There particles A, B and C have masses m, 2m and m respectively. They lie on a smooth horizontal table connected by light inextensible strings AB and BC. The string are taut and <ABC=120∘. An impulse is applied to particle A along BA so that it acquires a velocity u. Find the initial speeds of B and C.

The correct Answer is:vB=2√3111u,vc=4u11
Step by step video, text & image solution for There particles A, B and C have masses m, 2m and m respectively. They lie on a smooth horizontal table connected by light inextensible strings AB and BC. The string are taut and lt ABC = 120^(@). An impulse is applied to particle A along BA so that it acquires a velocity u. Find the initial speeds of B and C. by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 11 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Similar Questions
Three particles A,B and C of respective masses m1,m2 and m3 lie on a smooth horizontal surface, and an fastened to two light inextensible strings as shown in Fig. The particle A is imparted an impulse J along −−→BA . Find the initial speed of each particle.
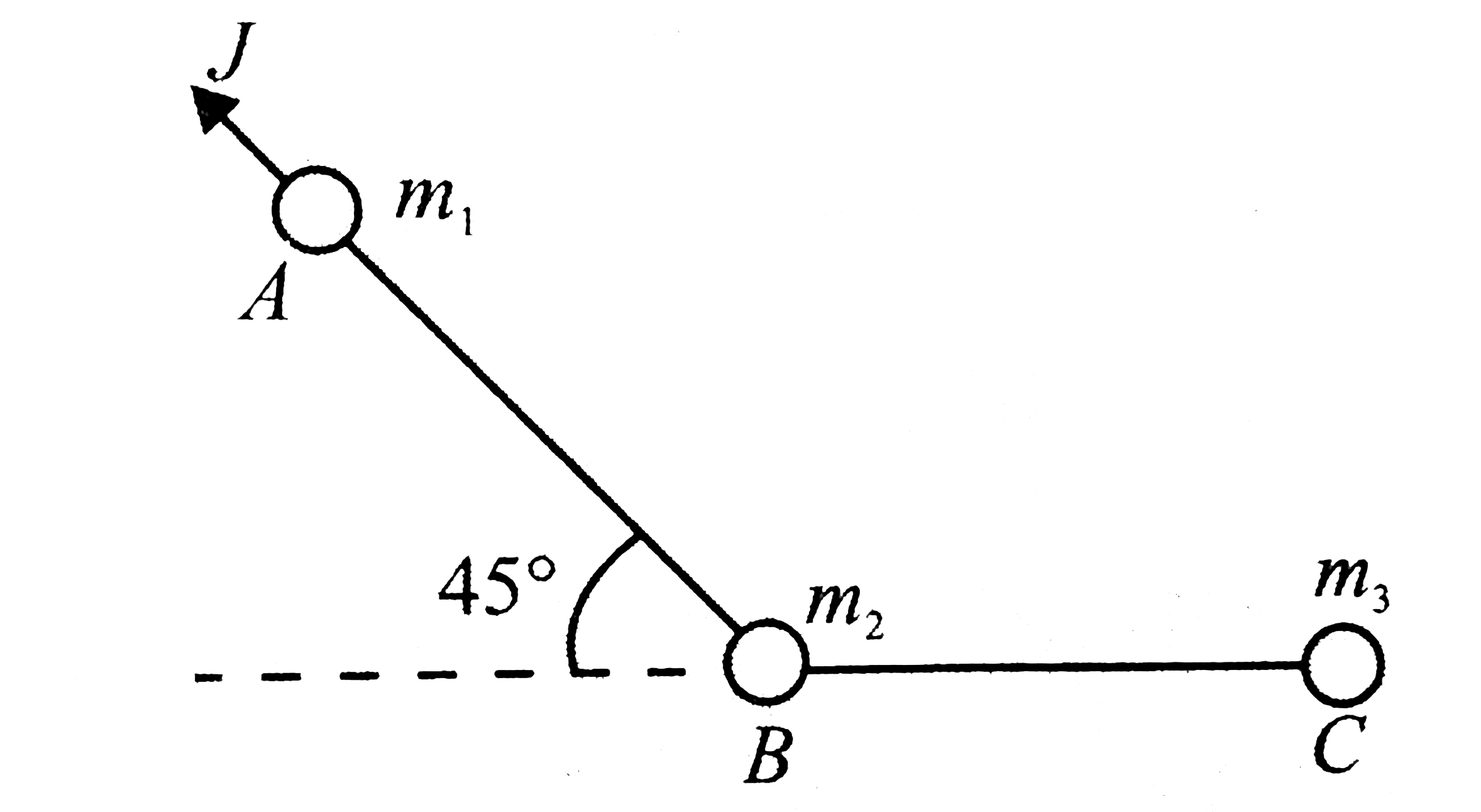
View SolutionTwo particles A and B of equal masses lie close together on a horizontal table and are connected by a light inextensible string of length l. A is projected vertically upwards with a velocity √10gl. Find the velocity with which it reaches the table again.
View Solution
Knowledge Check
Three identical particles A, B and C of mass m lie on a smooth horizontal table. Light inextensible strings which are just taut connect AB and BC and ∠ABC is 135° . An impulse J is imparted to the particle C in the direction BC. Mass of each particle is m. Choose the correct options.
