Complete the following reactions by supplying the products and the reagents
(CH3)2C=CH2H2O,H2SO4−−−−−−−→[A]C6H6−−−−−−−−−→conc.H2SO4[B]
To complete the reactions given in the question, we will break down the steps involved in each reaction.
1. Identify the Starting Material:
The starting material is (CH₃)₂C=CH₂, which is isobutylene (or 2-methylpropene).
2. First Reaction:
The first reaction involves the hydration of isobutylene in the presence of water (H₂O) and sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄).
- Mechanism:
- The double bond in isobutylene will react with a proton (H⁺) from sulfuric acid, forming a carbocation.
- The more stable carbocation will be formed on the more substituted carbon (the one attached to two methyl groups).
- Water will then attack this carbocation, leading to the formation of an alcohol.
- Product (A): The product formed is 2-methylpropan-2-ol (tert-butyl alcohol), represented as (CH₃)₃COH.
3. Second Reaction:
The second reaction involves the conversion of the alcohol formed in the first step to an alkene using benzene (C₆H₆) and concentrated sulfuric acid (conc.H₂SO₄).
- Mechanism:
- The alcohol will first be protonated by sulfuric acid to form an oxonium ion.
- This oxonium ion will then lose a water molecule, leading to the formation of a double bond, resulting in an alkene.
- Product (B): The product formed is isobutylene again, which is (CH₃)₂C=CH₂.
Final Products:
- (A): 2-methylpropan-2-ol (tert-butyl alcohol) - (CH₃)₃COH
- (B): Isobutylene - (CH₃)₂C=CH₂
Summary of Reactions:
1. (CH₃)₂C=CH₂+H₂O+H₂SO₄→(CH₃)₃COH (A)
2. (CH₃)₃COH+C₆H₆+conc.H₂SO₄→(CH₃)₂C=CH₂ (B)
The starting material is (CH₃)₂C=CH₂, which is isobutylene (or 2-methylpropene).
The first reaction involves the hydration of isobutylene in the presence of water (H₂O) and sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄).
- Mechanism:
- The double bond in isobutylene will react with a proton (H⁺) from sulfuric acid, forming a carbocation.
- The more stable carbocation will be formed on the more substituted carbon (the one attached to two methyl groups).
- Water will then attack this carbocation, leading to the formation of an alcohol.
- Product (A): The product formed is 2-methylpropan-2-ol (tert-butyl alcohol), represented as (CH₃)₃COH.
The second reaction involves the conversion of the alcohol formed in the first step to an alkene using benzene (C₆H₆) and concentrated sulfuric acid (conc.H₂SO₄).
- Mechanism:
- The alcohol will first be protonated by sulfuric acid to form an oxonium ion.
- This oxonium ion will then lose a water molecule, leading to the formation of a double bond, resulting in an alkene.
- Product (B): The product formed is isobutylene again, which is (CH₃)₂C=CH₂.
- (A): 2-methylpropan-2-ol (tert-butyl alcohol) - (CH₃)₃COH
- (B): Isobutylene - (CH₃)₂C=CH₂
1. (CH₃)₂C=CH₂+H₂O+H₂SO₄→(CH₃)₃COH (A)
2. (CH₃)₃COH+C₆H₆+conc.H₂SO₄→(CH₃)₂C=CH₂ (B)
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
C6H5−C≡C−CH3HgSO4−−−→H2SO4A
A_E01_135_O01.png) B
B_E01_135_O02.png) CC6H5−C∣OH=CHCH3DC6H5−CH=C∣OH−CH3
CC6H5−C∣OH=CHCH3DC6H5−CH=C∣OH−CH3CH3CNCH3MgBr(2 mol)−−−−−−−−−−−→H3O+Aconc. H2SO4−−−−−−−→B
A and B areA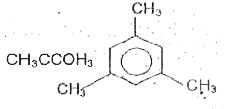 B(CH3)3COH,(CH3)2C=CH2C(CH3)2CHOH,CH3CH=CH2DNone is correct
B(CH3)3COH,(CH3)2C=CH2C(CH3)2CHOH,CH3CH=CH2DNone is correctIn this reaction , (CH3)3C−CH2OHConc.H2SO4−−−−−−−−→170∘CX
X isA(CH3)2C=CHCH3BCH3≡CHC(CH3)2CHCH2CH3DCH3−CH2−C∣CH3=CH2
CH3CH2OHH2SO4(conc.)−−−−−−−−−→443K[A]H2O/H+−−−−−→[B]PCI5−−→[C]
View SolutionCH≡CHH2O−−−−−−−−−→HgSO4/H2SO4[A]LiAlH4/H−−−−−−→[B]H2SO4(conc.)−−−−−−−−−→443K[C]
View SolutionWhat is the final major product of the following reaction
CH3−CH2−C=C−H
NaNH2−−−−→CH3CH2CH2−Br−−−−−−−−−−→HgSO4−−−→H2SO4 ?
View SolutionCH3−Ch2−c=HgSO4−−−→H2SO4, the compound A is
View SolutionWhat are the product in the following reaction ?
CH3−CH3∣C=CH2K2Cr2O7+−−−−−−→dil.H2SO4
View Solution

