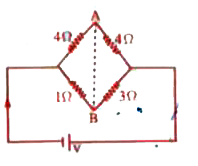
Consider the circuit diagram . The connecting wires are assumed to be perfect conducting.
STATEMENT-1 : The current in branch AB is zero.
and
STATEMENT -2 : The potential difference between A & B is zero
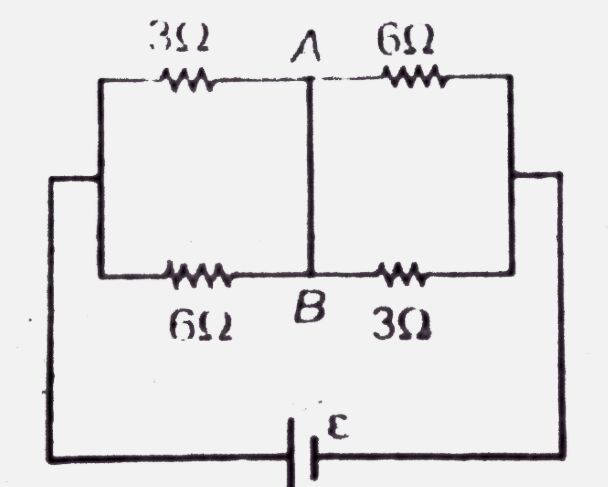
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True, Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True, Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True
Statement-1 is False , Statement-2 is True
The correct Answer is:4
Step by step video & image solution for Consider the circuit diagram . The connecting wires are assumed to be perfect conducting. STATEMENT-1 : The current in branch AB is zero. and STATEMENT -2 : The potential difference between A & B is zero by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 12 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Topper's Solved these Questions
- CURRENT ELECTRICITYBOOK - AAKASH INSTITUTECHAPTER - CURRENT ELECTRICITYEXERCISE - ASSIGNMENT SECTION-J(MATRIX-MATCH TYPE QUESTIONS)
2 Videos
- CURRENT ELECTRICITYBOOK - AAKASH INSTITUTECHAPTER - CURRENT ELECTRICITYEXERCISE - ASSIGNMENT SECTION-H( INTEGER ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS)
3 Videos
- CURRENT ELECTRICITYBOOK - AAKASH INSTITUTECHAPTER - CURRENT ELECTRICITYEXERCISE - ASSIGNMENT SECTION-C(OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTION ))
3 Videos
- COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS BOOK - AAKASH INSTITUTECHAPTER - COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS EXERCISE - ASSIGNMENT SECTION D (Assertion-Reason)
10 Videos
- DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER BOOK - AAKASH INSTITUTECHAPTER - DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER EXERCISE - ASSIGNMENT (SECTION-D)
10 Videos
Similar Questions
Column I lists physical quantities for a uniform current carrying conductor . These quantities depend on quantities given in column II. Match entries in column I to all the quantities in column II on which it depends.
Column IColumn II(A)Resistivity(p)Length of conductor(B)Current through the conductor for a given potential difference across the condcutor(q)Electric field in conductor(C)Current density in condcutor for a given potential difference across the conductor (r)Temperature of conductor(D)Thermal power generated per unit volume for given value of potential difference across the conductor(s)Nature of conductor(t)Area of condcutor
View SolutionConsider a wire of length l , area of cross-section A and resistivity ρ and resistance 15Ω. Its length is increased by applying a force on it and its length increases by four times of its original length. Find the new resistance in ohms of the wire.
View SolutionA cell supplies a current of 2A to an exertnal resistance of 2Ω and a current of 1 ampere to another external resistance of 4.5Ω connected across the cell separately . Select the correct alternative (s).
View SolutionSTATEMENT 1 : The audio frequency signals (20 Hz to 20 kHz) cannot be transmitted without distortion over long distances
STATEMENT-2: Noise has its greatest effect when the signal is weak
View SolutionA : Every metal has a definite work function , still all photoelectrons do not come out with the same energy it incident radiation is monochromatic .
R : Work function is the minimum energy required for the electron in the highest level of conduction band to get out of the metal . Not all electrons in the metal belong to this level rather they occupy a continuous band of levels .
View SolutionWhat resistor should be connected in parallel with the 20Ω resistor in branch ADC in the circuit shown in fig. so that potential difference between B and D may be zero ?
