Two moles of an ideal gas undergo the following process :
(a) a reversible isobaric expansion from (P atm, VL) to (P atm , 2VL).
(b) a reversible isochoric change of state from (P atm , 2V,L) to (P/2 atm, 2VL)
(c) a reversible isothermal compression from (P/2 atm, 2VL) to (P atm, VL).
Sketch with labels each of the processes on the same P−V diagram.
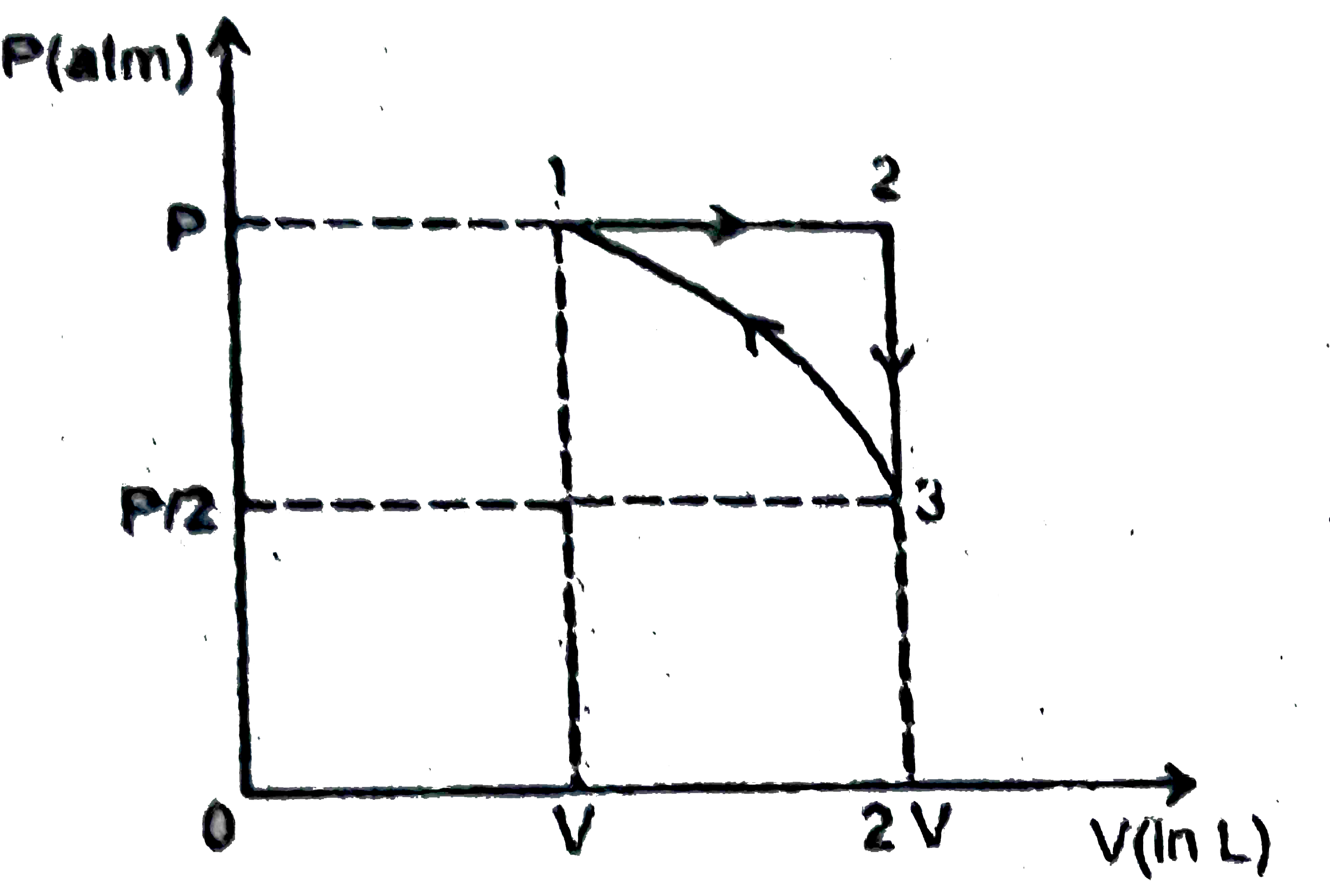

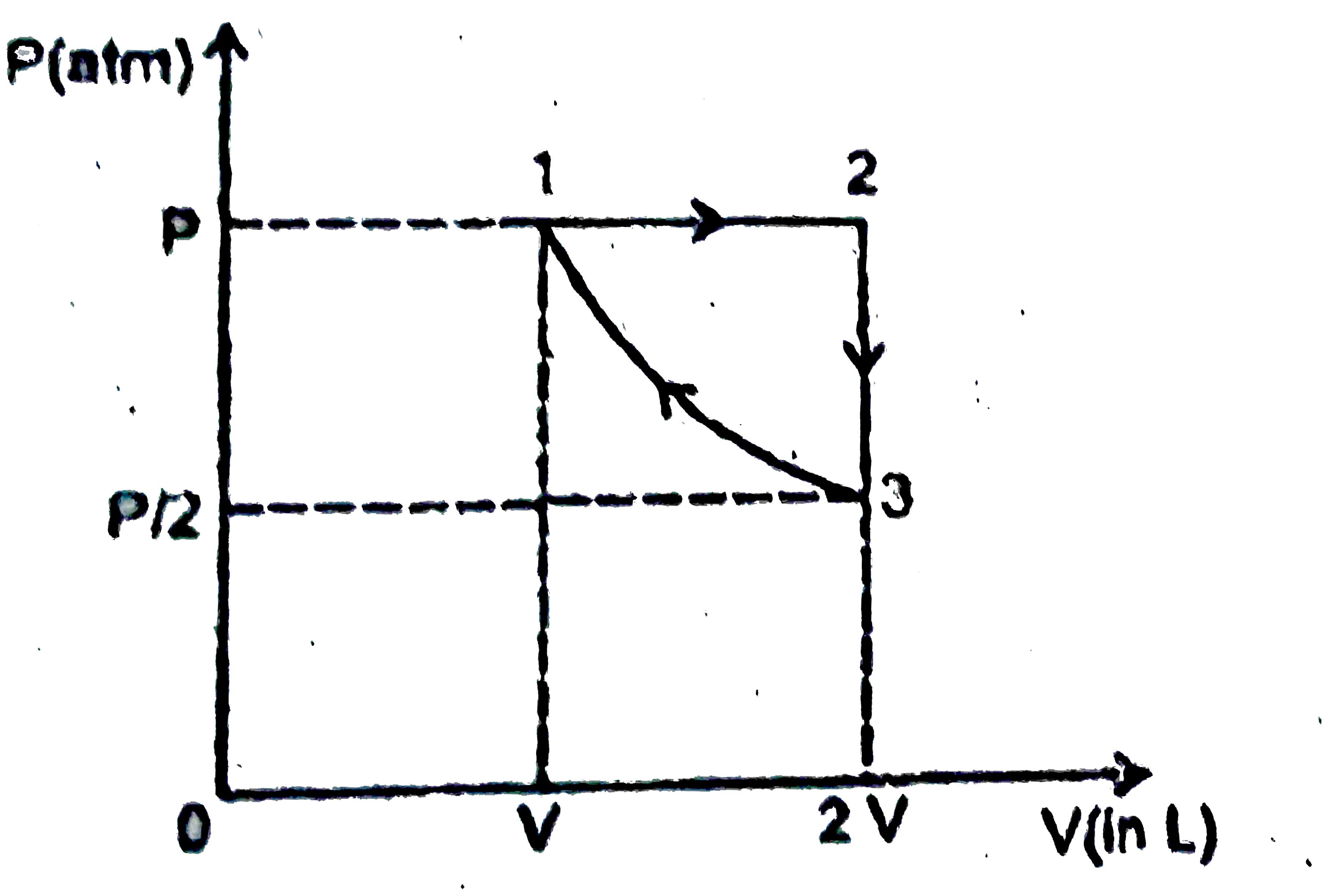

The correct Answer is:3
Step by step video, text & image solution for Two moles of an ideal gas undergo the following process : (a) a reversible isobaric expansion from ( P atm, V L) to ( P atm , 2V L). (b) a reversible isochoric change of state from ( P atm , 2V,L) to (P//2 atm, 2V L) (c ) a reversible isothermal compression from (P//2 atm, 2V L) to (P atm, V L). Sketch with labels each of the processes on the same P-V diagram. by Chemistry experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 11 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Similar Questions
Two moles of a perfect gas undergo the following processes:
a. A reversible isobaric expansion from (1.0atm,20.0L) to (1.0atm,40.0L).
b. A reversible isochroic change of state from (1.0atm,40.0L) to (0.5atm,40.0L)
c. A reversible isothermal expansion from (0.5atm,40.0L)→(1.0atm,20.0L).
i. Sketch with lables each of the processes on the same P−V diagram.
ii. Calculate the total work (w) and teh total heat change (q) involved in the above process.
iii. What will be the values of ΔG and ΔH for the overall process?
