A thin rod of mass m and length l is free to rotate on a smooth horizontal plane about its one fixed end. When it is at rest, it receives a horizontal impulse J at its other end, at angle of 37∘ with the length. Choose incorrect option immediately after impact:
Angular momentum of the rod about fixed axis of rotation is 0.6Jl
Angular velocity of the rod fixed of rotation is 1.8Jml
Kinetic energy of the rod is 0.2J2m
Linear velocity of the centre of mass of the rod is 910Jm
The correct Answer is:C

Jsin37∘l=ml23ω=L
K.E.=12Iω2
V=l2ω.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- TEST PAPERSBOOK - RESONANCECHAPTER - TEST PAPERSEXERCISE - PT-01
30 Videos
- TEST PAPERSBOOK - RESONANCECHAPTER - TEST PAPERSEXERCISE - Pt-02
30 Videos
- TEST PAPERSBOOK - RESONANCECHAPTER - TEST PAPERSEXERCISE - PART - II PHYSICS
107 Videos
- SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION BOOK - RESONANCECHAPTER - SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION EXERCISE - Advanced Level Problems
13 Videos
- TEST SERIESBOOK - RESONANCECHAPTER - TEST SERIESEXERCISE - PHYSICS
127 Videos
Similar Questions
Which of the following statement is not correct regarding cathode rays :
View SolutionThe statement that is not correct for the periodic classification of elements is :
View SolutionA force F is applied on a block of mass 5kg as shown in figure. Co-efficient of friction between the wall and clock is √32.(g=10m/s2)
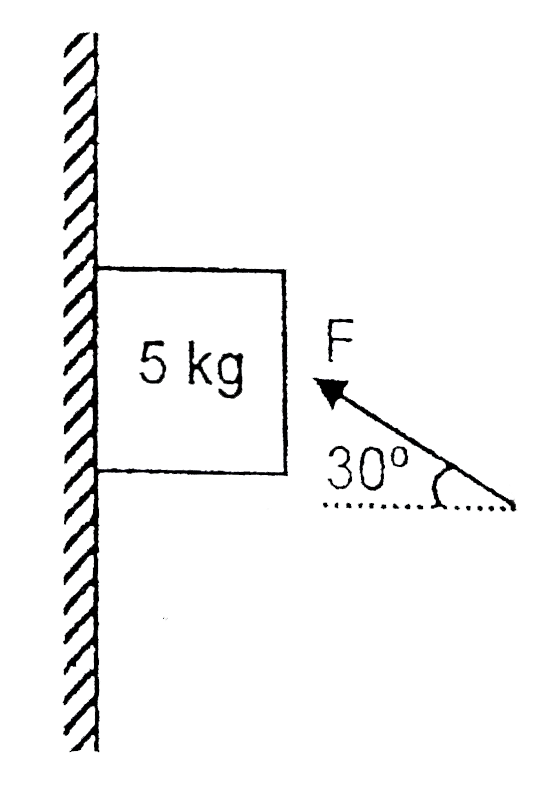
Select correct option(s)
View SolutionWhat would be the period of the free oscillations of the system shown here if mass M1 is pulled down a little force constant of the spring is k, mass of fixed pulley is negligible and movable pulley is smooth
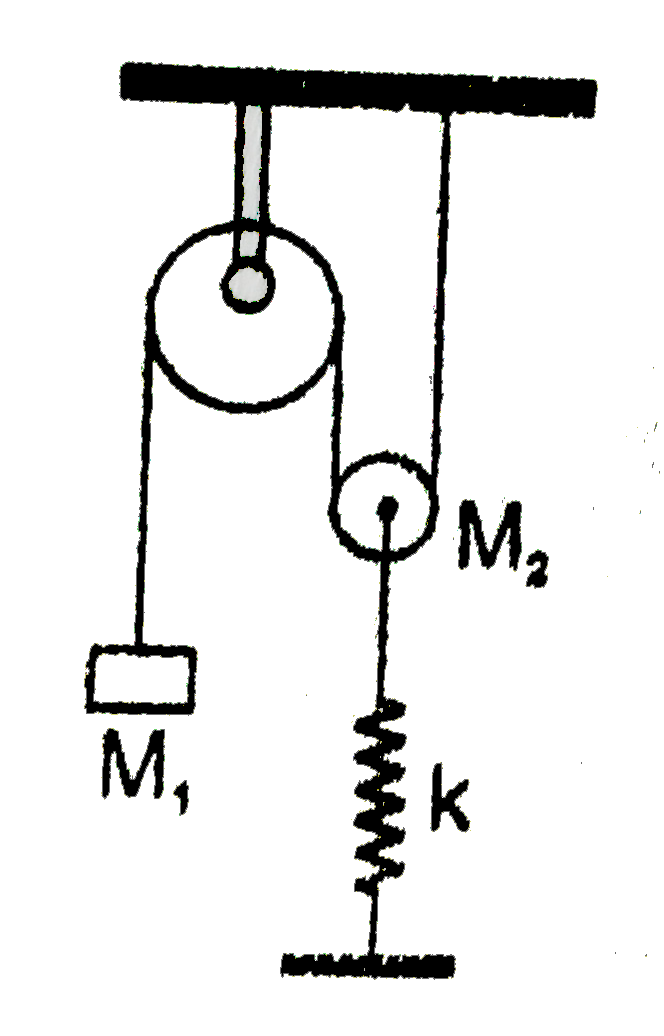
View SolutionA time varying voltage is applied across A & B such that voltage across capacitor is given by VC=2sin2t. What is maximum potential difference across the reistance?

