A ring shaped tube has uniform cross sectional area and its entire volume is 2V0. The tube is well insulated from the surrounding. Inside the tube there is an adiabatic fixed wall S1 and another movable adiabatic partition S2. Initially, the movable partition is diametrically opposite to S1 and the two halves of the tube have equal amount of an ideal gas (g = 1.5) at same pressure P0. Now, a heater H is switched on which supplies heat slowly to one of the chambers. Heater is kept on till the partition S2 moves through the quarter of the circle. At this position the heater is switched off and the partition S2 remains in equilibrium. Neglect any friction as well as heat loss to the surrounding through the walls of the tube. Find the heat supplied by the heater to the gas.
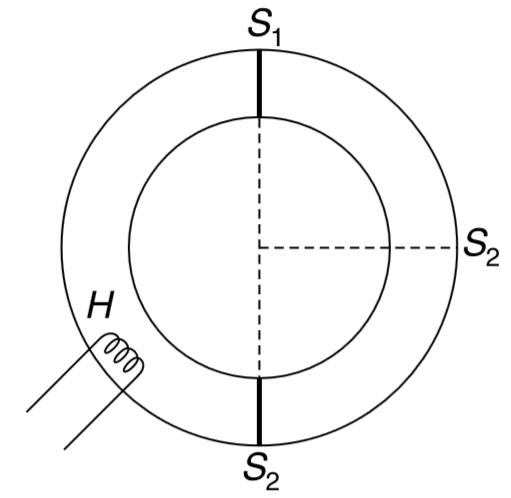
The correct Answer is:4(2√2−1)P0V0
Step by step video, text & image solution for A ring shaped tube has uniform cross sectional area and its entire volume is 2V_(0). The tube is well insulated from the surrounding. Inside the tube there is an adiabatic fixed wall S_(1) and another movable adiabatic partition S_(2). Initially, the movable partition is diametrically opposite to S1 and the two halves of the tube have equal amount of an ideal gas (g = 1.5) at same pressure P_(0). Now, a heater H is switched on which supplies heat slowly to one of the chambers. Heater is kept on till the partition S_(2) moves through the quarter of the circle. At this position the heater is switched off and the partition S_(2) remains in equilibrium. Neglect any friction as well as heat loss to the surrounding through the walls of the tube. Find the heat supplied by the heater to the gas. by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 11 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Similar Questions
An adiabatic cylindrical tube is fitted with an adiabatic separator as shown in figure. Initial separator is in equilibrium and divides a tube in two equal parts. The seperator can be slide into the tube by an extermal mechanism. An ideal gas (γ=1.5) is injected in the two slides at equal pressure and temperature. Now separator is slid to a piston where it divides the tube in the ratio 7:3 The ratio of the temperature in the two parts of the vessel is √n:√7 find n.
