When 100mL of 1.0MHCl was mixed with 100mL of 1.0MNaOH in an insulated beaker at constant pressure, a temperature increase of 5.7∘C was measured for the beaker and its contents (Expt.1). Because the enthalpy of neutralisation of a strong acid with a strong base is constant (−57.0kJmol−1) this experiment couldbe used to measure the calorimeter constant. In a second experiment (Expt.2), 100mL of 2.0M acetic acid Ka=2.0×10−5) was mixed with 100mL of 1.0MNaOH (under identical conditions to Expt. 1) where a temperature rise of 5.6∘C was measured.
The pH of the solution after Expt. 2 ils
2.8
4.7
5.0
7.0
The correct Answer is:D
Step by step video, text & image solution for When 100mL of 1.0M HCl was mixed with 100 mL of 1.0 M NaOH in an insulated beaker at constant pressure, a temperature increase of 5.7^(@)C was measured for the beaker and its contents (Expt.1). Because the enthalpy of neutralisation of a strong acid with a strong base is constant (-57.0kJmol^(-1)) this experiment couldbe used to measure the calorimeter constant. In a second experiment (Expt.2), 100mL of 2.0M acetic acid K_(a)=2.0xx10^(-5)) was mixed with 100mL of 1.0M NaOH (under identical conditions to Expt. 1) where a temperature rise of 5.6^(@)C was measured. The pH of the solution after Expt. 2 ils by Chemistry experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 12 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Match the reactions in Column I with nature of the reactions/type of the products in Column II
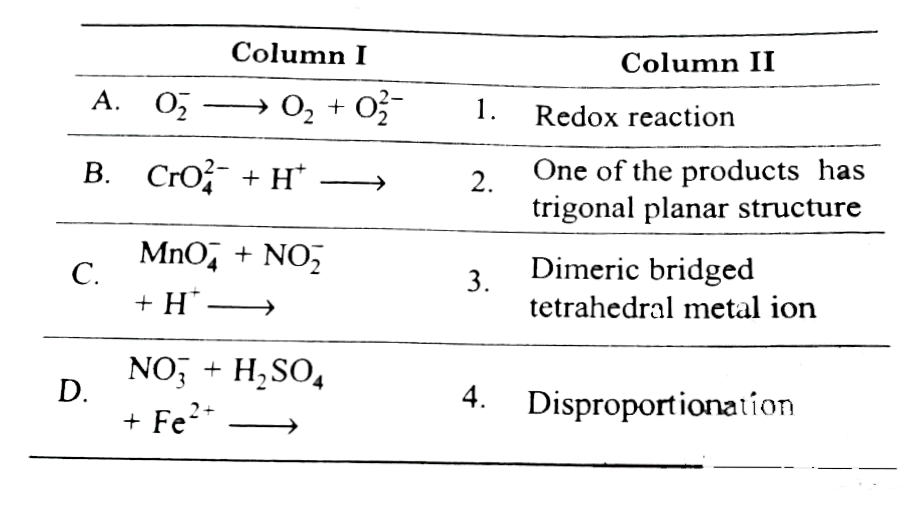
View SolutionWhen 100 mL of 1.0 M HCl was mixed with 100 mL of 1.0 M NaOH in an insulated beaker at constant pressure, a temerature increase of 0.7^(@) C was measured for the beaker and its contents (Expt. 1 ) . Because the enthalpy of neutralization of a strong acid with a strong base is a constant (-57.0 kJ "mol"^(-1) ), the experiment could be used to measure the calorimeter constant. In a second experiment (Expt. 2), 100 mL of 2.0 M acetic acid (K_(a)=2.0xx10^(-5)) was mixed with 100 mL of 1.0 M NaOH . (under identical conditions of Expt.1) where hte temperature rise of 5.6^(@)C was measured. (Consider heat capacity of all solutions as 4.2 J g^(-1) K^(-1) and density of all solutions as 1.0 m mL^(-1) ) Enthalpy of dissociation (in kJ "mol"^(-1) ) of acetic acid obtained from Expt. 2 is
View SolutionWhen 100 mL of 1.0 M HCl was mixed with 100 mL of 1.0 M NaOH in an insulated beaker at constant pressure, a temerature increase of 0.7^(@) C was measured for the beaker and its contents (Expt. 1 ) . Because the enthalpy of neutralization of a strong acid with a strong base is a constant (-57.0 kJ "mol"^(-1) ), the experiment could be used to measure the calorimeter constant. In a second experiment (Expt. 2), 100 mL of 2.0 M acetic acid (K_(a)=2.0xx10^(-5)) was mixed with 100 mL of 1.0 M NaOH . (under identical conditions of Expt.1) where hte temperature rise of 5.6^(@)C was measured. (Consider heat capacity of all solutions as 4.2 J g^(-1) K^(-1) and density of all solutions as 1.0 m mL^(-1) ) The pH of the solution after Expt. 2 is
View SolutionWhen 50 mL of a strong acid is added to 50 mL of a strong base temperature rises by 4.5∘C. What will be the increase in temperature when 100 mL of same acid is mixed with 100 mL of the same base?
