The following diagram represents an electrical circui containing two uniform resistance wires A and B connected to a single ideal cell. Both wires have same length, but thickness of wire B is twice that of wire A. The conducting wires connecting A and B to the ideal cell are resistanceless. The dependence of electric potential on position along the length of two wires is given in option.
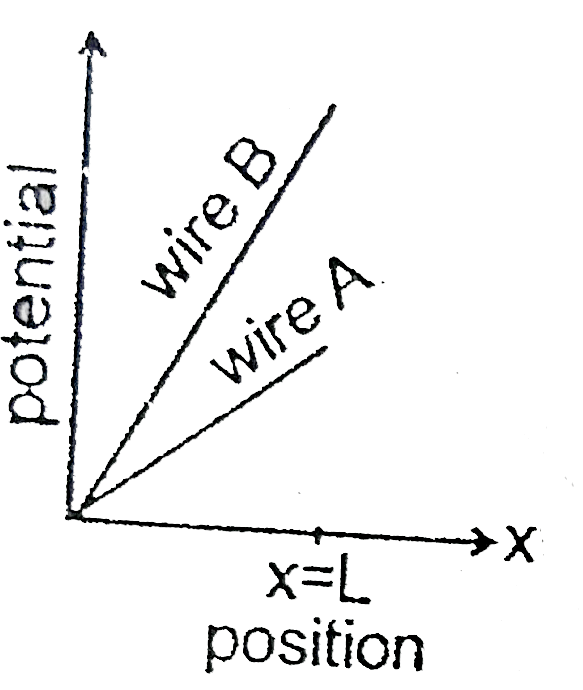
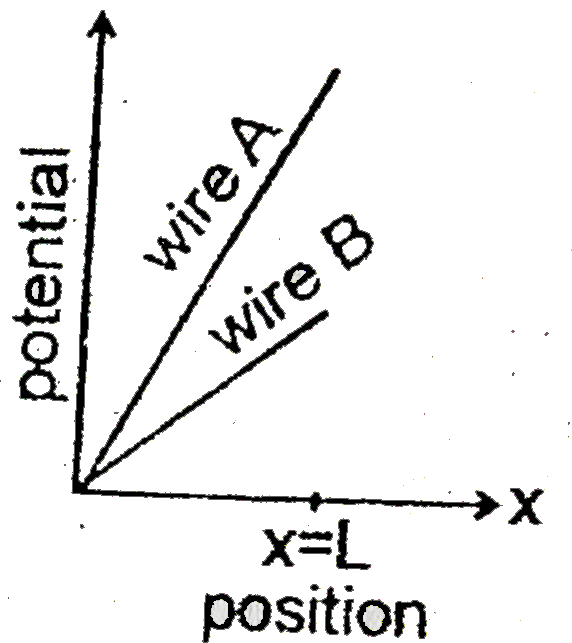
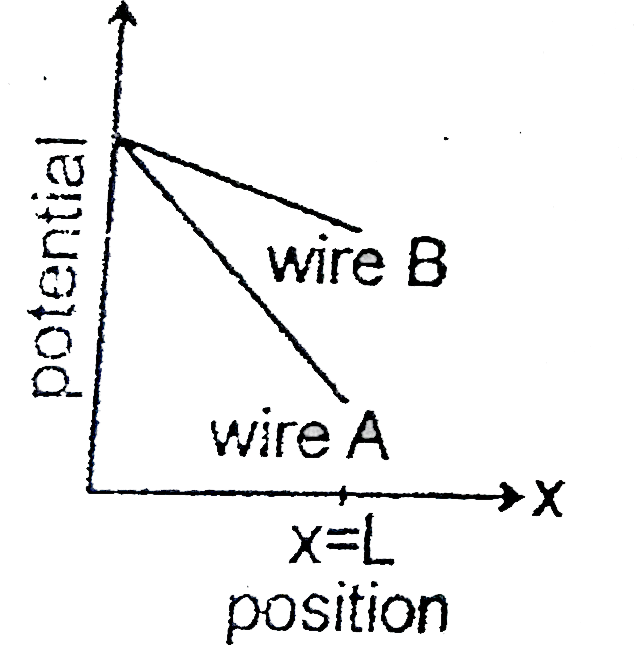
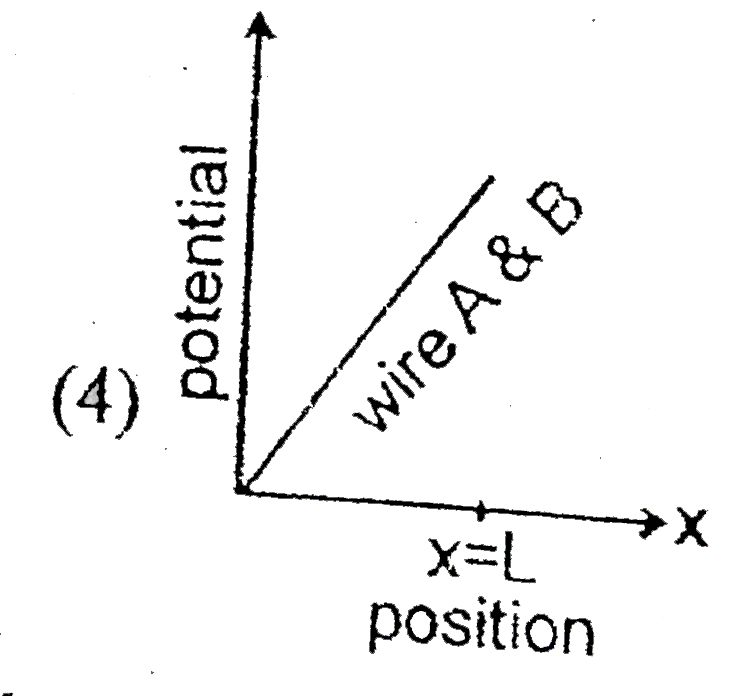
The correct Answer is:D
The electric field in wire A or B is uniform. Hence potential V in wires shall be linear function of x.
At x=0 (i.e., at left end ) V=0.
∴VA=m1x and VB=m2x
Since at right end i.e., at x=L potential of both wires is again same ∴m1=m2
Hence VA=VB=mx
where m is a positive constant.
Similar Questions
Wires A and B have resistivities pA and pB. If the diameter of the wire B is twice that of A and the Two wires have same resistance, then LbLA is
View SolutionTwo wires A and B have equal lengths and are made of the same material. But the diameter of A is twice that of wire B. Then for a given load
View SolutionTwo wires A and B have the same cross section and are made of the same material but the length of wire A is twice that of B. Then for a given load
View SolutionTwo copper wires A and B have the same mass. The resistance of wire A is 0.5 Omega and the length of wire B is double that of wire A. Find the resistance of wire B.
View SolutionThrough which of the following two wires, does the electric current flow more easily? (a) A thick wire (b) a thin wire of the same material and of the same length when connected to the same source. State the reason.
View SolutionTwo wires A and B have equal lengths and aremade of the same material , but diameter of wire A is twice that of wire B . Then, for a given load,
View SolutionTwo uniform wires A and B are of the same total metal and have equal masses. The radius of wire A is twice that of wire B. The total resistance of A and B when connected in parallel is
View SolutionTwo wires A and B have the same cross section and are made of the same material, but the length of wire A is twice that of B. Then, for a given load
View Solution
