The figure shows an insulated cylinder divided into three parts A,B and C. Pistons I and II are connected by a rigid rod and can move without friction inside the cylinder. Piston I is perfectly conducting while piston II is perfectly insulating. The initial state of the gas (γ=1.5) present in each compartment A,B and C is as shown. Now , compartment A is slowly given heat through a heater H such that the final volume of C becomes 4V09. Assume the gas to be ideal and find.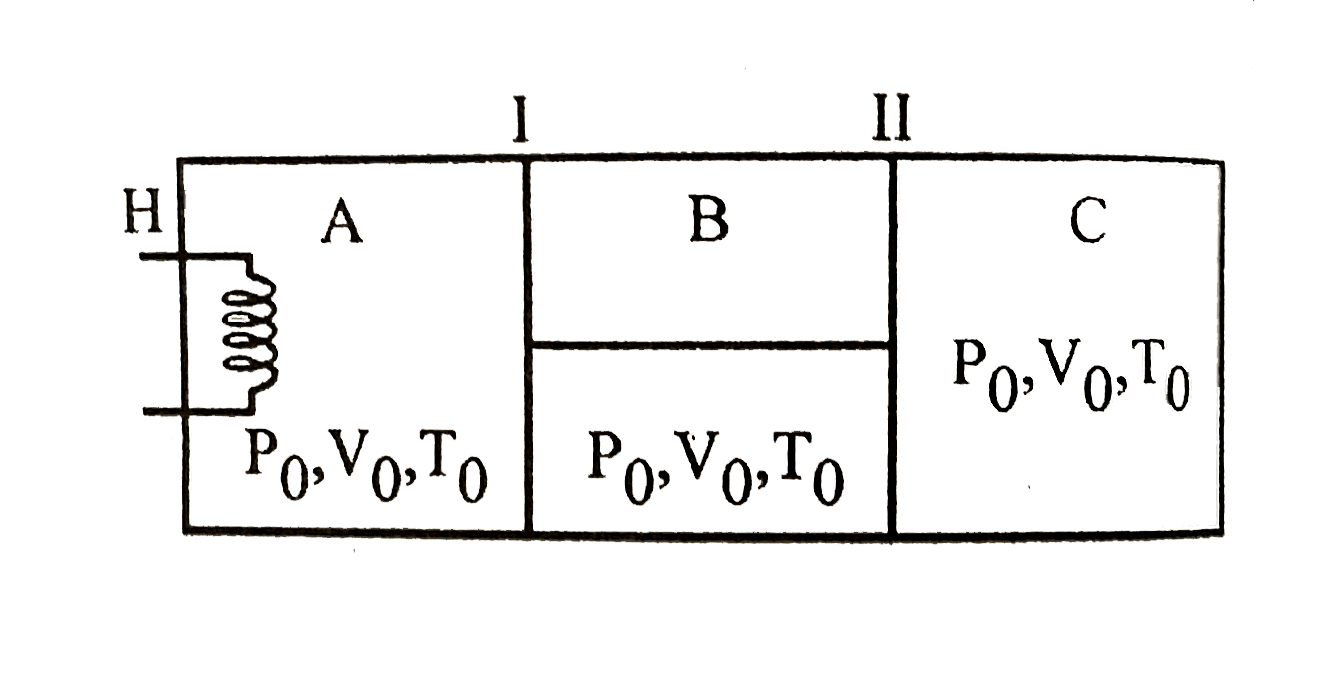
Final pressures in each compartment A,B and C
Final temperatures in each compartment A,B and C
Heat supplied by the heater
Work done by gas in Aand B
Heat flowing across piston I.