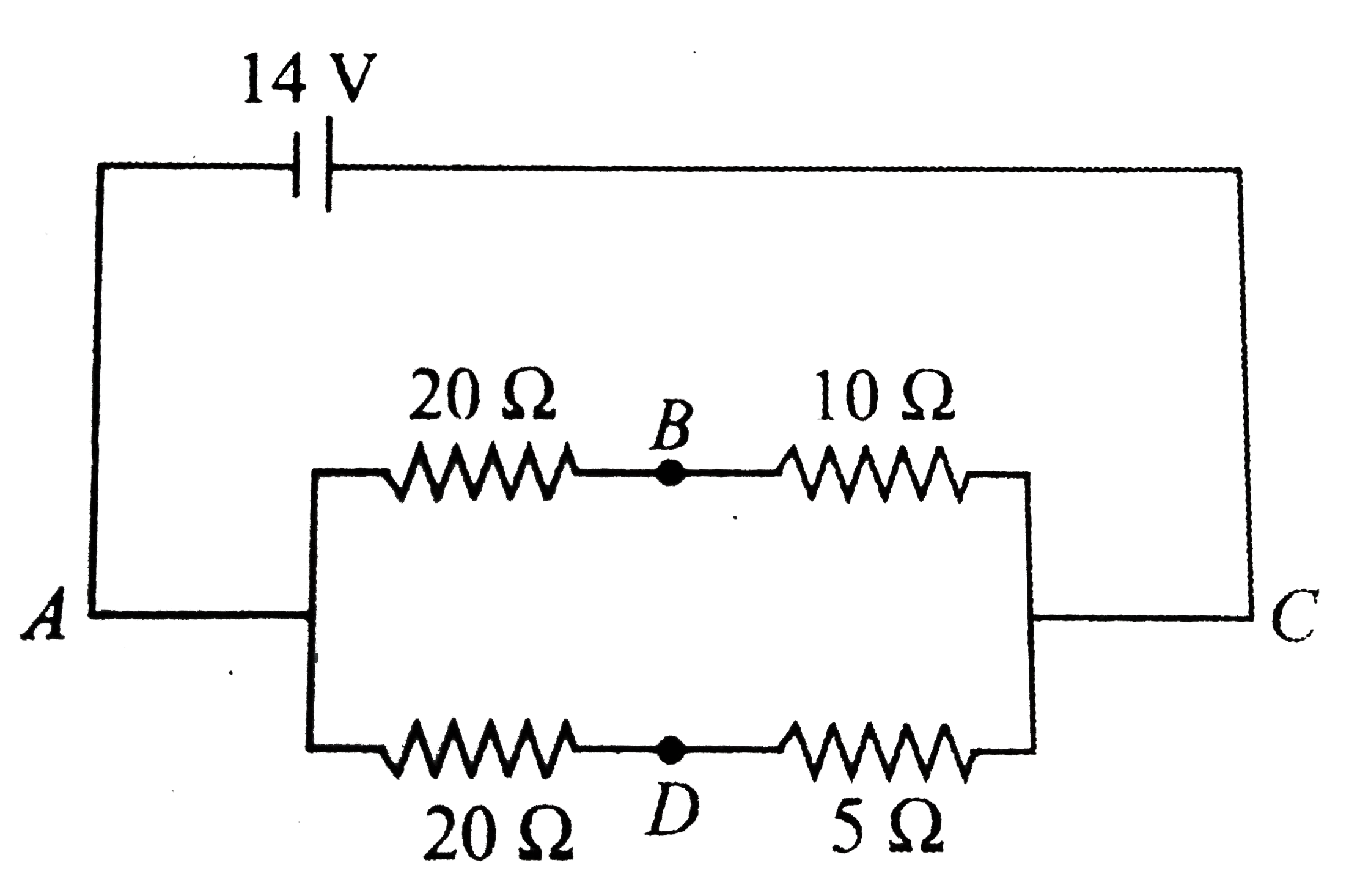
View SolutionStatement I: A conducting body is connected to the earth, hence it is electrically neutral. Statement II: The potential of a conducting body connected to the earth is zero.
View SolutionStatement-1: If potential difference between two points is zero and resistance between those points is zero, current may flow between the points.
Statement-2: Kirchhoff's 1st law is based on conservation of charge.