View SolutionThe water flowing through the same tube having two different cross section areas has different flow rates .
View Solution
Knowledge Check
If cross- sectional area of limb I is A1 and that of limb II is A2 then velocity of the liquid in the tube will be, (cross- sectional area of tube is very small)
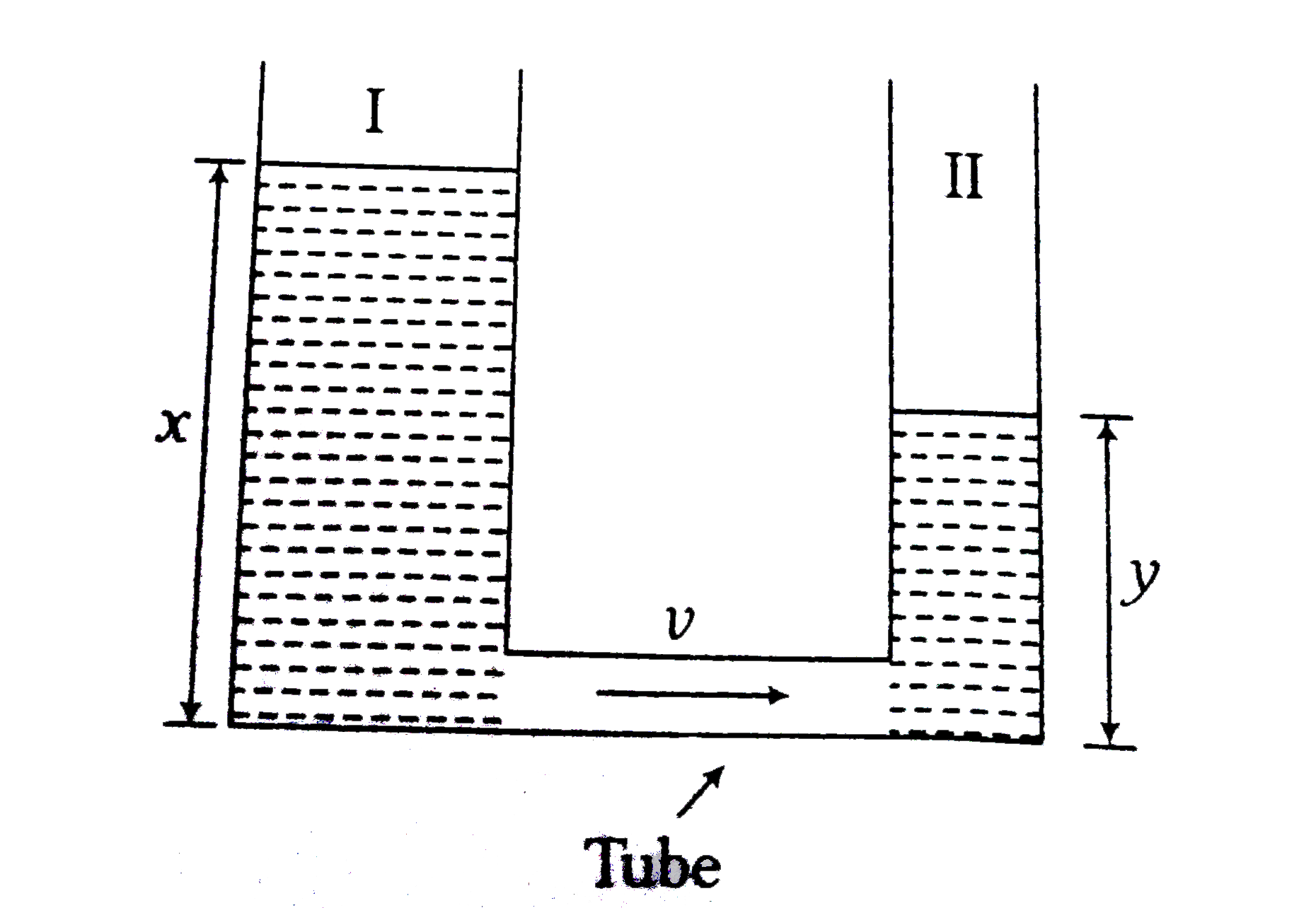 A√2g(x−y)BA1A2√2g(x−y)CA2A1√2g(x−y)DNone of these
A√2g(x−y)BA1A2√2g(x−y)CA2A1√2g(x−y)DNone of theseIn the figure, the cross-sectional area of the smaller tube is a and that of the larger tube is 2a. A block of mass m is kept in the smaller tube having the base area that of the tube. The difference between water levels of the two tubes is
 AP0ρg+maρBP0ρg+m2aρCmaρDm2ρa
AP0ρg+maρBP0ρg+m2aρCmaρDm2ρaA uniform tube of volume V contains an ideal monatomic gas at a uniform pressure P the temperature of the gas varies linearly along te length of the tube ad T and 2 T are the temperature at the ends.
AThe number of moles of the gas in the tube is PVRTln2BThe number of moles of the gas in the tube is PVRTln4CThe internal energy of the gas in the tube is (3/2)PVDThe internal energy of the gas in the tube is (3/2)nRT.
A liquid moves in a smoothh tube of uniform cross section. Find the pressure P2 at point 2 of the tube if the pressure at point 1 of the extended tube is P1 and the vertical distance between points 1 and 2 is h. brgt

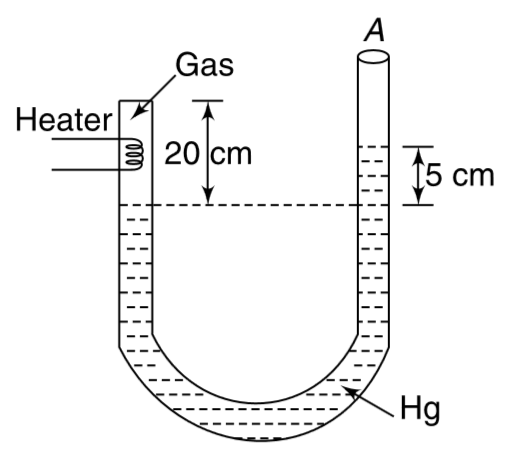
View SolutionOne end of an insulating U tube is sealed using insulating material. A mono atomic gas at temperature 300 K occupies 20 cm length of the tube as shown. The level of mercury on two sides of the tube differ by 5 cm. The other end of the tube is open to atmosphere. Area of cross section of the tube is uniform and is equal to 0.01m2. The gas in the tube is heated by an electric heater so as to raise its temperature to 562.5 K. Assume that no heat is conducted to mercury by the gas.
