A gas is enclosed in a cylinder with a freely movable piston. The load on the piston is gradually decreased. The temperature of the gas can be changed by placing the cylinder in hot and cold heat reservoirs. The figure shown P−Vgraph of such a cylinder. What intermediate can be drawn the nature of change in the temperature of the gas ? " "
" " 
We draw two isotherms representing constant temperatures T1 and T2sucn that T2passes through initial and final points 1 and 2 and T1passes through certain intermediate point 3 . The curve closer to origin re[resents lower temperaturature. Hence the gas is heated in the section 1-3 and cooled in the section 1-2.
Similar Questions
A gas is filled in a cylinder fitted with a piston at a definite temperature and pressure. Explain on the basis of kinetic theory why on pulling the piston out, the pressure of decreases.
View SolutionA gas filled in a cylinder fitted with movable piston is allowed to expand. What is the nature of the work done by the gas?
View Solution
Knowledge Check
A gas is enclosed in a metal container with a movable piston on top. Heat is added to the gas by placing a candle ame in contact with the container's bottom. Which of the following is true about the temperature of the gas?
 AThe temperature must go up, if the piston remains stationaryBThe temperature must go up, if the piston is pulled out dramaticallyCThe temperature must go up no matter what happens to the pistonDThe temperature must go down no matter what happens to the piston
AThe temperature must go up, if the piston remains stationaryBThe temperature must go up, if the piston is pulled out dramaticallyCThe temperature must go up no matter what happens to the pistonDThe temperature must go down no matter what happens to the pistonA gas is filled in the cylinder shown in fig. The two pistons are joined by a string. If the gas is heated, the right piston will
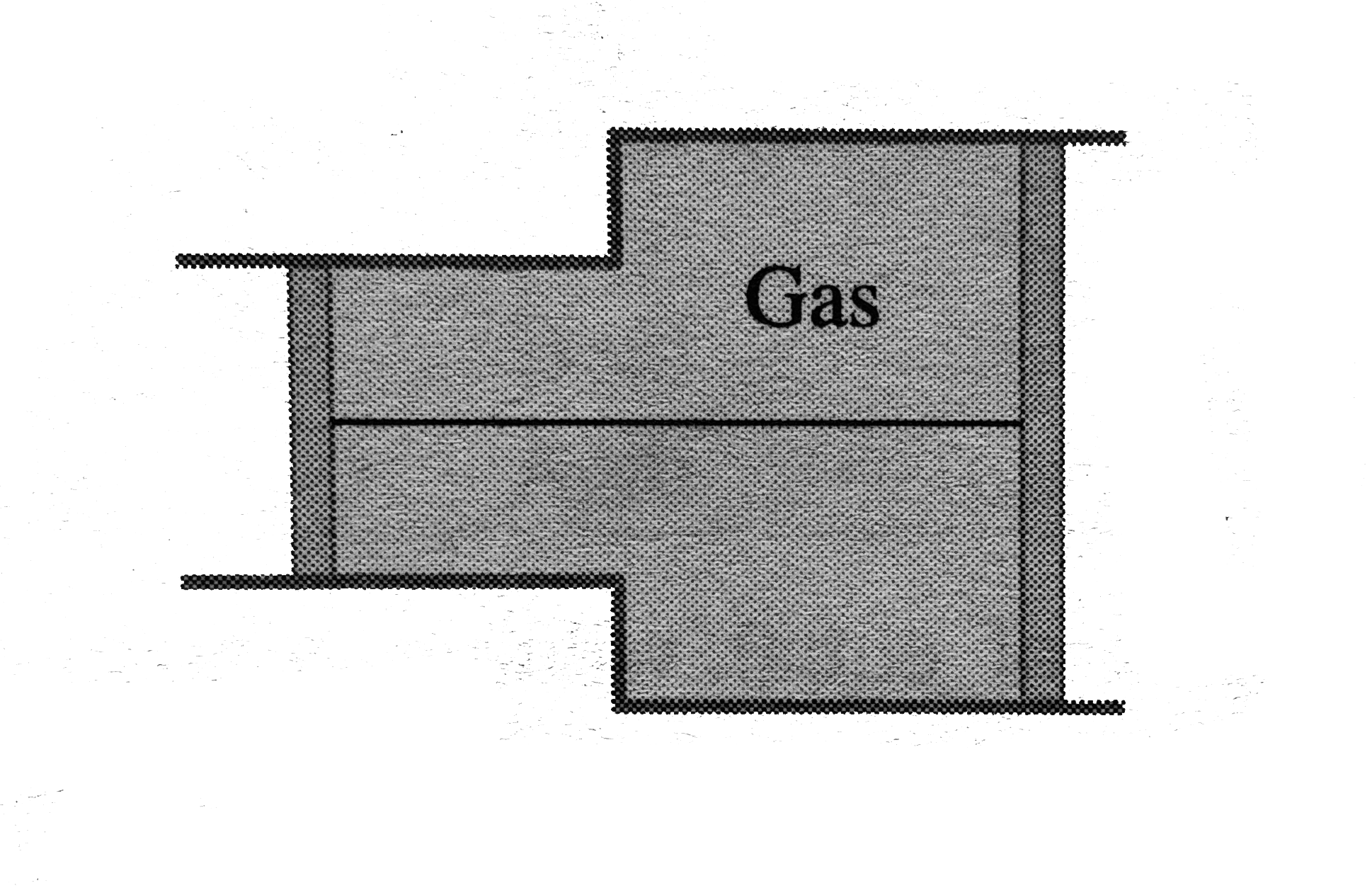 Amove toward leftBmove toward rightCremain stationaryDnone of these
Amove toward leftBmove toward rightCremain stationaryDnone of theseA match ignites within in an oxygen-filled cylinder that has a movable piston. The piston is moved so quickly that no heat escapes. What kind of change is demonstrated in this process?
AAn isobaric changeBAn adiabatic changeCAn isochoric changeDA change of heat capacity
A gas filled in a cylinder fitted with a movable piston is compressed. What is the nature of work done by the applied force?
View Solution(i) An adiabatic cylinder contains an ideal gas. It is fitted with a freely movable insulating piston. In one experiment the piston is pulled out very fast to double the volume of the gas. In another experiment starting from same initial state, the piston is pulled out very slowly to double the volume of the gas. At the end of which experiment the final pressure of the gas will be higher?
(ii) An ideal gas is contained in a cylinder fitted with a movable piston. In an experiment ‘A’ the gas is allowed to perform a work W(>0) on the surrounding during an isobaric process and thereafter the pressure of the gas is reduced isochorically to half the initial value. At the end of the experiment the temperature of the gas is TA. In a different experiment ‘B’ the pressure of the gas is reduced to half in an isochoric process and then the gas performs a work W on the surrounding during an isobaric process. At the end of the experiment the gas temperature is TB. Which is higher, TA or TB?
View SolutionA gas is filled in a cylinder fitted with a piston at a definite temperature and pressure. Explain on the basis of kinetic theory, the pressure of the gas increases by raising its temperature.
View SolutionAn ideal gas enclosed in a cylinder fitted with a frictionless and weightless piston, pushes it outside. What would be the sign convention for the work ?
View SolutionA gas is enclosed in a cylinder with a piston. Weights are added to the piston, giving a total mass of 2.20 kg. As a result the gas is compressed and the weights are lowered 0.25 m. At the same time, 1.50 J of heat evolved from the system. What is the change in internal energy of the system ?
View Solution

