A light stick of length l rests with its one end against the smooth wall and other end against the smooth horizontal floor as shown in the figure. The bug starts at rest from point B and moves such that the stick always remains at rest. aP is the magnitude of acceleration of but of mass m, which depends upon its distance of x from the top end of the stick. Choose the correct option (s)
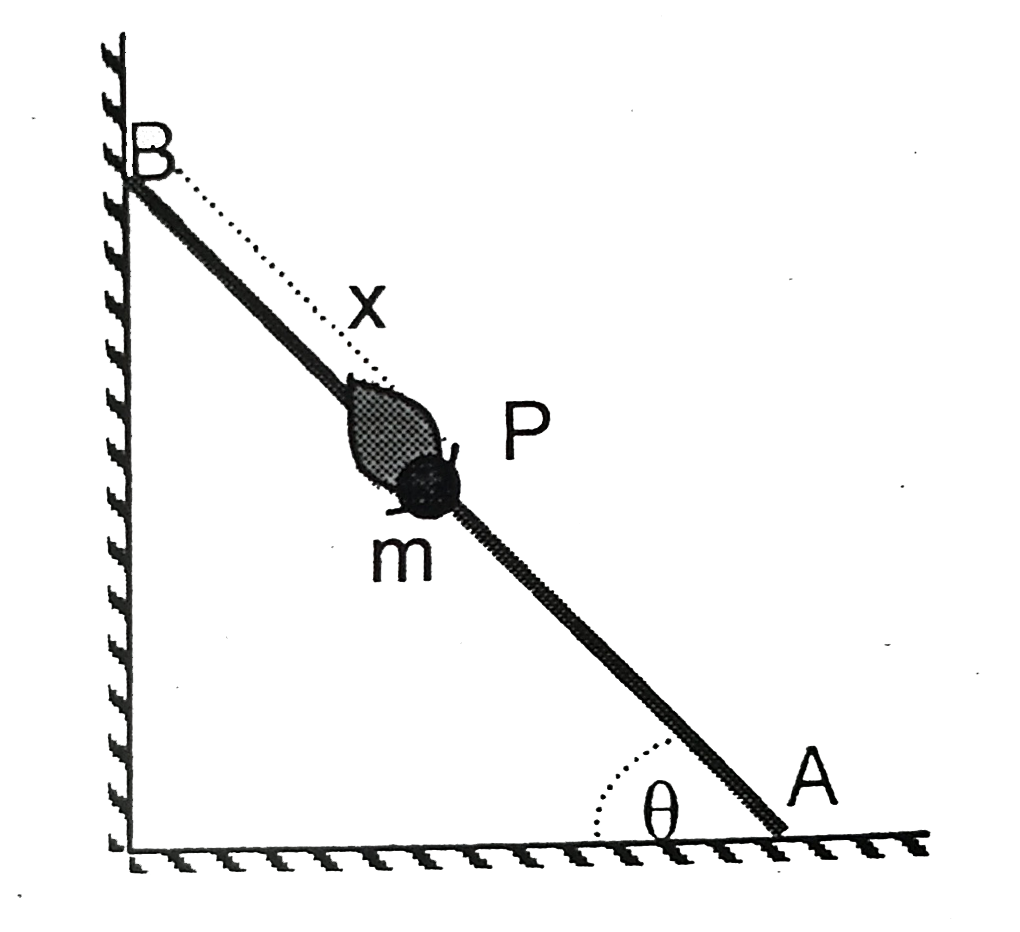
aP=gsinθ(1−dl)
aP=gcosθ(1−xl)
The time taken by the but to reach the bottom of the stick having started at the top end from rest is π2√lsinθ3g
The time taken by the but to reach the bottom of the stick having started at the top end from rest is π2√lsinθ2
The correct Answer is:A, D
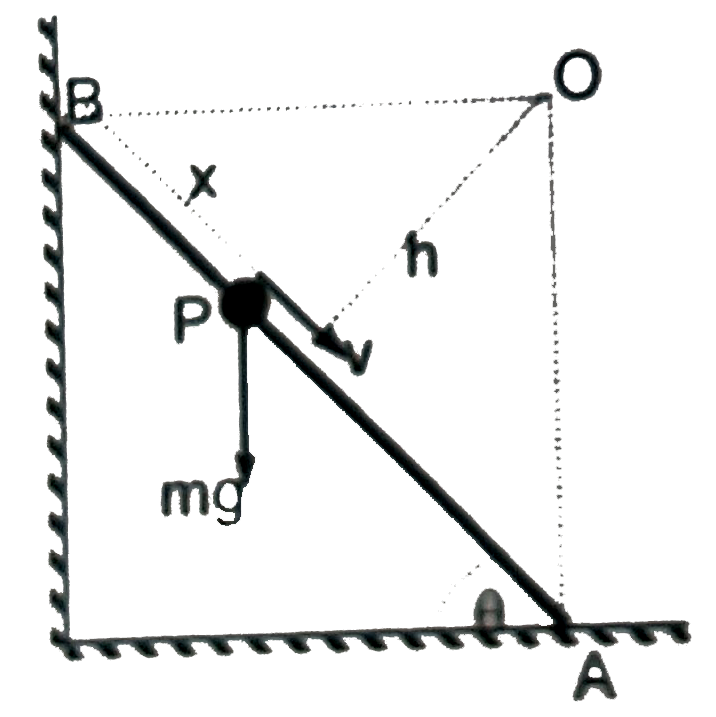
Consider the bug at point P at any time t, moving with speed v along the stick, so L=mvhmvlsinθcosθ⇒ Angular momentum of bug
about pooint O
⇒τ=dLdt=(mlsinθcosθ)dvdt
⇒mg(l−x)cosθ=(mlsinθcosθ)dvdt
⇒dvdt=gsinθ(1−xl)
⇒dvdt+glsinθx=gsinθ⇒ Equation of SHM with mean position at point A
⇒T=2π√lsinθg
Time required =T4=π2√lsinθ2
Topper's Solved these Questions
- TEST PAPERSBOOK - FIITJEECHAPTER - TEST PAPERSEXERCISE - PHYSICS
747 Videos
- SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTIONBOOK - FIITJEECHAPTER - SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTIONEXERCISE - Assignment Problems (Objective) (Level-II)
20 Videos
- WORK, ENERGY AND POWER BOOK - FIITJEECHAPTER - WORK, ENERGY AND POWER EXERCISE - COMPREHENSIONS ( Comprehension-II)
5 Videos
Similar Questions

A particle of mass 3m is projected from point-A with speed 3v0 as shown in figure. When the particle is at point P, it explodes in three identical particles choose the INCORRECT statement regarding the physical quantities just before and just after explosion
View SolutionA particle moves in x-y plane according to the equation ¯r=(ˆi+2ˆj)Acosωt. The motion of the particle is
View SolutionThe potential energy function for the force between two in a diatomic molecule can approximately be expressed as U(x)=ax12−bx4, where a and b are positive constants, and x is the distance between the atoms. Answer the following question by selecting most appropriate alternative.
The graph between potential energy vs x will be
View SolutionA uniform rod of length l and mass 2 m rests on a smooth horizontal table. A point mass m moving horizontally at right angles to the rod with velocity v collides with one end of the rod and sticks it. Then
View SolutionA rod of length l is siding such that one of its ends is always in contact with a vertical wall and its other end is always in contact with horizontal surface. Just after the rod is relased from rest, the magnitude of acceleration of end points of the rod is and b respectively. The angular acceleration of road at this istant will be
