In a machine, a fluid from a compressor, which is at high pressure, is allowed to pass through a nozzle. Cross section of the nozzle is shown in the fiuge. The nozzle consists of two sections of radii r1 and r2. The nozzle is fixed on a stand with the help of a clamp. the clamp is a circular ring of radius r1 and width b. The fluid from the compressor is at a presssure of n times the atmospheric pressure p0. assume that the entrie system is horizontal the fluid is ideal and the flow is steady.
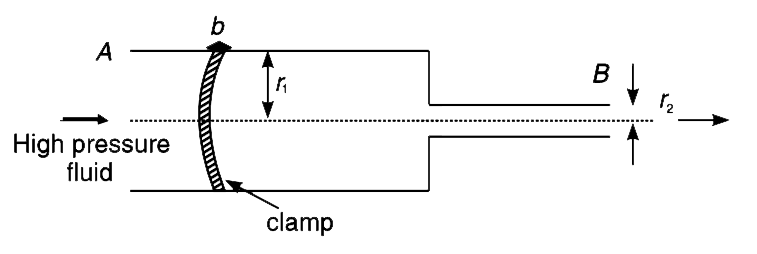
(a) what should be the volume flow rate so that pressure of the fluid at end B reduces to half of its value at end A?
(b) If the entire system is kept in gravity free space and the net force on the nozzle due to the fluid flow is F then determine the minimum radial pressure that should be applied on the clamp. so the nozzle remains in place. Coefficient of friction betwwen clamp and nozzle is μ.
(c) If a small hole is punched anywhere on the thinner part of the nozzle (close to end B) what should be the volume flow rate of the fluid so that it does not gush out?
The correct Answer is:(a) Q=πr21r21√nP0ρ(r41−r42)
(b) F2πμr1b
(c) Q=πr21r22
⎷2(n−1)P0ρ(r41−r42)
Step by step video, text & image solution for In a machine, a fluid from a compressor, which is at high pressure, is allowed to pass through a nozzle. Cross section of the nozzle is shown in the fiuge. The nozzle consists of two sections of radii r_(1) and r_(2). The nozzle is fixed on a stand with the help of a clamp. the clamp is a circular ring of radius r_(1) and width b. The fluid from the compressor is at a presssure of n times the atmospheric pressure p_(0). assume that the entrie system is horizontal the fluid is ideal and the flow is steady. (a) what should be the volume flow rate so that pressure of the fluid at end B reduces to half of its value at end A? (b) If the entire system is kept in gravity free space and the net force on the nozzle due to the fluid flow is F then determine the minimum radial pressure that should be applied on the clamp. so the nozzle remains in place. Coefficient of friction betwwen clamp and nozzle is mu. (c) If a small hole is punched anywhere on the thinner part of the nozzle (close to end B) what should be the volume flow rate of the fluid so that it does not gush out? by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 11 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Similar Questions
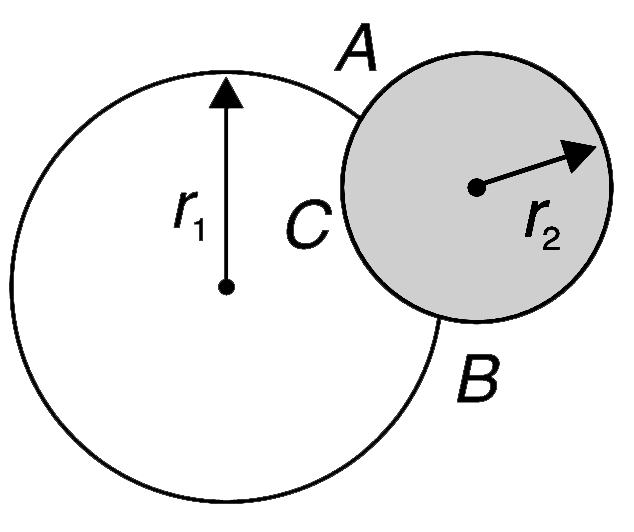
Two soap bubbles of radii r1andr2 are attached as shown. Find the radius of curvature of the common film ACB.
