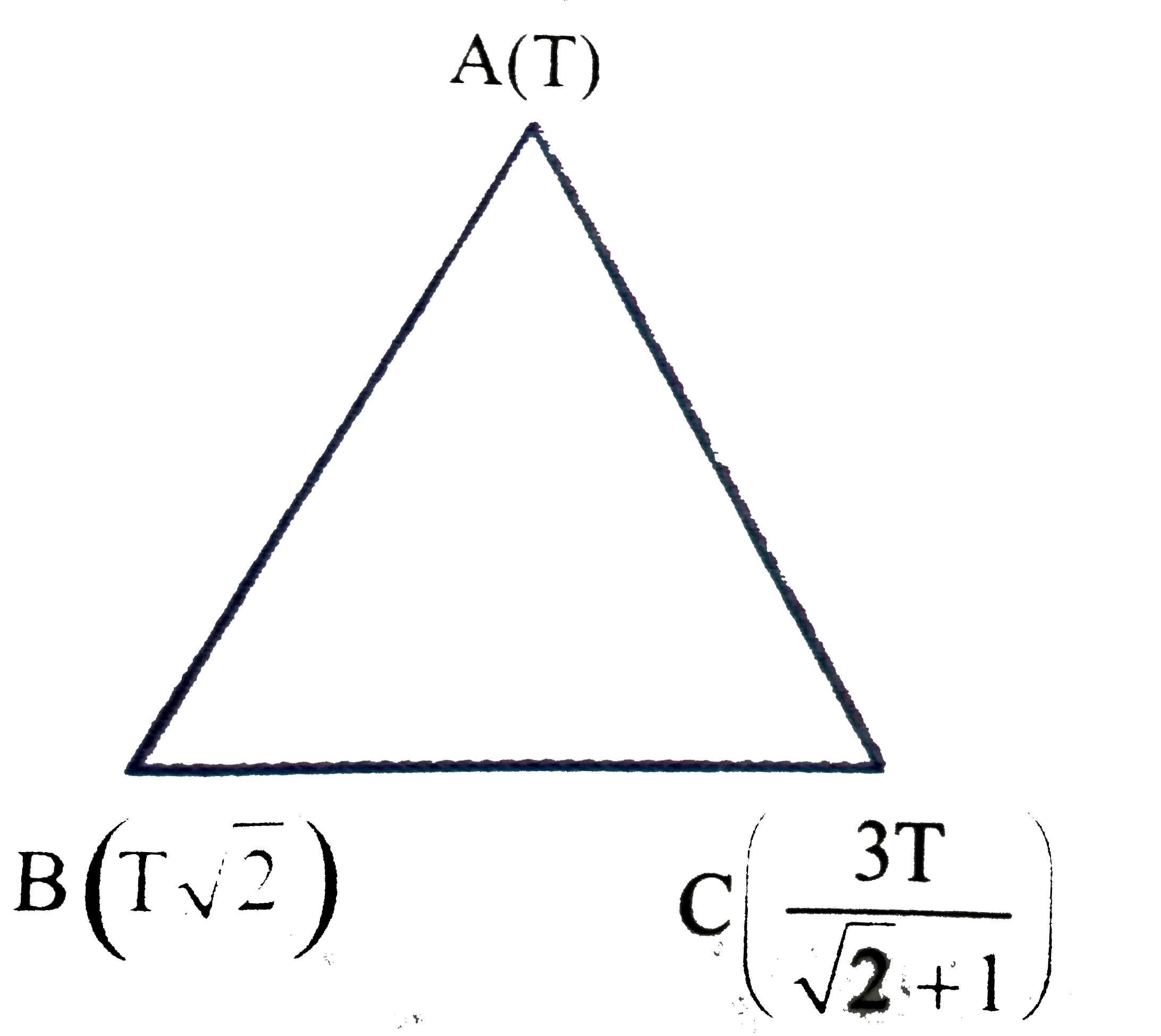
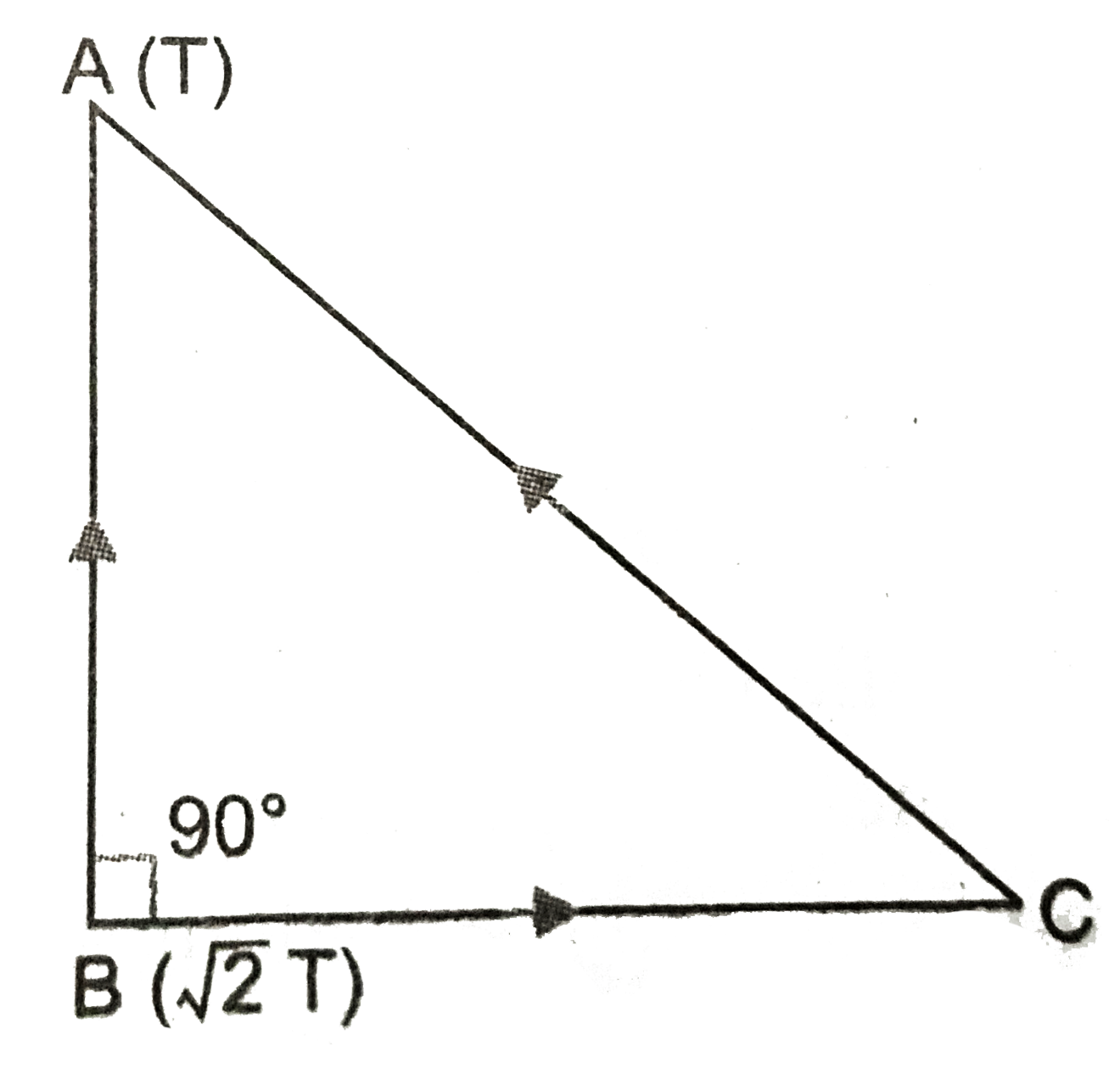
The three rods of same meterial and crosssectional area from the sides of a triangle ABC The points A,B and C are maintained at temperature TT√2 and 3T(√2+1) respectively Assuming that only heat conducting takes place the system is in steady state, find the angle at B The temperature difference per unit length along SB and CA is equal
 .
