What is its name.
View SolutionA negative pion with negative energy T= 50MeV disintergrated during its flight into a moun and a neutrino. Find the energy of the neutrino outgoing at right angles to the pion's motion derection.
View SolutionA neutral pion disintegrated during its flight into two gamma quants with equal energies. The angle of divergence of gamma quanta is Θ=60∘. Find the kinetic energy of the pion and of each gamma quantum.
View SolutionA particle of mass m experienced an elastic collision with a stationary particle of mass 2m . What fraction of the kinetic energy does the striking particle lose if recoils at the right angles to its original motion direction.
View SolutionA particle with the potentila energy shown in the graph is moving to the right. It has 1.0J of kinetic energy at x=1.0m. Where the particle reverses its direction of motion?
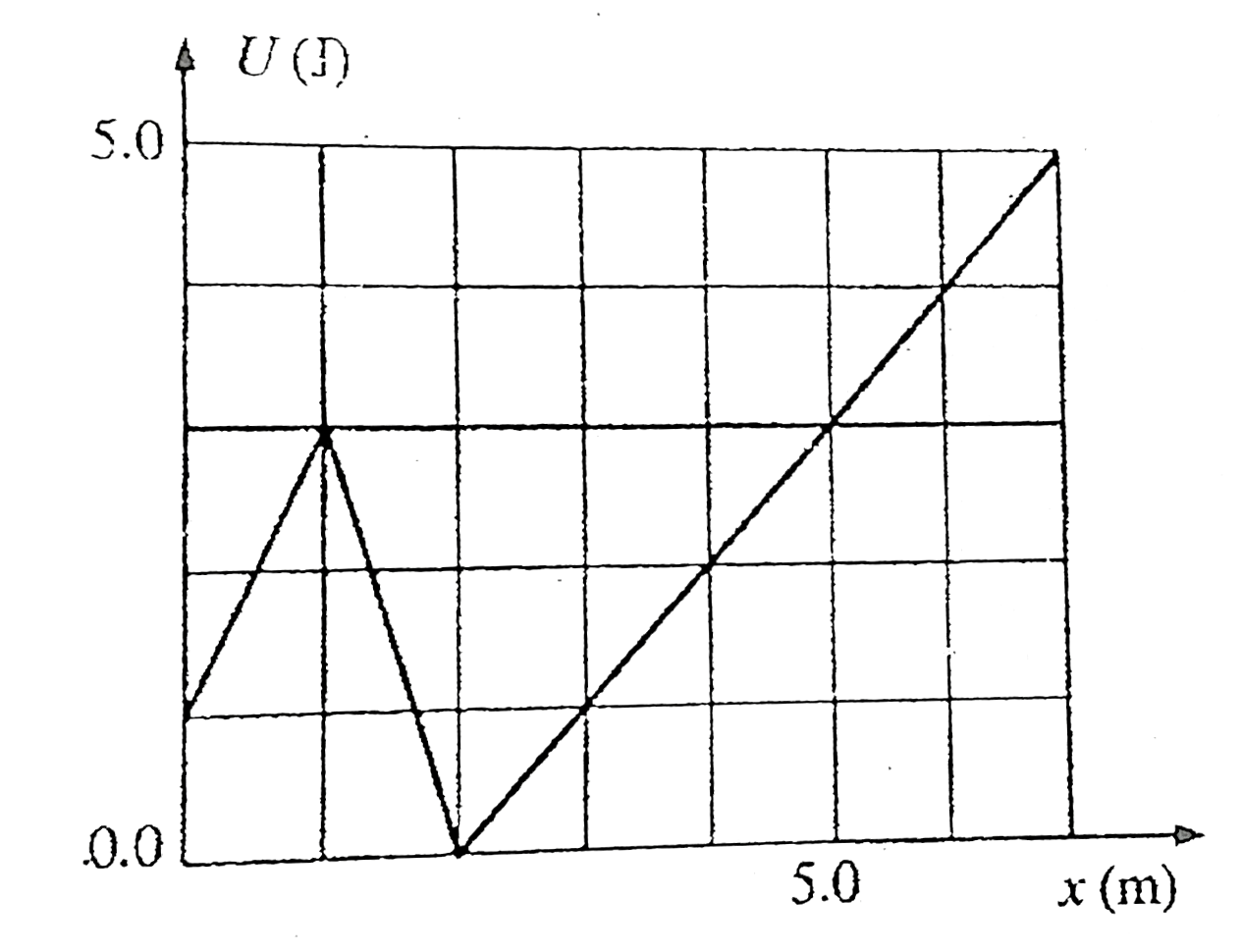
View SolutionFind the energy of the reaction .^(14)N(alpha, p) .^(17)O , if the kinetic energy of the incoming alpha -particle is T_(alpha) = 4.0 MeV & the proton outgoing at an angle theta = 60^(@) to the motion direction of the alpha -particle has a kinetic energy T_(p) = 2.09 MeV .
View Solution

