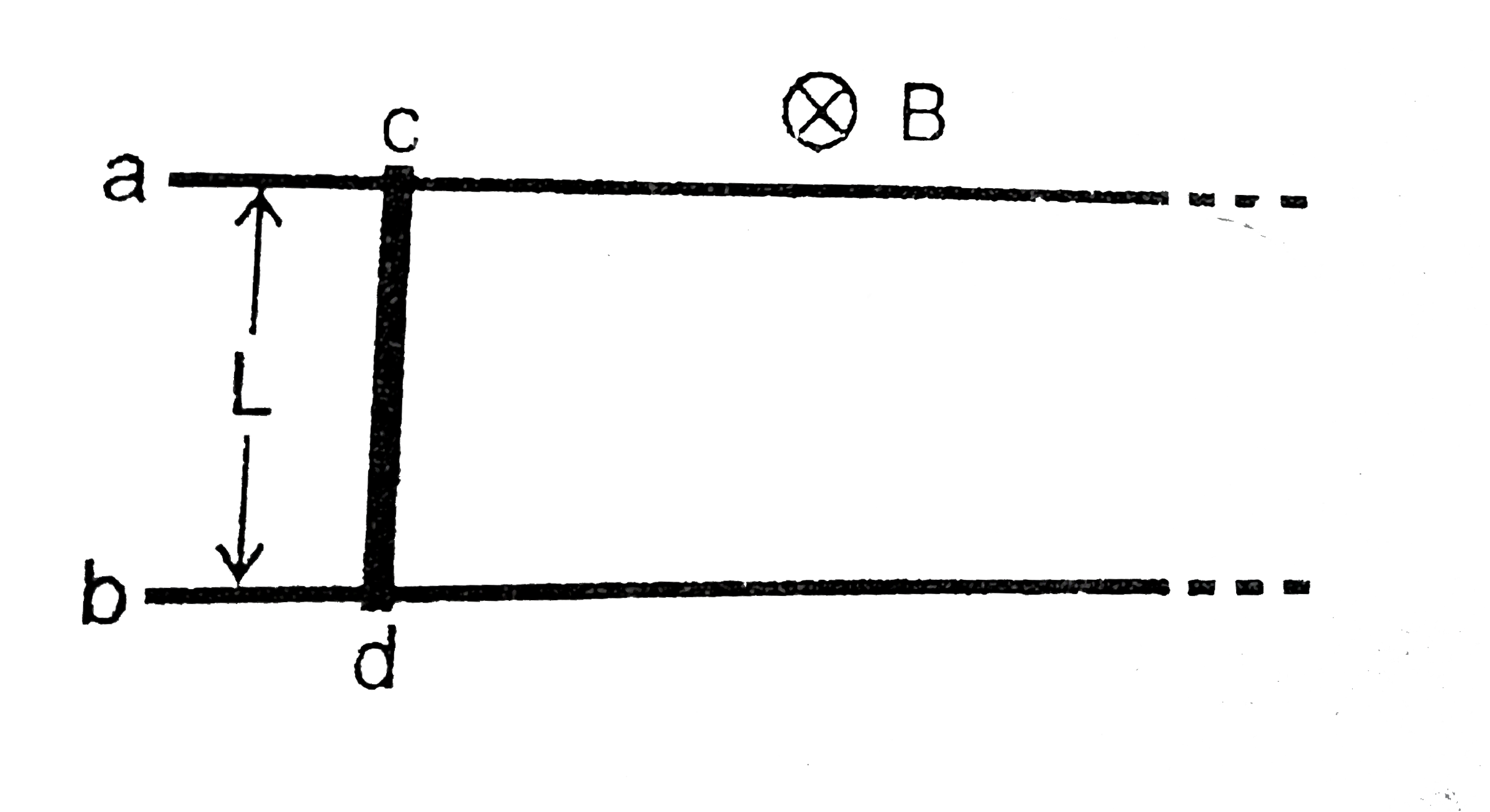
In the shown figure, there are two long fixed parallel conducting rails (having negligible resistance) and are separated by distance L. A uniform rod of resistance R and mass M is placed at rest on frictionless rails. Now at time t=0, a capacitor having charge Q0 and capacitance C is connected across rails at ends a and b such that current in rod (cd) is from c towards d and the rod is released. A uniform and constant magnetic field having magnitude B exists normal to plane of paper as shown. (Neglect acceleration due to gravity)
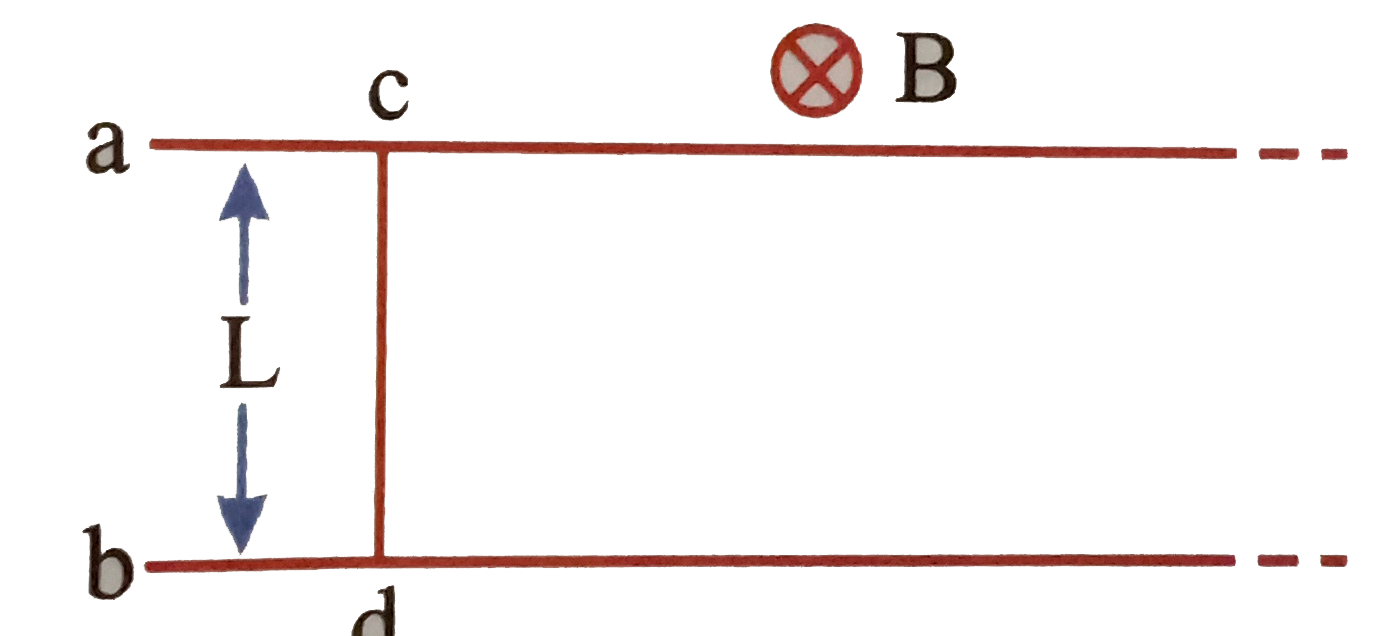
When the speed of rod is v, the charge on capacitor is :
(Q0−RMLBCv)
(Q0−MRC2Bv)
(Q0−MLBv)
(Q0−MRCBv)
The correct Answer is:C
At any instant t, the charge on capacitor q, velocity of rod v and the current I through rod are as shown.
mdvdt=BIL=B(−dqdt)L ...(1)
Ϸ underset(0)overset(v) (int) m d v = -underset(Q_(0))overset(q)(int)BL dq
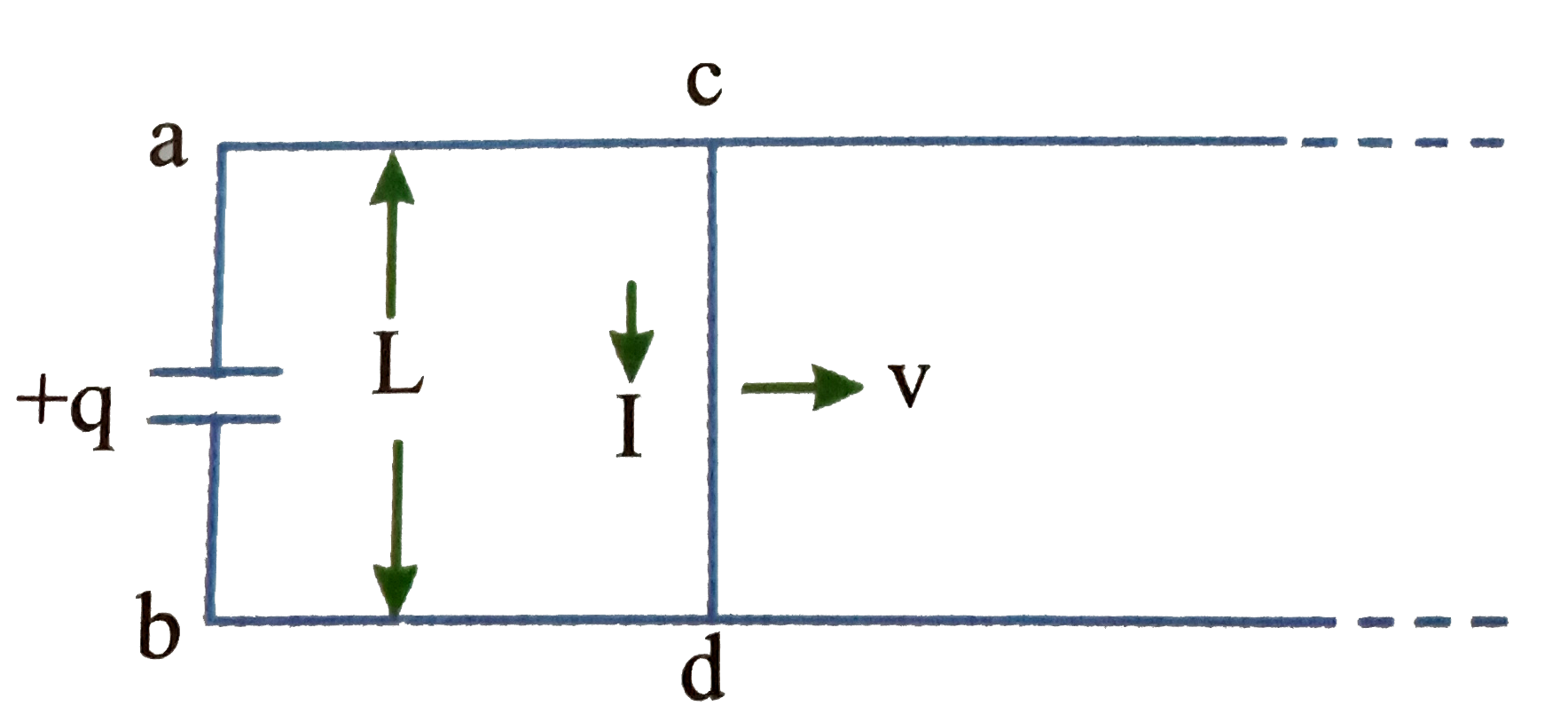
solving we get q=Q0−MvBL ...(2)