.
30∘
45∘
60∘
90∘
The correct Answer is:D
TB>TA heat will flow from B to A and from C to B to remain in steady state. The conduction formula is ΔQΔT=KALΔT
TCTA=3√2+TA and TA−Tc=√2(TC−TA√2)
TA−TcL√2=(Tc−TA√2)L=TC−TBL
from this we can find that LCB=L,LAC=L√2
and for which LAB=L∴haTB=90∘ .
Similar Questions
Four rods of identical cross-sectional area and made from the same metal form the sides of square. The temperature of two diagonally opposite points are T and√2T respectively in the steady state. Assuming that only heat conduction takes place, what will be the temperature difference between other two points
View SolutionThree rods of same cross sectional area are made of same material and form the sides of a right-angled isosceles triangle PQR, right angled at Q. P and Q are maintained at temperature T and 2T, respectively. If the temperature of end R is T', then what is the ratio of T'/T. Assume that only heat conduction takes place.
View Solution
Knowledge Check
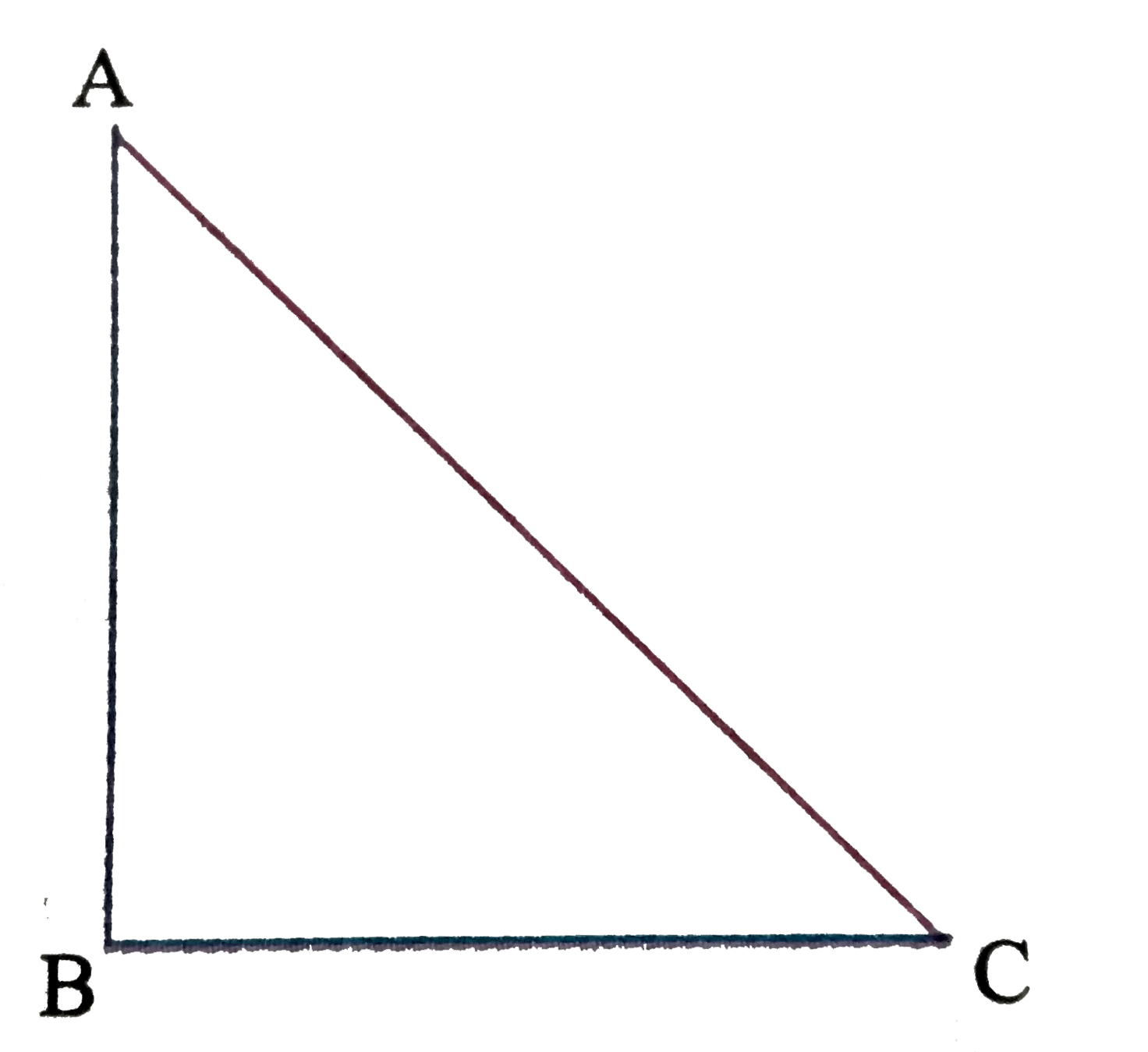
Three rods of identical cross-sectional area and made from the same metal form the sides of an insosceles triangle ABC right angled at B The pints A and B are maintained at temperatures T and √T respectively in the steady state Assuming that only heat conduction takes place, temperature of point C is .