The correct Answer is:(a)finla pressure in A=278P0=Final pressure in C, finla pressure in B=214P0
(b)finla temperature in (AandB)=214t0,finla temperature in C=32T0,
(c) 18P0V0,
(d)Work done by gas in A=+P0V0Work done by gas in B=0,
(e)172P0V0
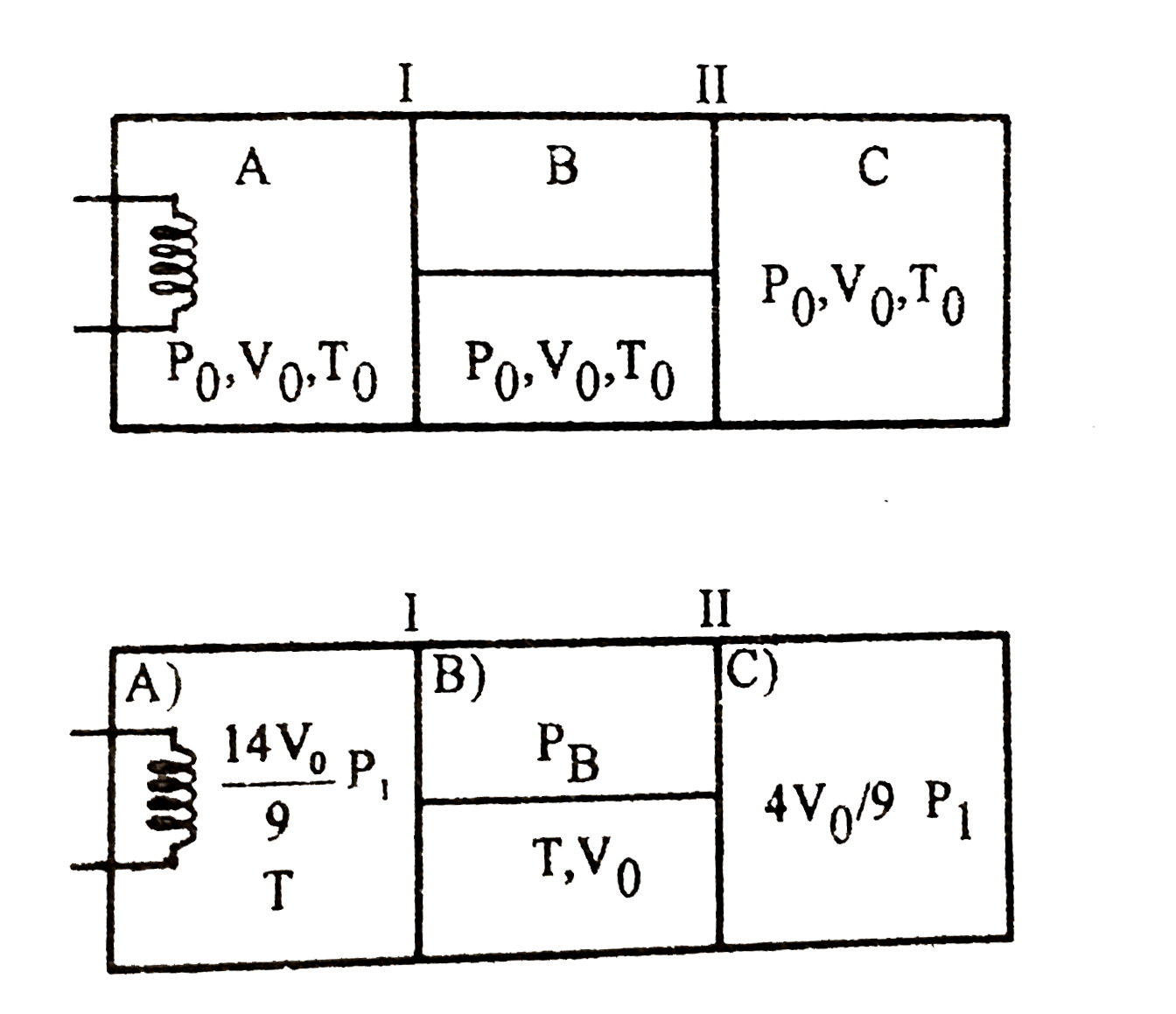

(a)For compartment -C
PVr=constant
P0V320=P1(4V09)32
P1=P0(94)32=27p08
P1= Final pressure in A = finla pressure in c as movable pistion is in equilibrium Temperature in compartment A
P0V0T0=P1(14V09)T0⇒P0V0T0=(278)P0×(149)V0T
Temperature in A = Temperture in B(as conducting) For C
P0V0T0=4V09×27P08Tc
Tc=4×279×8T0=32T0
pressure in 'B' = P_(B)<br>Then
PBT=P0T0⇒PB=P0TT0=214T0P0T0=214P0
Heat supplical by heat r =Qb
△Qb=nCv△(T)=f2(nRT2−nRT1)
=f2(V0)(PB−P0)
f2V0(174P0)
=17fP0V08 ltbRgt r=1.5⇒f=4
Q△b=172P0V0
ForA"
PA=Pc
VA=W0−Vc
dVA=dVc
WA=∫PAdVA−∫PcdVc
=−Wc
=[PiVi−PfVFR1]
=[Pfc−PicVicr1]
WA=4V09×27P08−P0V01/2
=P0v01/2=P0V0
△UA=f2(nR△TA)=(P1×14V09−P0V0)f2
=(278P0×14V09−P0V0)f2
(214P0V0−P0v0)f2
=(174P0V0)×2
=△Q=174P0V0+172P0v0
=18P0V0
Wa=P0V0
Heatflow=△Qb=172P0V0
Similar Questions
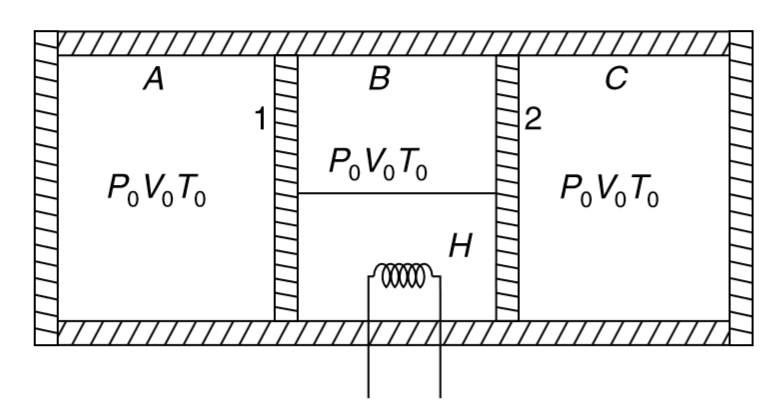
An insulated cylinder is divided into three parts A, B and C. Pistons 1 and 2 are connected by a rigid rod and can slide without friction inside the cylinder. Piston 1 is perfectly conducting while piston 2 is perfectly insulating. Equal quantity of an ideal gas is filled in three compartments and the state of gas in every part is same (P0V0T0). Adiabatic exponent of the gas is g = 1.5. The compartment B is slowly given heat through a heater H such that the final volume of gas in part C becomes 4V09
(a) Calculate the heat supplied by the heater.
(b) Calculate the amount of heat flow through piston 1.
(c) If heater were in compartment A, instead of B how would your answers to (a) and (b) change?
View SolutionA Perfect gas is enclosed in a vertical cylinder filled with a piston of mass m. The gas is heated by passing constant current I through a heating coil of resistance R placed inside the cylinder. At what speed v must the piston move upward in order that temperature of the gas may remain unchanges? Assume ideal insulating walls and piston and there is no fusion.