View Solutionस्थित दाब पर ऊष्मारोधी बीकर (insulated beaker) में 100 मिली HCl (1.0 M) को 100 मिली NaOH (1.0 M) के साथ मिश्रित करने पर बीकर तथा उसकी अन्तर्वस्तुओं का तापमान 5.7∘C बढ़ जाता है। (प्रयोग 1) प्रबल अम्ल के साथ प्रबल क्षारक की उदासीनीकरण (neutralisation) एन्थैल्पी एक नियतांक (-57.0 किलोजूल मोल-') होने के कारण इस प्रयोग का उपयोग कैलोरीमीटर स्थिरांक (calorimeter constant) को मापने में किया जा सकता है। एक दूसरे प्रयोग (प्रयोग 2) में 100 मिली ऐसीटिक अम्ल 2.0 M, (K, = 20 x 10) को 100 मिली NaOH (1.0 M) के साथ मिश्रित करने पर (प्रयोग 1 की समांक अवस्था में) 5.6∘C तापमान वृद्धि मापित की गई। (सभी विलयनों की ऊष्माधारिता 4.2 जूल ग्राम-'केल्विन । तथा सभी विलयनों का घनत्व 1.0 मिली^(-1) है)
Q प्रयोग 2 से प्राप्त ऐसीटिक अम्ल की वियोजन एन्थैल्पी (dissociation enthalpy) (किलोजूल मोल ^(-1)) में है।
View Solutionस्थित दाब पर ऊष्मारोधी बीकर (insulated beaker) में 100 मिली HCl (1.0 M) को 100 मिली NaOH (1.0 M) के साथ मिश्रित करने पर बीकर तथा उसकी अन्तर्वस्तुओं का तापमान 5.7∘C बढ़ जाता है। (प्रयोग 1) प्रबल अम्ल के साथ प्रबल क्षारक की उदासीनीकरण (neutralisation) एन्थैल्पी एक नियतांक (-57.0 किलोजूल मोल-') होने के कारण इस प्रयोग का उपयोग कैलोरीमीटर स्थिरांक (calorimeter constant) को मापने में किया जा सकता है। एक दूसरे प्रयोग (प्रयोग 2) में 100 मिली ऐसीटिक अम्ल 2.0 M, (K, = 20 x 10) को 100 मिली NaOH (1.0 M) के साथ मिश्रित करने पर (प्रयोग 1 की समांक अवस्था में) 5.6∘C तापमान वृद्धि मापित की गई। (सभी विलयनों की ऊष्माधारिता 4.2 जूल ग्राम-'केल्विन । तथा सभी विलयनों का घनत्व 1.0मिली−1 है)
Qप्रयोग 2 के पश्चात् विलयन का pH है
View Solutionजब प्रबल अम्ल की 50 mL मात्रा को किसी प्रबल क्षार की 50 mL मात्रा के साथ मिलाया जाता है तो तापमान 4.5∘C बढ़ जाता है। उस समय तापमान में कितनी वृद्धि होगी जब समान अम्ल की 100 mL मात्रा को समान क्षार की 100 mL मात्रा के साथ मिलाया जाएगा?
View SolutionTemperature of beaker and its contents when 100 mL HCl (1.0M) is mixed with 100mL NaOH (1.0M) in an insulated beaker at constant pressure 5.7^(@)C Increases (experiment 1). The depolarizing enthalpy of a strong base with strong acid is a constant (-57.0 kJ "mol"^(-1)) Due to this, this experiment can be used to measure calorimeter constants in another experiment (experiment 2) with 100 mL of acetic acid. (2.0M, K_(a)=2.0xx10^(-5)) When mixed with 100 mL NaOH (1.0M) (in a homogeneous state of experiment 1) 5.6^(@)C Temperature rise was measured. (Heat capacity of all solutions 4.2J g^(-1)K^(-1) And density of all solutions 1.0gmL^(-1) is) The dissociation enthalpy of acetic acid obtained from experiment 2 (kJ "मोल"^(-1) In)
View Solution