View SolutionA strip of wood mass M and length l is placed on a smooth horizontal surface. An insect of mass m starts from rest at one end of the strip and walks to the other end in time t , moving with a constant speed.
View SolutionAn insect of mass m is initially at one end of a stick of length L and mass M, which rests on a smooth floor. The coefficientg of friction between the insect and the stick is k. The minimum time in which the insect can reach the other end of the stick is t. Then t2 is equal to
View SolutionA stick of length L=2.0m is leaned against a wall as shown. It is released from a position when θ=60∘. The end A of the stick remains in contact with the wall and its other end B remains in contact with the floor as the stick slides down. Find the distance travelled by the centre of the stick by the time it hits the floor.
View SolutionA uniform rod of length l and mass 2m rests on a smooth horizontal table. A point of mass m moving horizontally at right angle to the rod with velocity v collides with one end of the rod and sticks to it, then:
View SolutionA rod of length I leans by its upper end against a smooth vertical wall, while its other end leans against the floor. The end that leans against the wall moves uniformly downward. Then:
View SolutionA ladder of length 20 feet rests against a smooth vertical wall. The lowerend, which is on a smooth horizontal floor is moving away from the wall at the rate of 4 feet/sec. If the lower end is 12 feet away from the wall, then the rate at which the upper end move, is
View SolutionA ladder weighing 20kg wt rests with its one end against a smooth vertically wall and the other end against the smooth floor. If the inclination of the ladder to the horizontal is 60^(@) then calculate the horizonatl force required at the lower end so that is does not slip.
View SolutionA uniform rod of mass m and length L is at rest on a smooth horizontal surface. A ball of mass m, moving with velocity v0, hits the rod perpendicularly at its one end and sticks to it. The angular velocity of rod after collision is
View SolutionA rod of leng th 'l' rests at a point A against a smooth vertial wall while end B is on the floor as shown in the fig. If the end Amoves uniformly downwards, what will be the velocity of the end B if x is the distance of point B from wall.
View SolutionA stick of length l rests againsts the floor and a wall of a room. If the stick begins to slide on the floor, then the locus of its middle point is
View SolutionA stick of length I rests against the floor and a wall of a room. If the stick begins to slide on the floor, then the locus of its middle point is
View Solution

