Carbylamine reaction is given by
C6H5NHCH3
CH3NH2
(CH2)2NH
(CH3)3N
The correct Answer is:B
Step-by-Step Solution
1. Understanding the Carbylamine Reaction:
The carbylamine reaction involves the reaction of a primary amine with chloroform (CHCl₃) in the presence of alcoholic potassium hydroxide (KOH) and heat. The product formed is an isocyanide (or carbylamine).
2. Identifying the Reactants:
The reactants required for the carbylamine reaction are:
- A primary amine (RNH₂)
- Chloroform (CHCl₃)
- Alcoholic potassium hydroxide (KOH)
3. Mechanism of the Reaction:
- The hydroxide ion (OH⁻) from KOH abstracts a hydrogen atom from chloroform, forming a dichlorocarbene intermediate (CCl₂).
- This dichlorocarbene is electron-deficient and reacts with the primary amine (RNH₂).
- The nitrogen in the amine donates its lone pair to the electron-deficient carbon, forming a bond.
- Subsequent steps involve the removal of chloride ions (Cl⁻) and the formation of the isocyanide (RNC).
4. Identifying Primary Amines:
In order to determine which option gives the carbylamine reaction, we need to identify which of the given amines is a primary amine:
- Option A: Contains one aryl group and one alkyl group (secondary amine).
- Option B: Contains only one alkyl group (primary amine).
- Option C: Contains two alkyl groups (secondary amine).
- Option D: Contains three alkyl groups (tertiary amine).
5. Conclusion:
The only option that contains a primary amine is Option B (CH₃NH₂). Therefore, this is the correct answer as it will undergo the carbylamine reaction.
Final Answer:
The carbylamine reaction is given by Option B: CH₃NH₂ (methylamine), which is a primary amine.
---
The carbylamine reaction involves the reaction of a primary amine with chloroform (CHCl₃) in the presence of alcoholic potassium hydroxide (KOH) and heat. The product formed is an isocyanide (or carbylamine).
The reactants required for the carbylamine reaction are:
- A primary amine (RNH₂)
- Chloroform (CHCl₃)
- Alcoholic potassium hydroxide (KOH)
- The hydroxide ion (OH⁻) from KOH abstracts a hydrogen atom from chloroform, forming a dichlorocarbene intermediate (CCl₂).
- This dichlorocarbene is electron-deficient and reacts with the primary amine (RNH₂).
- The nitrogen in the amine donates its lone pair to the electron-deficient carbon, forming a bond.
- Subsequent steps involve the removal of chloride ions (Cl⁻) and the formation of the isocyanide (RNC).
In order to determine which option gives the carbylamine reaction, we need to identify which of the given amines is a primary amine:
- Option A: Contains one aryl group and one alkyl group (secondary amine).
- Option B: Contains only one alkyl group (primary amine).
- Option C: Contains two alkyl groups (secondary amine).
- Option D: Contains three alkyl groups (tertiary amine).
The only option that contains a primary amine is Option B (CH₃NH₂). Therefore, this is the correct answer as it will undergo the carbylamine reaction.
The carbylamine reaction is given by Option B: CH₃NH₂ (methylamine), which is a primary amine.
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
Carbylamine reaction is given only by
Aprimary aminesBsecondary aminesCtertiary aminesDquatenary amineCarbylamine reaction is NOT given by
AC2H5NH2B(C6H5)NH2CCH3NH2D(CH3)3NThe carbylamine reaction is
A B
B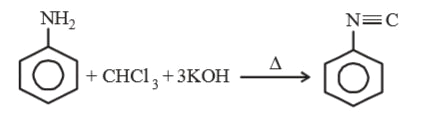 C
C D
D