Also, qC=BLV+IR=BLv−Rdqdt ...(3)
form equaiton (1) and (3)
qC=BLv+mRBLdvdt .....(4)
from (4) when dvdt=0Ϸ=qC=BLv ......(5)
From (2) and (5). At instant acceleration is zero
v=Q0LBM+B2L2C and q=B2L2CQ0M+B2L2C
Similar Questions
Figure-5.39 shows two vertical smooth rails AB and CD separated by a distance l. Ends A and C are connected with capacitor of capacitance C. A rod PQ of mass m is horizontally kept in touch with both rails as shown. If it is released at t=0 and it remains in contact with rails during its fall, find the charge on capacitor as function of time. Neglect resistance of connecting wires and rails.

View SolutionIn the figure shown a conducting rod of length l, resistance R and mass m is moved with a constant velocity v. The magnitude field B varies with time t as B=5t, what t is time in second. At t=0 the area of the loop containing capacitor and the rod is zero and the capacitor is uncharged. the rod started moving at t=0 on the fixed smooth conducting rails which have negligible resistance. Find the current in the circuit as a function of time t.
View SolutionA rod with resistance R lies across frictionless conducting rails in a constant uniform magnetic field →B, as shown in the following figure. Assume the rails have negligible resistance. The magnitude of the force that must be applied by a person to pull the rod to the right at constant speed v is
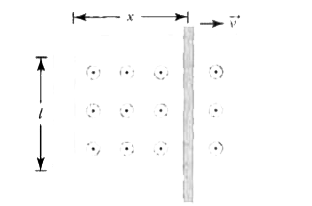
View SolutionA conducting rod of length is moved at constant velocity v0 on two parallel, conducting, smooth, fixed rails, that are placed in a uniform constant magnetic field B perpendicular to the plane for the rails as shown in Fig. A resistance R is connected between the two ends of the rails.
Then which of the following is/are correct:

View SolutionA metallic rod of mass m and resistance R is sliding over the 2 conducting frictionless rails as shown in Fig. An infinitely long wire carries a current I0. The distance of the rails from the wire are b and a respectively.