 .A3T√2+1BT√2+1CT3(√2−1)DT√2−1
.A3T√2+1BT√2+1CT3(√2−1)DT√2−1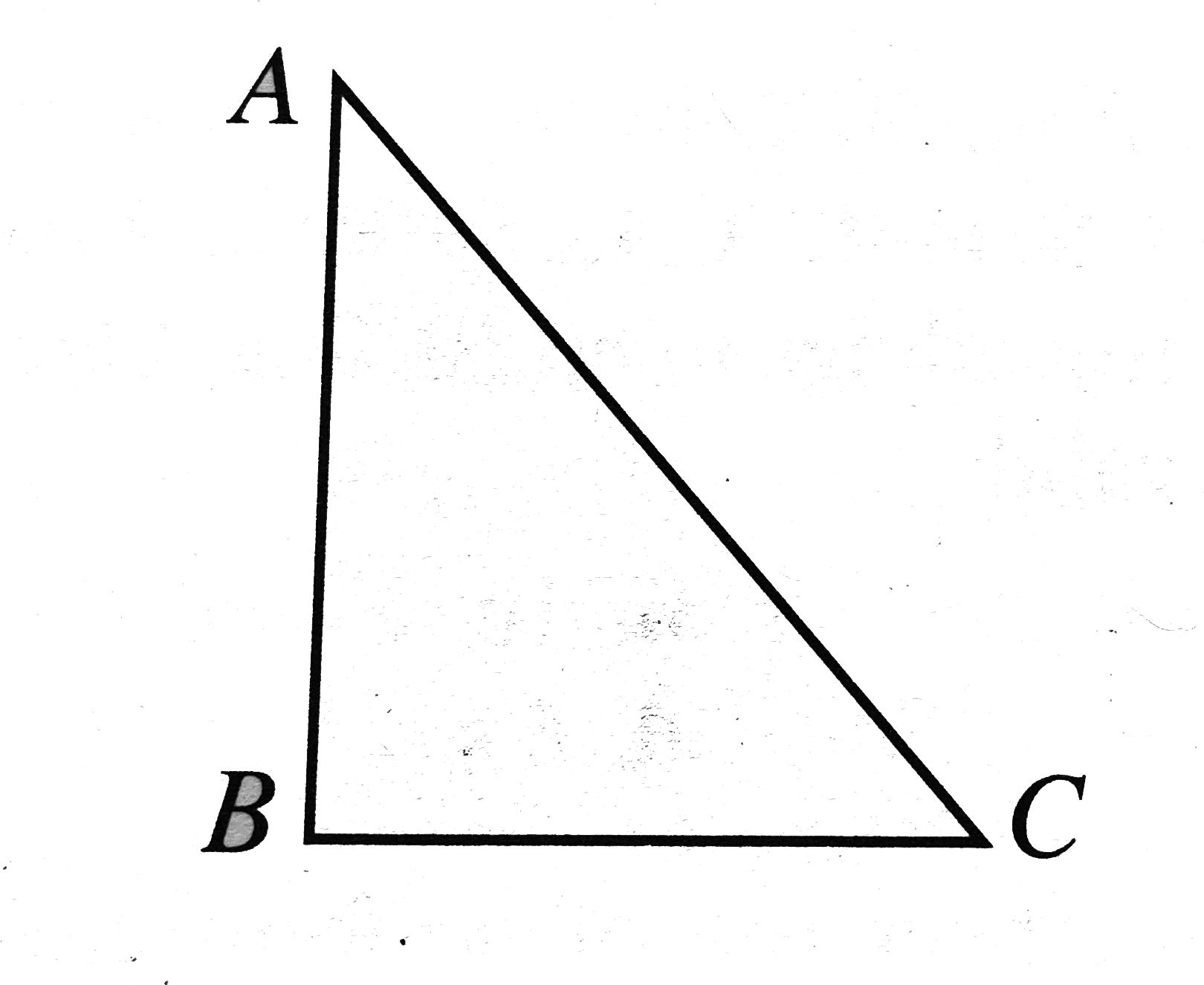
Three rods of identical cross-sectional area and made from the same metal form the sides of an isosceles Delta ABC right angled at B. The points A and B are maintained at temperetures T and √2T, respectively in the steady state. Assuming that only heat conduction takes place, temperature of point C isA3T√2+1BT√2+1CT3(√2−1)DT√2−1Three rods of identical cross-sectional area and made from the same metal form the sides of an isosceles triangle ABC right angled at B as shown in the figure. The points A and B are maintained at temperature T and (√2)T respectively in the steady state. Assuming that only heat conduction takes place, temperature of point C will be
 AT(√2)−1BT(√2)+1C3T(√2)+1DT(√3)(√2−1)
AT(√2)−1BT(√2)+1C3T(√2)+1DT(√3)(√2−1)
Four identical rods AB, CD, CF and DE are joined as shown in figure. The length, cross-sectional area and thermal conductivity of each rod are l, A and K respectively. The ends A, E and F are maintained at temperature T1 , T2 and T3 respectively. Assuming no loss of heat to the atmospere, find the temperature at B.

View SolutionThree rods of identical cross-sectional area and made from the same metal, from the sides of an isosceles triangle ABC right angled at B, as shown in Fig .7(CF).23. The points A and B are maintained at temperature T and √2T respectively in the steady. Assuming that only heat conduction takes place, temperature of point C will be
View SolutionThree rods of identical cross-sectional area and made from the same metal form the sides of an isosceles triangle ABC right angled at B as shown in the figure. The points A and B are maintained at temperature T and (√2)T respectively in the steady state. Assuming that only heat conduction takes place, temperature of point C will be

View SolutionThree rods of identical cross-sectional area and made from the same metal form the sides of an equilateral triangle ABC The points A and B are maintained at temperature √3T and T respectively In the steady state, the temperature of the point C is TC Assuming that only heat conduction takes place, the value of TC/T is equal to .
View SolutionThree rods of identical area of cross-section and made from the same metal from the sides of an isosceles triangle. ABC, right angled at B. The points A and B are maintained at temperatures T and √2T respectively. In the steady state the temperature of the point C is TC.
Assuming that only heat conduction takes place , TCT is equal to
View Solution