(a) Find the final length of the gas column.
(b) Find the amount of heat supplied by the heater to the gas.
View SolutionWater flows through the tube shown in figure. The areas of cross section of the wide and the narrow portions of the tube are 5cm2and2cm2 respectively. The rate of flow of water through the tube is 500cm3s−1 . Find the difference of mercury levels in the U-tube.
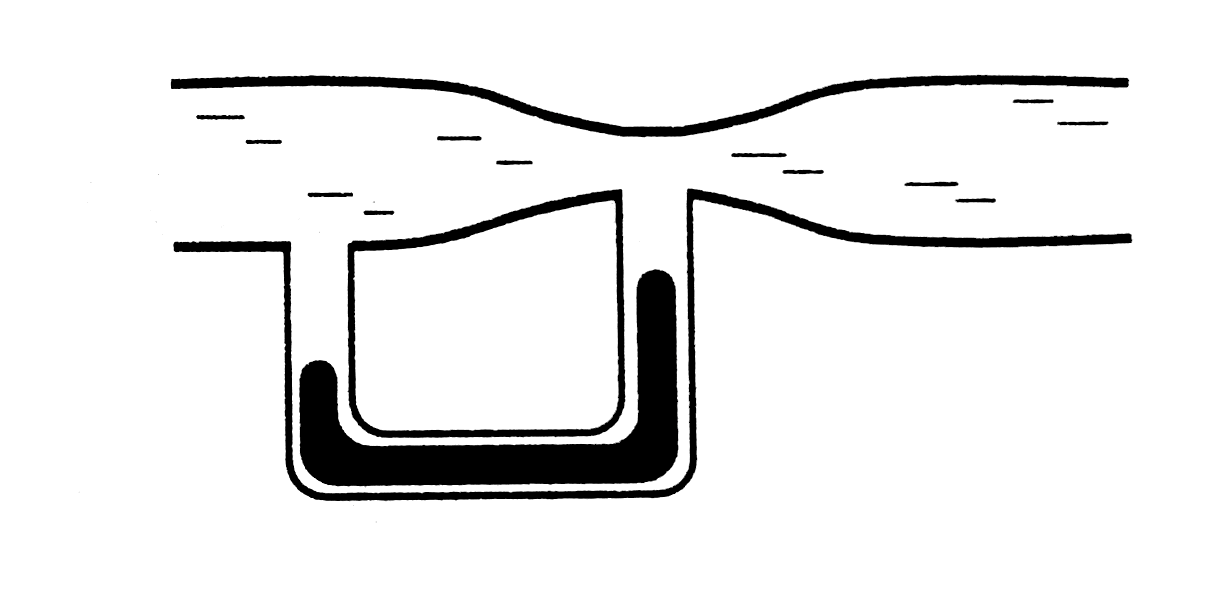
View SolutionWater flows through the tubes shown in figure. The areas of cross-section of the wide and the narrow portions of the tube are 5cm2 and 2cm2 respectively. The rate of flow of water through the tube is 500cm3/s. Find the difference of mercury levels in the U-tube.
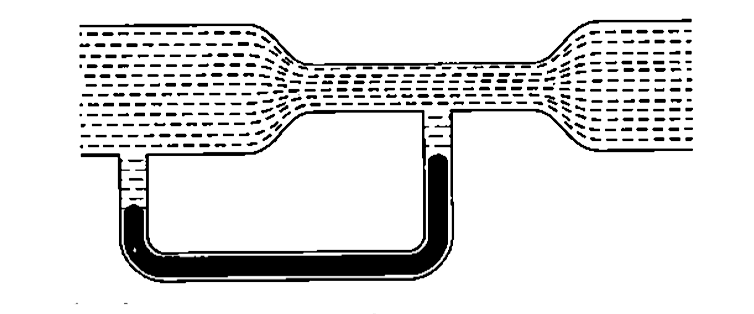
View SolutionFigure shows a cylindridcal tube with a adibatic walls and fitted with an adiabatic separtor. The separator can be slid into the tube by an external mechanism. An ideal gas(γ=1.5) is injected in the two sides at equal pressures and temperatures . The separator remains in equilibrium at the middel. It is now slid to a position where it divides the tube in the ratio 1:3 Find the ratio of the tempertures in the two parts of the vessel.

View Solution
