Two identical source moving parallel to each other at seperation 'd' are producing sounds of frequency 'f' and are moving with constant velocity v0. A stationary .observer 'O' is on the line of motion of one of the sources. Then the variation of beat frequency heard by O with time is best represented by: (as they come from large distance and go to a large distance)
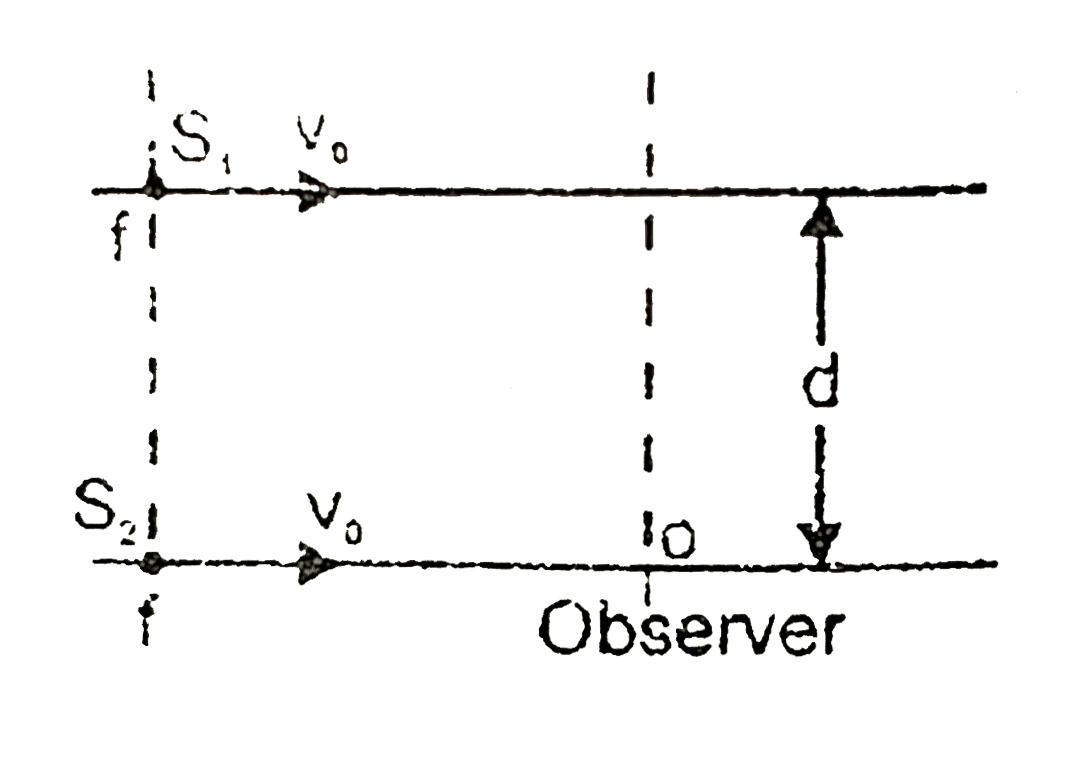
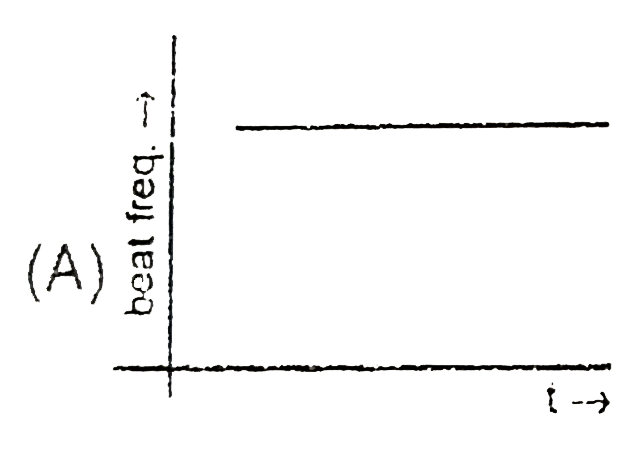
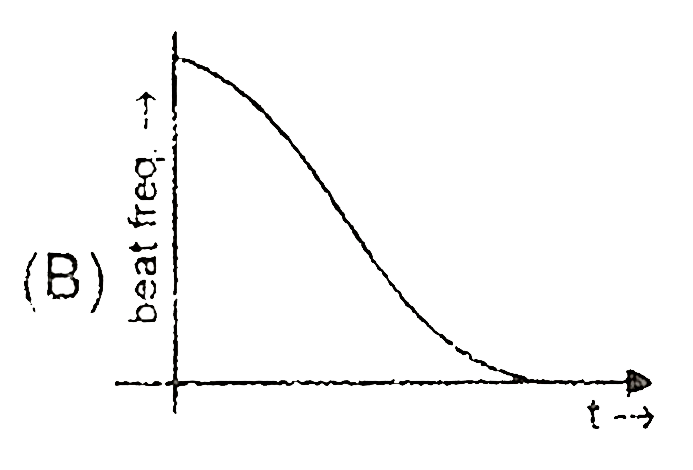
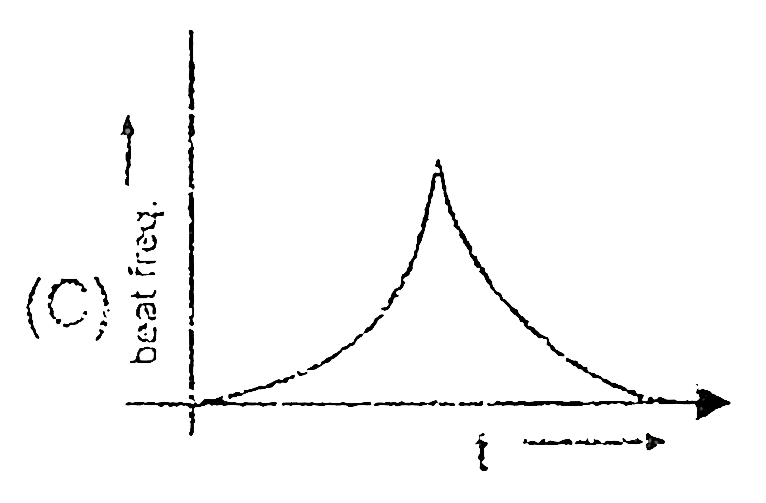
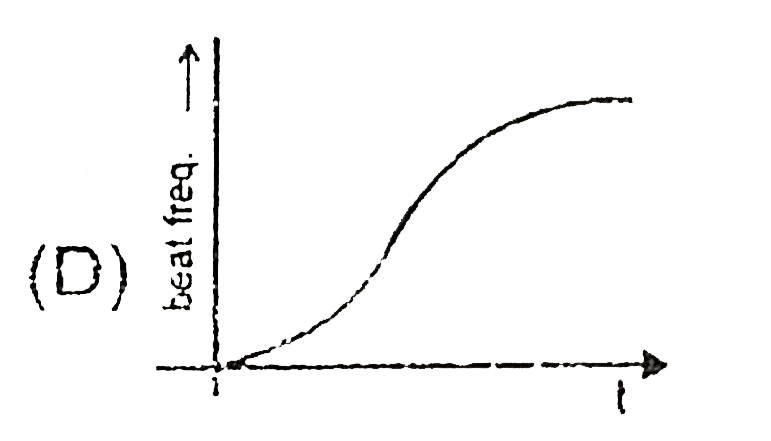
The correct Answer is:C
Topper's Solved these Questions
- SOUND WAVESBook:RESONANCEChapter:SOUND WAVESExercise:Exercise- 2 PART - II
Explore 20 Videos
- SOUND WAVESBook:RESONANCEChapter:SOUND WAVESExercise:Exercise- 2 PART - III
Explore 21 Videos
- SOUND WAVESBook:RESONANCEChapter:SOUND WAVESExercise:Exercise- 1 PART - II
Explore 30 Videos
- SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTIONBook:RESONANCEChapter:SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTIONExercise:Exercise
Explore 28 Videos
- STRING WAVESBook:RESONANCEChapter:STRING WAVESExercise:Exercise
Explore 32 Videos
Similar Questions
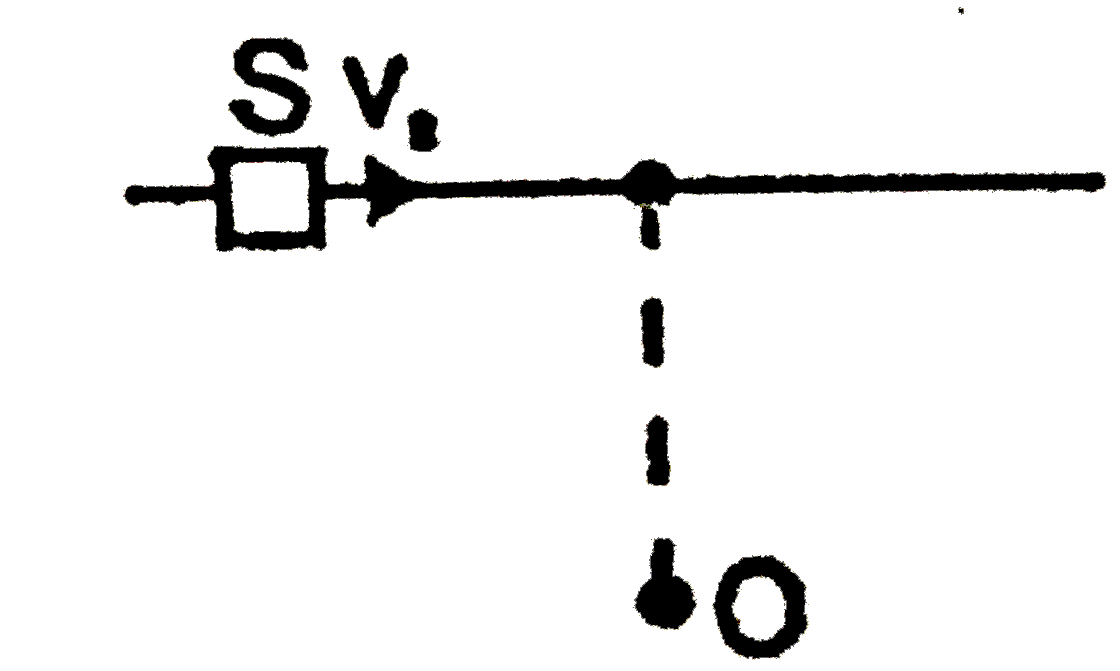
The source (S) of sound is moving constant velocity v0 as shown in diagram. An observer O listens to the sound emmited by the source. The observed frequency of the sound
View SolutionA source of frequency 'f' is stationary and an obsercer starts moving towards it at t=0 with constant small acceleration. Then the variation of observed frequency 'f' registered by the observer with time is best represented as
View Solution
Knowledge Check
The source (S) of sound is moving constant velocity v0 as shown in diagram. An observer O listens to the sound emmited by the source. The observed frequency of the sound
 Acontinuously decreasesBcontinuously increasesCfirst decreases then increasesDfirst increases then decreases.