View SolutionFor the given isotherm (P in atm and V in L) for one mole of an ideal gas, which follows Boyle's law, what will be the approx value of temperature ? (R = 0.0821 L "atm"//"mol" K)
View SolutionOne mole of an ideal gas undergoes a change of state (2.0) atm, 3.0 L) to (2.0 atm, 7.0 L) with a change in internal energy (DeltaU) = 30 L-atm. The change in enthalpy (DeltaH) of the process in L-atm :
View SolutionIf 1.5 L of an ideal gas at a apressure of 20 atm expands isothermally and reversibly to a final volume of 15 L, the work done by the gas in L atm is:
View SolutionA sample of an ideal gas is expanded from 1 dm^(3) to 3 in a reversible process for which P=KV^(3) , with K=1//5 (atm//dm^(3)) , what is work done by gas (L atm)
View SolutionTwo moles of a perfect gas undergo the following processes: (a) a reversible isobaric expansion from (1.0 atm , 20.0 L) to (1.0 atm, 40.0 L) (b) a reversible isochroic change of state from (1.0 atm , 40.0L) to (0.5 atm , 40.0 L) (c) a reversible isothermal compression from (0.5 atm,40.0 L ) to (1.0atm, 20.0L) Calculate the magnitude of work (W) done in L.atm
View SolutionTwo moles of a perfect gas undergo the following processes:
a. A reversible isobaric expansion from (1.0atm,20.0L) to (1.0atm,40.0L).
b. A reversible isochroic change of state from (1.0atm,40.0L) to (0.5atm,40.0L)
c. A reversible isothermal expansion from (0.5atm,40.0L)→(1.0atm,20.0L).
i. Sketch with lables each of the processes on the same P−V diagram.
ii. Calculate the total work (w) and the total heat change (q) involved in the above process.
iii. What will be the values of ΔH for the overall process?
View SolutionTwo moles of a perfect gas undergoes the following process : (i) a reversible isobaric expansion from (1.0 atm, 20.0 L) to (1.0 atm, 40.0 L). (ii) a reversible isochoric change of state from (1.0 atm, 40.0 L ) to (0.5 atm, 40.0 L). (iii) a reversible isothermal expansion from (0.5 atm, 40.0 L )to (1.0 atm, 20.0 L) (i) Sketch with labels each procsses on the same P- V diagram. (ii) Calculate the total work (w) and the total heat (Q) involved in the above process. (iii) What will be values of Delta U, Delta H and Delta S for overall process ?
View SolutionTwo moles of a perfect gas undergo the following process: (a) A reversible isobaric expansion from (1.0 atm, 20.0 litre) to (1.0 atm,40.0litre). (b) A reversible isochoric change of state from (1.0 atm, 40.0 litre) to (1.0 atm, 40.0 litre). (b) A reversible isochoric change of state from (1.0 atm, 40.0 litre) to (0.5 atm, 40.0 litre). (c) A reversible isothermal compression from (0.5atm, 40.0 litre) to (1.0 atm, 20.0 litre). (i) Sketch with labels each of the process on the same P−V diagram. (ii) Calculate the total work (W) and the total heat change (q) involved in the above process. (iii) What will be the value of ΔU,ΔH and ΔS for the overall process?
View SolutionIf 1.5 L of an ideal gas at a pressure of 20 atm expands isothermally and reversibly to a final volume of 15 L the work done by the gas in L atm is
View SolutionOne mole of an ideal gas undergoes a change of state (2.0) atm, 3.0 L) to (2.0 atm, 7.0 L) with a change in internal energy (DeltaU) = 30 L-atm. The change in enthalpy (DeltaH) of the process in L-atm :
View SolutionOne mole of an ideal gas undergoes change of state from (4 L, 3 atm) to (6 L, 5 atm). If the change in internal energy is 45 L-atm then the change of enthalpy for the process is
View SolutionOne mole of an ideal gas undergoes change of state from (4 L, 3 atm) to (6 L, 5 atm). If the change in internal energy is 45 L-atm then the change of enthalpy for the process is
View SolutionTwo moles of a perfect gas undergo the following processes : (a) a reversible isobaric expansion from (1.0 atm, 20.0 L) to (1.0 atm, 40.0 L) (b) a reversible isochoric change of state from (1.0 atm, 40.0 L) to (0.5 atm, 40.0 L) (c ) a reversible isothermal compression from (0.5 atm, 40.0 L) to (1.0 atm, 20.0 L) (i) Sketch the labels of each of the processes on the same p-V diagram. (ii) Calculate the total work (W) and the total heat change (q) involved in the above processes. (iii) What will be the values of DeltaU, DeltaH and DeltaS for the overall process ?
View SolutionTwo moles of a perfect gas undergo the following processes:
a. A reversible isobaric expansion from (1.0atm,20.0L) to (1.0atm,40.0L).
b. A reversible isochroic change of state from (1.0atm,40.0L) to (0.5atm,40.0L)
c. A reversible isothermal expansion from (0.5atm,40.0L)→(1.0atm,20.0L).
i. Sketch with lables each of the processes on the same P−V diagram.
ii. Calculate the total work (w) and teh total heat change (q) involved in the above process.
iii. What will be the values of ΔG and ΔH for the overall process?
View Solution