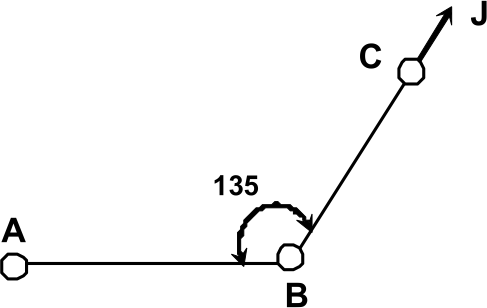 ASpeed of A just after the impulse imparted is √2J7mBSpeed of B just after the impulse imparted is √10J7mCSpeed of C just after the impulse imparted is 3J7mDSpeed of A just after the impulse imparted is 2J7m
ASpeed of A just after the impulse imparted is √2J7mBSpeed of B just after the impulse imparted is √10J7mCSpeed of C just after the impulse imparted is 3J7mDSpeed of A just after the impulse imparted is 2J7mTwo particles of equal mass m at A and B are connected by a rigid light rod AB lying on a smooth horizontal table. An impulse J is applied at A in the plane of the table and perpendicular at AB. Then the velocity of particle at A is :
AJ2mBJmC2JmDzeroTwo particle of equal mass m at A and B are connected by a rigid light rod AB lying on a smooth horizontal table. An impulse J is applied at A in the plane of the table and perpendicular at AB. The velocity of particle at A is
AJ2mBJmC2JmDzero
Two particles (A and B) of masses m and 2m are joined by a light rigid rod of length L. The system lies on a smooth horizontal table. The particle (A) of mass m is given a sharp impulse so that it acquires a velocity u perpendicular to the rod. Calculate maximum speed of particle B during subsequent motion. By what angle θ will the rod rotate by the time the speed of particle B become maximum for the first time ?

View SolutionTwo particles A and B of mass 2m and m respectively are attached to the ends of a light inextensible string of length 4a which passes over a small smooth peg at a height 3a from an inelastic table. The system is released from rest with each particle at a height a from the table. Find -
(i) The speed of B when A strikes the table
(ii) The time that elapses begore A first hits the table.
(iii) The time for which A is resting on the table after the first collision & begore it is first jerked off.
View SolutionTwo block of masses m1andm2 are lying on a frictionless horizontal table connected by a light string m2 is pulled by horizontal force F. Calculate the tension in the string .
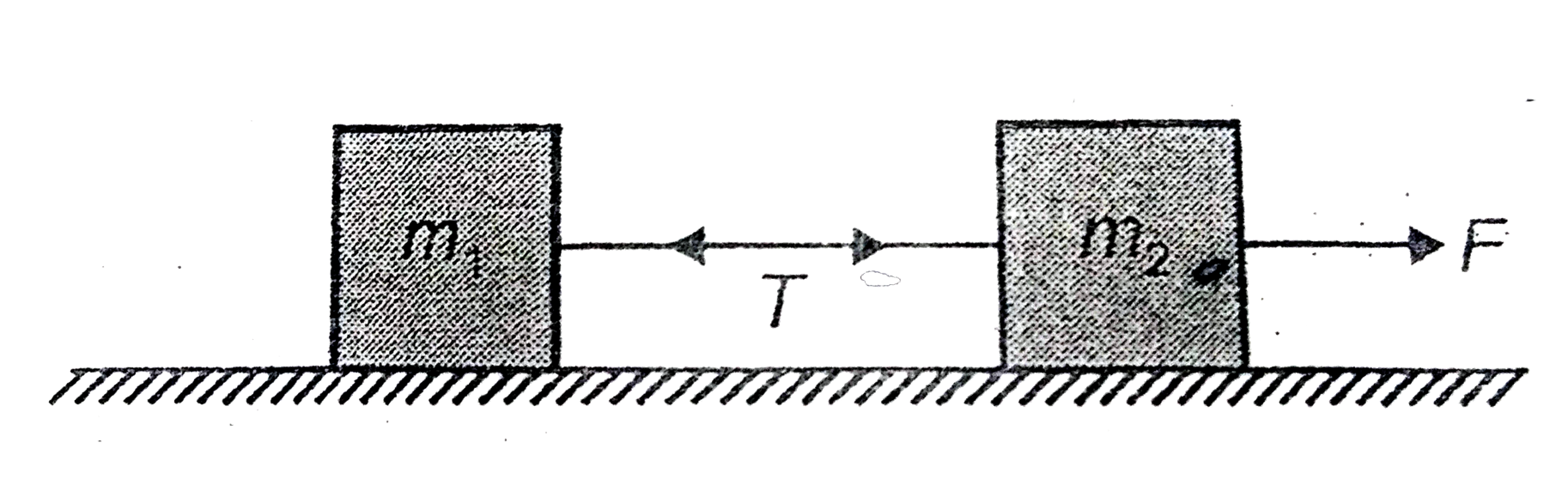
View SolutionTwo particle, each of mass m, are connected by a light inextensible string of length 2l. Initially they lie on a smooth horizontal table at points A ad B distant l apart the particle at A is projectd across the table with velocity u. find th speed with which the second particle begins to move if the direction. of u is :
(a). along BA
(b). at an angle of 120∘ with AB
(c) perpendicular to AB
In each case also calculate (in terms of ma nd u) the impulsive tension in the string.
View SolutionTwo blocks A and B of masses 3 m and m respectively are connected by a massless and inextensible string. The whole system is suspended by a massless spring as shown in figure. The magnitudes of acceleration of A and B immediately after the string is cut, are respectively:
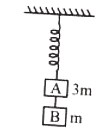
View Solution
