The terminal velocity of a ball in air is v, where acceleration due to gravity is g. Now the same ball is taken in a gravity free space where all other conditions are same. The ball is now pushed at a speed vv, then –
The terminal velocity of the ball will be v/2
The ball will move with a constant velocity
The initial acceleration of the ball is 2g in opposite direction of the ball's velocity
The ball will finally stop (Given that density of the ball ρ=2 times the density of air σ)
The correct Answer is:D
Step by step video, text & image solution for The terminal velocity of a ball in air is v, where acceleration due to gravity is g. Now the same ball is taken in a gravity free space where all other conditions are same. The ball is now pushed at a speed vv, then – by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 11 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Similar Questions
A solid sphere moves at a terminal velocity of 20ms−1 in air at a place where g=9.8ms−2. The sphere is taken in a gravity free hall having air at the same pressure and pushed down at a speed of 20ms−1
View SolutionIf rocket engine ejects fuel at the rate μ kg/s with relative velocity vr. At time t = 0, speed of rocket is u. Consider the value of acceleration due to gravity is constant and equal to g.
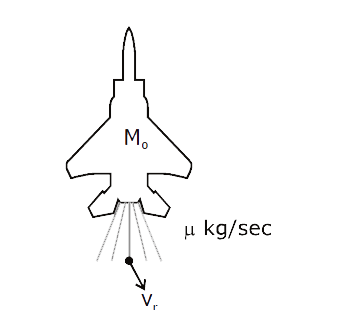
If rocket is in gravity free space then find velocity of rocket as function of time.
View Solution
Knowledge Check
The displacement of a body is given by s=12gt2 where g is acceleration due to gravity. The velocity of the body at any time t is
Agt36Bgt22CgtDgt2Time period of simple pendulum of length l at a place, where acceleration due to gravity is g and period T. Then period of simple pendulum of the same length at a place where the acceleration due to gravity 1.02 g will be
ATB1.02 TC0.99 TD1.01 TIf g is acceleration due to gravity at the equator when earth were at rest and g1 is acceleration due to gravity at the same place when earth spins with angular velocity ω, the relation between them is
Ag1=g(1−Rω2g)Bg1=g(1−Rω2)Cg1=g−R2ωDg=g1−R2ω
A rubber ball is dropped from a height of 5m on a plane, where the acceleration due to gravity is not shown. On bouncing it rises to 1.8m. The ball loses its velocity on bouncing by a factor of
View SolutionFind the value of a and b in the following cases :
(a) The velocity v of the ball falling freely under gravity is proportional to gahb, where g is the acceleration due to gravity, h is the height from which the ball is dropped.
(b) The kinetic energy K of a rotating body is proportional to Iaωb where I is the moment if inertia and ω is the angular speed.
(c ) The time-period T of spring pendulum is proportiona to makb, where m is the mass of block attached to the spring and k is the spring constant.
The speed of sound v in a gaseous medium is proportional to Paρb, where P is the pressure and ρ is the density of medium.
View SolutionA uniform ball of radius r is placed on the top of a sphere of radius R = 10 r. It is given a slight push due to which it starts rolling down the sphere without slipping. The spin angular velocity of the ball when it breaks off from the sphere is ω=√pq(gr), where g is the acceleration due to gravity and p and q are the smallest integers. What is the value of p+q?
View SolutionThe terminal velocity v of a small steel ball ofradius r fal ling under gravity through a column ofa viscous liquid of coefficient of viscosity η depends on mass of the ball m, acceleration due to gravity g, coefficient of viscosity η and radius r. Which of the following relations is dimensionally correct?
View SolutionA steel ball of mass m falls in a viscous liquid with terminal velocity v, then the steel ball of mass 8m will fall in the same liquid with terminal velocity
View Solution