View SolutionIn the circuit find the potential difference between point AandB. Assume that both the batteries have zero internal resistance
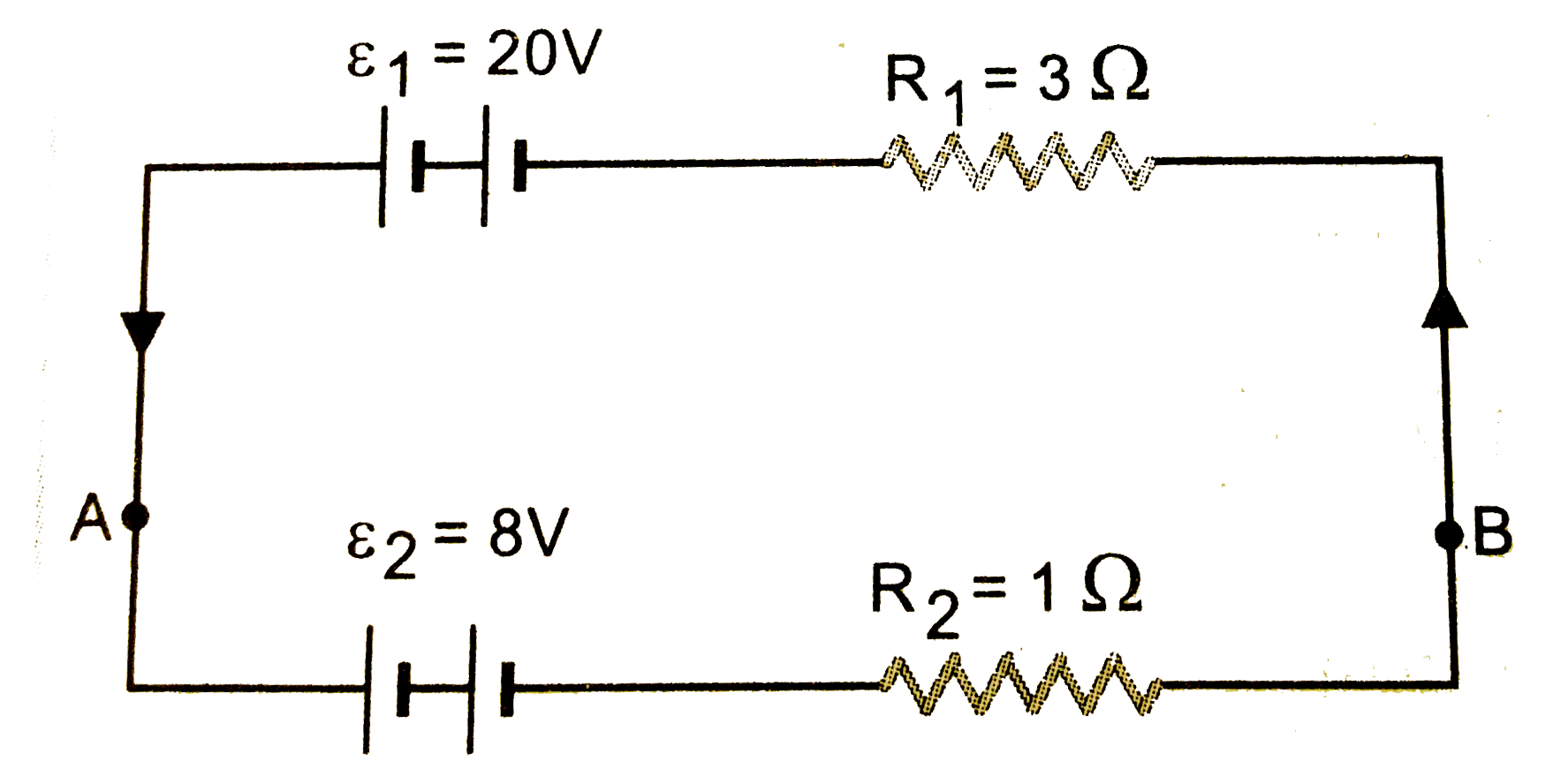
View SolutionIn the given electrical circuit, the potential difference between point A and B is (assume the battery is ideal and the conducting wires have almost zero resistance):
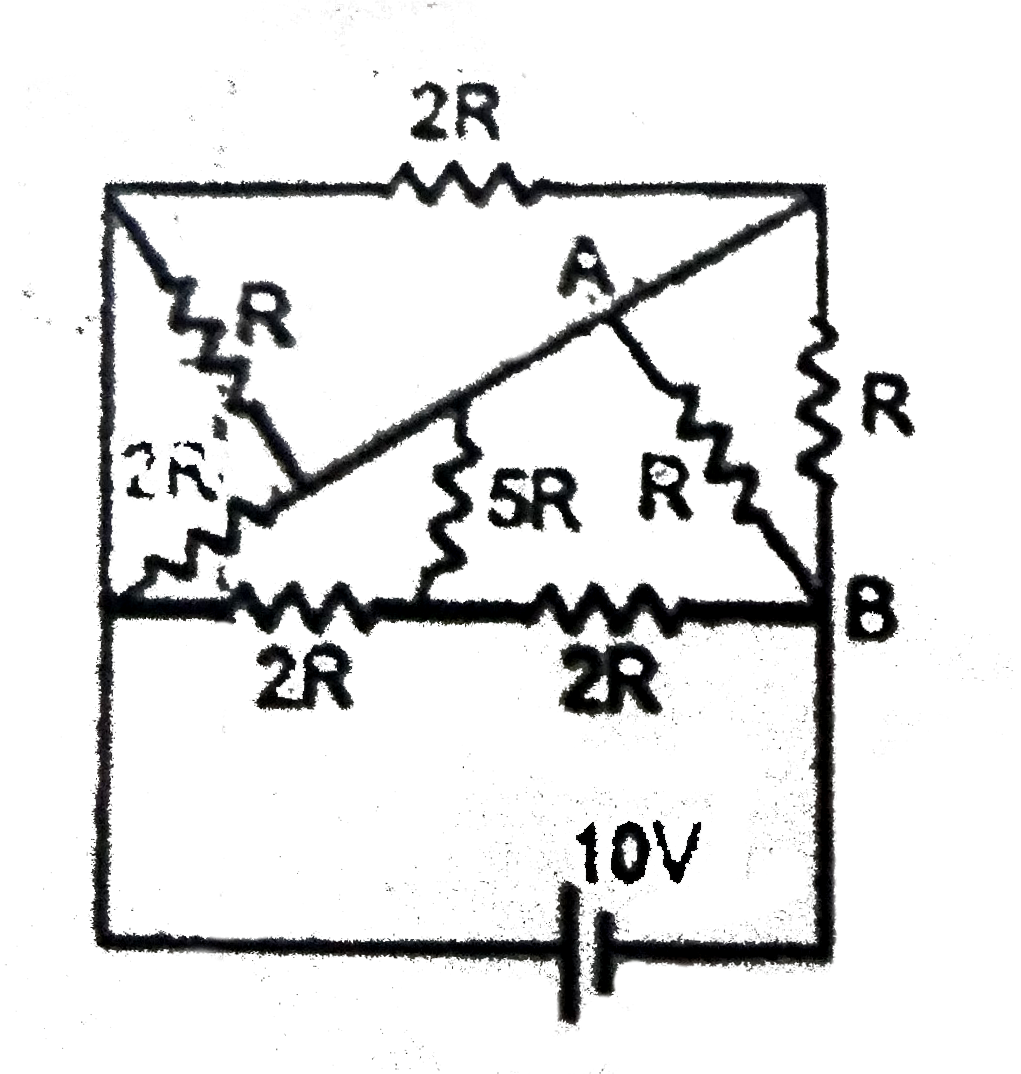
View SolutionIn the circuit shown if a conducting wire is connected between points A and B, the current in this wire will :-

View SolutionIn the circuit shown if a conducting wire is connected between points A and B, the current in this wire will :-

View Solutionकथन 1 : परम् शून्य ताप पर नैज अर्धचालक की चालकता शून्य हो जाती है ।
कथन 2 : परम शून्य ताप पर नैज अर्धचालक के चालन बैंड पूर्णतः खली होते है ।
View SolutionStatements: - In series LCR circuit, the difference between current and voltage is never zero. Reason: Voltage and current are never in the same art.
View SolutionIn the circuit shown, if a conducting wire is connected between points A and B, the current in this wire will
View Solution

