Consider the following Borh-Habber's cycle for formation of MX3(s).
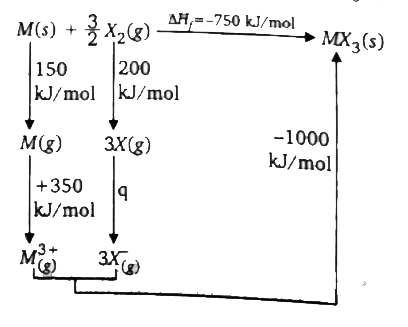
Then calculate value q150, here q1 is electron affinity of X(g) in kJ/mol.
The correct Answer is:4
−750=150+32×200+350+q−1000
q=3×ΔHBG=−550,
q1=5503=183,q150=3.66≈4.0
Topper's Solved these Questions
- PERIODIC PROPERTIESBook:VK JAISWALChapter:PERIODIC PROPERTIESExercise:Level 1
Explore 198 Videos
- PERIODIC PROPERTIESBook:VK JAISWALChapter:PERIODIC PROPERTIESExercise:Level 2
Explore 102 Videos
- PERIODIC PROPERTIESBook:VK JAISWALChapter:PERIODIC PROPERTIESExercise:MATCHTHE COLUMN
Explore 5 Videos
- p-BLOCK ELEMENTSBook:VK JAISWALChapter:p-BLOCK ELEMENTSExercise:SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS
Explore 36 Videos
- QUALITATIVE INORGANIC ANALYSISBook:VK JAISWALChapter:QUALITATIVE INORGANIC ANALYSISExercise:SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS
Explore 5 Videos
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
Which of the following has the least electron affinity in kJmol−1?
AOxygenBcarbonCNitrogenDBoronWhich of the following are the values of electron affinities in kJ/mol for the formation of O− and O2− from O?
A-142, -702B-141, 702C142, 702D−142,−142What is the ΔH of the following affinity.
Mgg+2Fg→Mg2+(g)+2F−(g).
If the electron affinity of
Fg=−328kJ mol−1 and first ionisation energy of Mg=737.7kJ mol−1 and second ionisation energy of Mg=1451kJ mol−1A1532.7kJ mol−1B1860.7kJ mol−1C2516.7kJ mol−1D2844.7kJ mol−1
Consider the following table
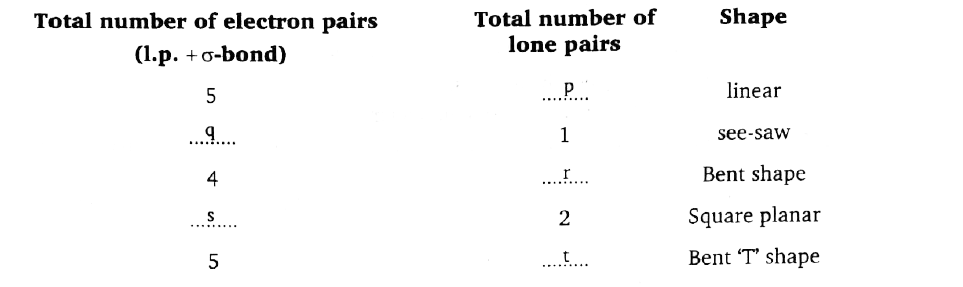
Then calculate value of "p+q+r-s-t".
View SolutionCalculate Q1,Q2andQ3,

View SolutionCalculate the lattice enthalpy of KCl from the following data by Born- Haber's Cycle.
Enthalpy of sublimation of K=89kJmol–1
Enthalpy of dissociation of Cl=244kJmol–1
Ionization enthalpy of potassium = 425kJmol–1
Electron gain enthalpy of chlorine = –355kJmol–1
Enthalpy of formation of KCl=–438kJmol−1
View SolutionThe ΔH0f(KF,s) is −563kJmol−1. The ionization enthalpy of K(g) is 419kJmol−1. and the enthalpy of sublimation of potassium is 88kJmol−1. The electron affinity of F(g) is 322kJmol−1 and F−F bond enthalpy is 158kJmol_1. Calculate the lattice enthalpy of KF(s).
The given data are as follows:
(i) K(s)+1/2F2(g)→KF(s) ΔH0f=−563kJmol−1
(ii) K(g)→K+(g)+e− Δ0Ioniz=419kJmol−1
(iii) K(s)→K(g) ΔH0sub=88kJmol−1
(iv) F(g)+e−→F−(g) ΔH0eg=−322kJmol−1
(v) F2(g)→2F(s) ΔH0diss=158kJmol−1
(vi) K+(g)+F−(g)→KF(s) ΔH0L=?
View SolutionThe ΔH0f(KF,s) is −563kJmol−1. The ionization enthalpy of K(g) is 419kJmol−1. and the enthalpy of sublimation of potassium is 88kJmol−1. The electron affinity of F(g) is 322kJmol−1 and F−F bond enthalpy is 158kJmol_1. Calculate the lattice enthalpy of KF(s).
The given data are as follows:
(i) K(s)+1/2F2(g)→KF(s) ΔH0f=−563kJmol−1
(ii) K(g)→K+(g)+e− Δ0Ioniz=419kJmol−1
(iii) K(s)→K(g) ΔH0sub=88kJmol−1
(iv) F(g)+e−→F−(g) ΔH0eg=−322kJmol−1
(v) F2(g)→2F(s) ΔH0diss=158kJmol−1
(vi) K+(g)+F−(g)→KF(s) ΔH0L=?
View Solution