Acontinuously decreasesBcontinuously increasesCfirst decreases then increasesDfirst increases then decreases.A source of frequency 'f' is stationary and an obsercer starts moving towards it at t=0 with constant small acceleration. Then the variation of observed frequency 'f' registered by the observer with time is best represented as
A B
B C
C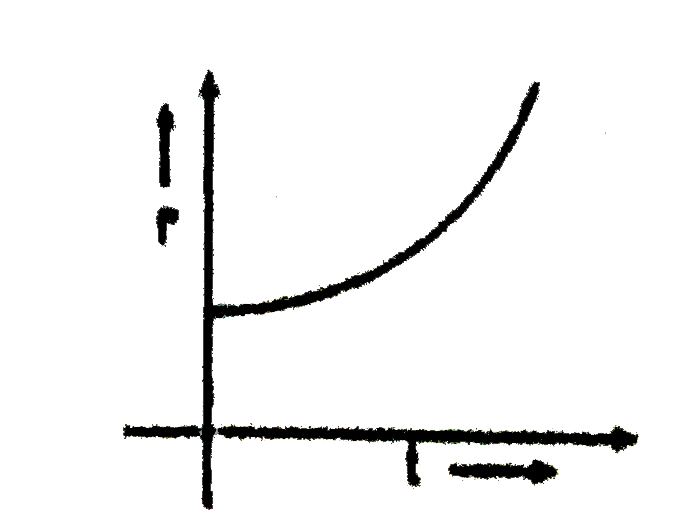 D
D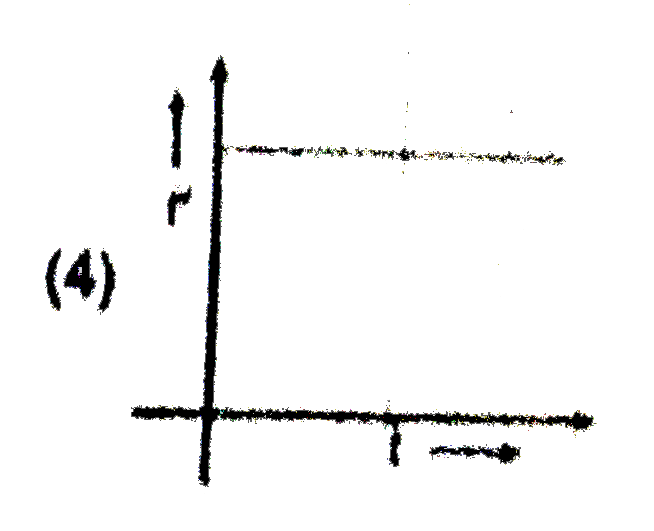
If a source of frequency n moving with velocity v crosses a stationary observer, then the change in the frequency of sound heard by the observer will be (velocity of sound = V)
A2nVvV2+v2B2nVv(V2−v2)C2nVv(V+v)D2nVv(V−v)
An observer moves with a constant acceleration towards a fixed source and start decelerating as soon as it passes the sound source. The variation of frequency f by observer with time t is best shown by
View SolutionA sound source S is moving along a straight track with speed v, and is emitting sound of frequency v0 (see figure). An observer is standing at a finite distance at the point O, from the track . The time variation of frequency heard by the observer is best respresent by :
(t0 represents the instant when the distance between the source and observer is minimum )
View SolutionA sound source S is moving along a straight track with speed v, and is emitting sound of frequency v0 (see figure). An observer is standing at a finite distance at the point O, from the track . The time variation of frequency heard by the observer is best respresent by :
(t0 represents the instant when the distance between the source and observer is minimum )
View SolutionA source of frequency 1 kHz is moving towards a stationary observer with velocity of 0.9 times that of sound. What is the frequency heard by the observer ?
View SolutionA source of sound crosses a stationary observer which is moving with uniform velocity v. If the velocity of sound in air is V, then the ratio of the apparent frequencies heard by the observer before and after the source crosses him would be -
View Solution