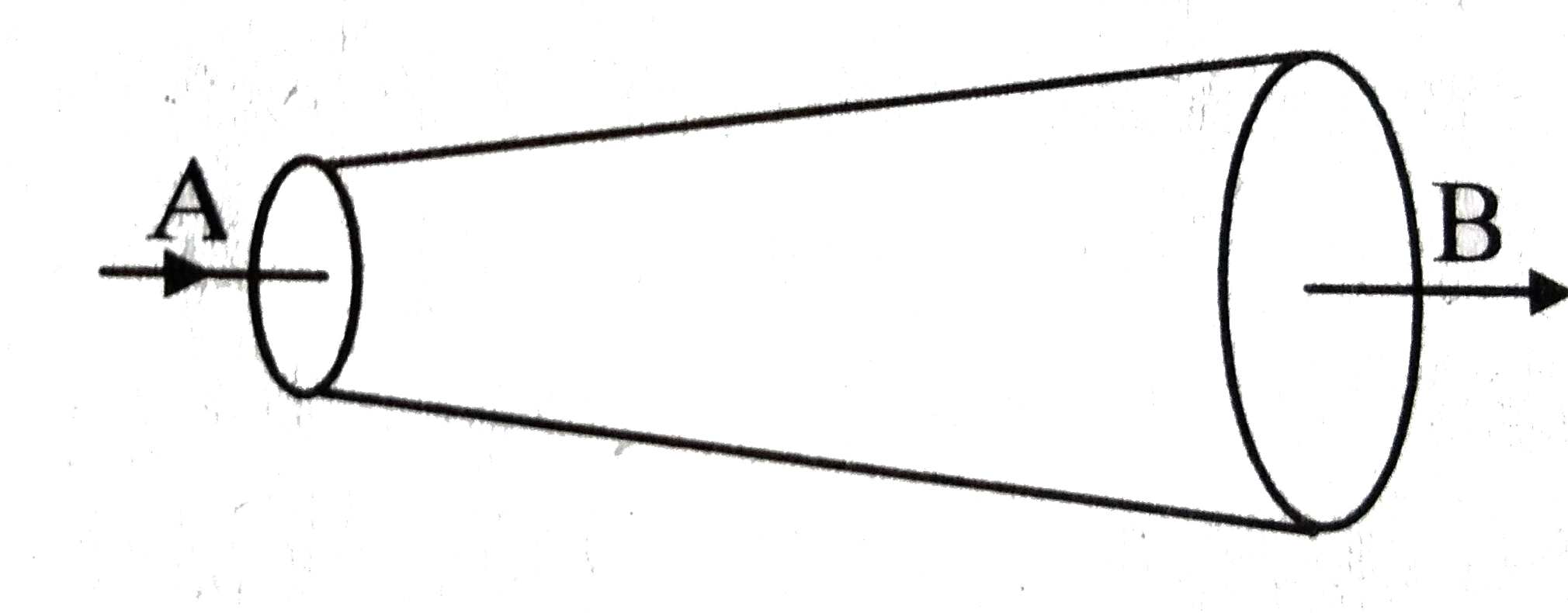
View SolutionAn ideal fluid flows through a pipe of circular cross - section with diameters 5 cm and 10 cm as shown in the figure. The ratio of velocities of fluid at A and B is

View Solution
Knowledge Check
If the sum of the circumferences of two circles with radii R1 and R2 is equal to the circumference of a circle of radius R, then
AR1+R2=RBR1+R2>RCR1+R2<RDNothing definite can be said about the relation among R1,R2 and R.If the sum of the areas of two circles with radii R1 and R2 is equal to the area of a circle of radius R, then
AR1+R2=RBR21+R22=R2CR1+R2<RDR21+R22<R2A current I flows an infinitely long wire with cross section in the form of a semi - circular ring of radius R. The magnitude of the magnetic induction along its axis is :
Aμ0I2π2RBμ0I2πRCμ0I4πRDμ0Iπ2R
An ideal fluid flows through a pipe of circular cross section with diameters 5 cm and 10 cm as shown. The ratio of velocities of fluid at A and B is
View SolutionFrom a uniform disc of radius R, a circular section of radius R/2 is cut out. The centre of the hole is at R/2 from the centre of the original disc. Locate the centre of mass of the resulating flat body.
View SolutionWater flow througyh a horizontal pipe whose internal diameter is 2.0cm at a speed of 1.0ms−1 What should be the diameter of the nozzle, If the water is to emerge at a speed of 4.0ms−1?
View SolutionA long straight wire of radius R carries a steady current which is uniformly distributed through the cross-section of the wire. The magnitudes of the magnetic field at distance r1 and r2 from the centre of the wire are B1 and B2 respectively. Then
View SolutionA current i passes through a wire of length l , radius of cross-section r and resistivity ρ . The rate of heat generation is
View Solution

