A diathermic piston divides adiabatic cylinder of volume V0 into two equal parts as shown in the figure. Both parts contain ideal monoatomic gases. The initial pressure and temperature of gas in left compartment are P0 and T0 while that in right compartment are 2P0 and 2T0. Initially the piston is kept fixed and the system is allowed to acquire a state of thermal equilibrium.
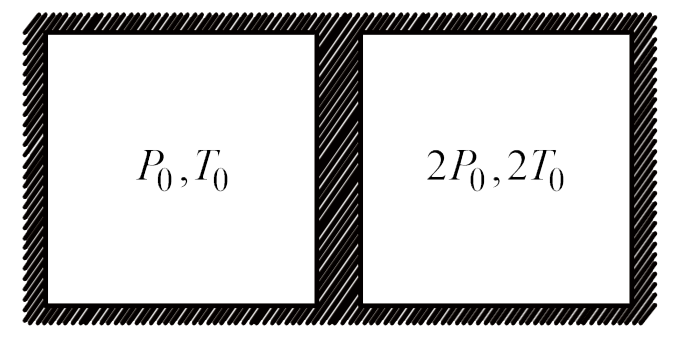
The heat that flown from right compartment to left compartment before thermal equilibrium is achieved is
P0V0
34P0V0
38P0V0
23P0V0
Step by step video & image solution for A diathermic piston divides adiabatic cylinder of volume V0 into two equal parts as shown in the figure. Both parts contain ideal monoatomic gases. The initial pressure and temperature of gas in left compartment are P0 and T0 while that in right compartment are 2P0 and 2T0. Initially the piston is kept fixed and the system is allowed to acquire a state of thermal equilibrium. The heat that flown from right compartment to left compartment before thermal equilibrium is achieved is by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 12 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Similar Questions
Two pistons having low thermal conductivity divide an adiabatic container in three equal parts as shown An ideal gas is present in the three parts AB&C having initial pressures as shown and same temperatures Now the pistons are releasef Then the final equilibrium length of part A after long time will be
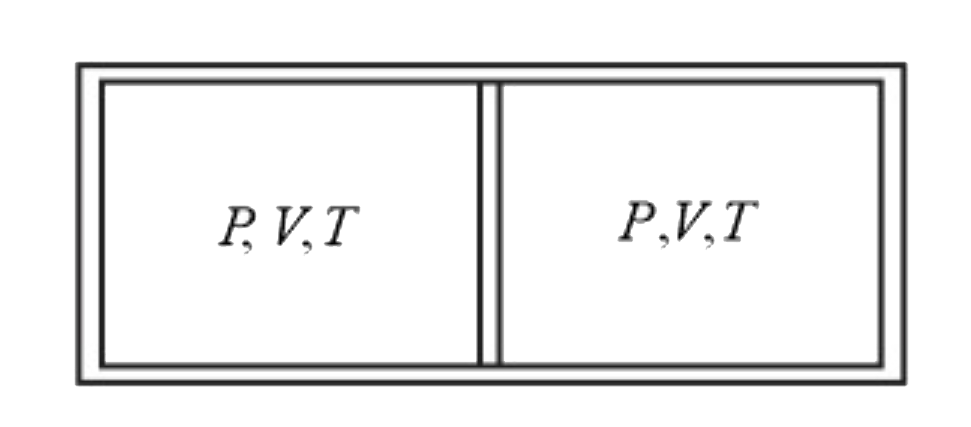
View SolutionA cylindrical vessel made of thermally insulating material is divided into two equal parts by an insulating and. Movable piston. Both parts contain ideal monoatomic gas . The gas in the left part is supplied heat such that the volume of right part becomes one-eight of its initial volume . Work done by the gas in the right part is
View SolutionA piston divides a closed gas cylinder into two parts. Initially the piston is kept pressed such that one part has a pressure P and volume 5V and the other part has pressure 8P and volume V, the piston is now left free. Find the new pressure and volume for the isothermal and adiabatic process. (γ = 1.5).
View SolutionThe figure shows an insulated cylinder of volume V containing monoatomic gas in both the compartments. The piston is diathermic. Initially the piston is kept fixed, and the system is allowed to acquire a state of thermal equilibrium. If the initial pressures and temperatures are as shown.
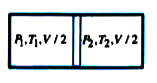
Calculate the final temperature and the final pressure. Now the pin which was keeping the piston fixed is removed and the piston set free to move. The piston is allowed to slide slowly, such that a state of mechanical equilibrium is also achieved (T1P2>P1T2)
View SolutionThe figure shows an insulated cylinder of volume V containing monoatomic gas in both the compartments. The piston is diathermic. Initially the piston is kept fixed, and the system is allowed to acquire a state of thermal equilibrium. If the initial pressures and temperatures are as shown.
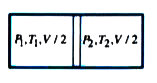
Calculate the final volume of gas in each compartment.
View SolutionA piston divides a closed gas cylinder into two parts. Initially the piston is kept pressed such that one part has a pressure P and volume 5Vand the other part has pressure 8P and volume V, the piston is now left free. Find the new pressure and volume for the isothermal and adiabatic process.
View SolutionA piston divides a closed gas cylinder into two parts. Initially the piston is kept pressed such that one part has a pressure P and volume 5V and the other part has pressure 8P and volume V, the piston is now left free. Find the new pressure and volume for the isothermal and adiabatic process. (γ=1.5).
View SolutionFigure shows an insulated cylinder of volume V containing monatomic gas in both the compartments. The pistone is diathermic. Initially the piston is kept fixed and the system is allowed to acquire a state of thermal equilibrium. The initial pressures and temperatures are as shown in the figure. Calculate

The final temperature
View Solution