View SolutionA thin unifrom rod of mass m and length l is free to rotate about its upper end When it is at rest. It receives an impulse J as its lowest point, normal to its length immediately after impact.
View SolutionA thin uniform rod of mass m and length l is free to rotate about its upper end. When it is at rest, it receives an impulse J at its lowest point, normal to its length immediately after impact,
View SolutionA thin uniform straight rod of mass 2 kg and length 1 m is free to rotate about its upper end. When at rest it receives an impulsive blow of 10 Ns at its lowest point, normal to its length as shown in figure. The kinetic energy of rod just after impact is
View SolutionA thin uniform straight rod of mass 2 kg length 1 m is free to rotate about its upper end when at rest. It receives an impulsive blow of 10 Ns at its lowest point, normal to its lengths as shown in figure. Find the kinetic energy of rod just after impact. .
View SolutionA uniform rod of mass M and length 2L lies on a smooth horizontal table. There is a smooth peg O fixed on the table. One end of the rod is kept touching the peg as shown in the figure. An impulse J is imparted to the rod at its other end. The impulse is horizontal and perpendicular to the length of the rod. Find the magnitude of impulse experienced by the peg.

View SolutionA rod AB of mass M and length L lies on smooth horizontal table impulse J is applied to end A as shown in the figure immediately after imparting the impulse :
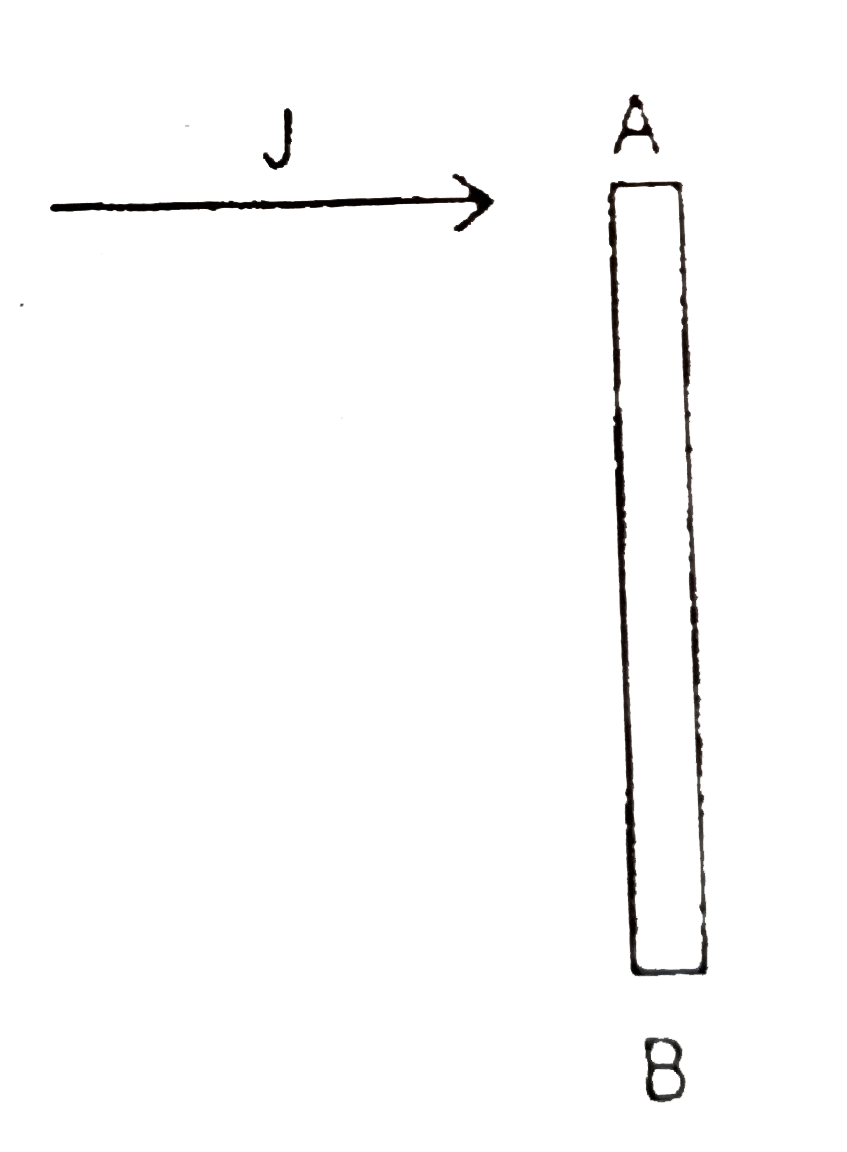
View SolutionA thin uniform rod of mass m and length l is free to rotate about its upper end. When it is at rest, it receives an impulse J at its lowest point, normal to its length. Immediately after impact,
View SolutionA uniform rod AB of mass m and length l is at rest on a smooth horizontal surface. An impulse J is applied to the end B perpendicular to the rod in horizontal direction. Speed of the point A of the rod after giving impulse is:
View SolutionA uniform rod of mass m and length l is at rest on smooth horizontal surface. An impulse P is applied to end B as shown. The point about which rod rotates just after impulse being applied is located at
View SolutionThe thin rod shown below has mases M and length L. A force F acts at one end as shown and the rod is free to rotate about the other end in horizontal plane. Initial angular acceleration of the rod is :
View Solution