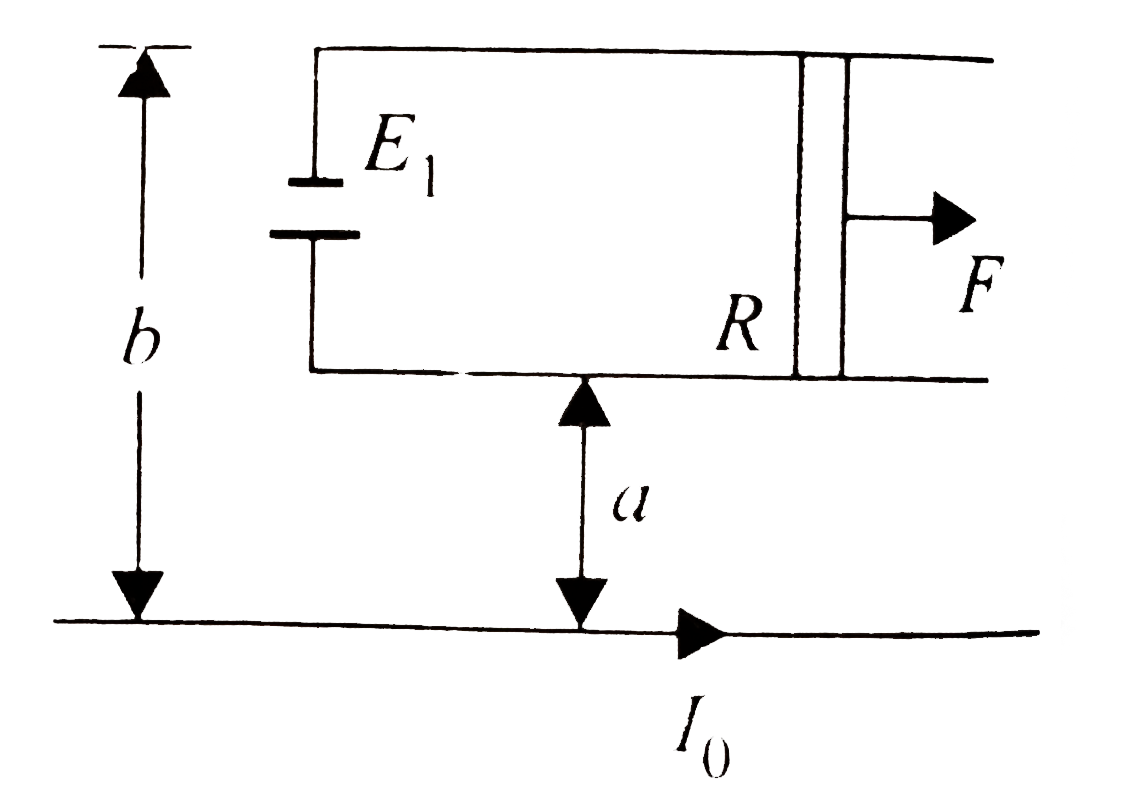
Find the value of current in the circuit if the rod slides with constant velocity v0
View SolutionIn the shown figure, there are two long fixed parallel conducting rails (having negligible resistance) and are separated by distance L . A uniform rod of resistance R and mass M is placed at rest on frictionless rails. Now at time t = 0 , a capacitor having charge Q_(0) and capacitance C is connected across rails at ends a and b such that current in rod (c d) is from c towards d and the rod is released. A uniform and constant magnetic field having magnitude B exists normal to plane of paper as shown. (Neglect acceleration due to gravity) When the speed of rod is v , the charge on capacitor is :
View SolutionIn the shown figure, there are two long fixed parallel conducting rails (having negligible resistance) and are separated by distance L.A uniform rod of resistance R and mass M is placed at rest on frictionless rails. Now at time t = 0, a capacitor having charge Q0 and capacitance C is connected across rails at ends a and b such that current in rod(cd) is from c towards d and the rod is released. A uniform and constant magnetic field having magnitude B exists normal to plane of paper as shown. (Neglect acceleration due to gravity)
When the acceleration of rod is zero, the speed of rod is :
View SolutionA conducting rod of length is moved at constant velocity v_(0) on two parallel, conducting, smooth, fixed rails, that are placed in a uniform constant magnetic field B perpendicular to the plane for the rails as shown in Fig. A resistance R is connected between the two ends of the rails. Then which of the following is/are correct:
View Solution