View Solution
Knowledge Check
A piston of mass m can move without friction in a uniform closed cylinder at one end. A gas is enclosed in it. For this situation mark the correct statement(s)
AIf cylinder is kept horizontal then pressure of gas must be equal to atmospheric pressure.BIf cylinder is kept vertical then pressure of gas may be greater than atmospheric pressure.CIf cylinder is kept vertical then pressure of gas must be greater than atmospheric pressureDIf cylinder is kept vertical then pressure of gas can’t be equal to atmospheric pressureA gas is filled in the cylinder shown in fig. The two pistons are joined by a string. If the gas is heated, the right piston will
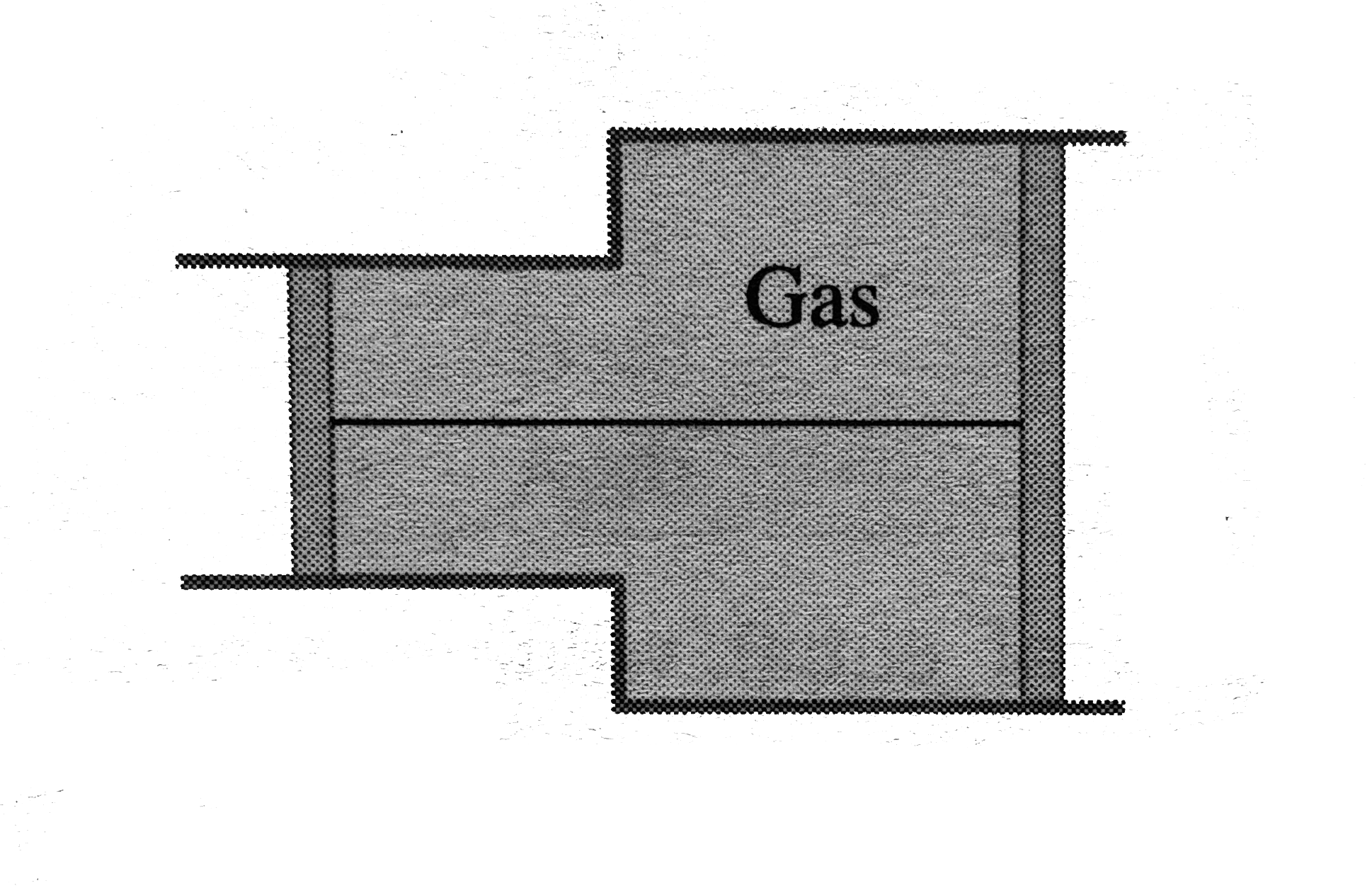 Amove toward leftBmove toward rightCremain stationaryDnone of these
Amove toward leftBmove toward rightCremain stationaryDnone of theseThe piston I s now pulled out slowly and held at a diatance 2L from the top. The pressure in the cylinder between its top and the piston will then be
AP0BP0/2CP02+MgϕR2DP02−Mgϕr2
An insulating cylinder contains equal volumes of He and O2 separated by a massless freely moving adiabatic piston as shown. The gas is compressed by moving the insulating piston so that volume of He becomes half. Select the correct alternative(s).
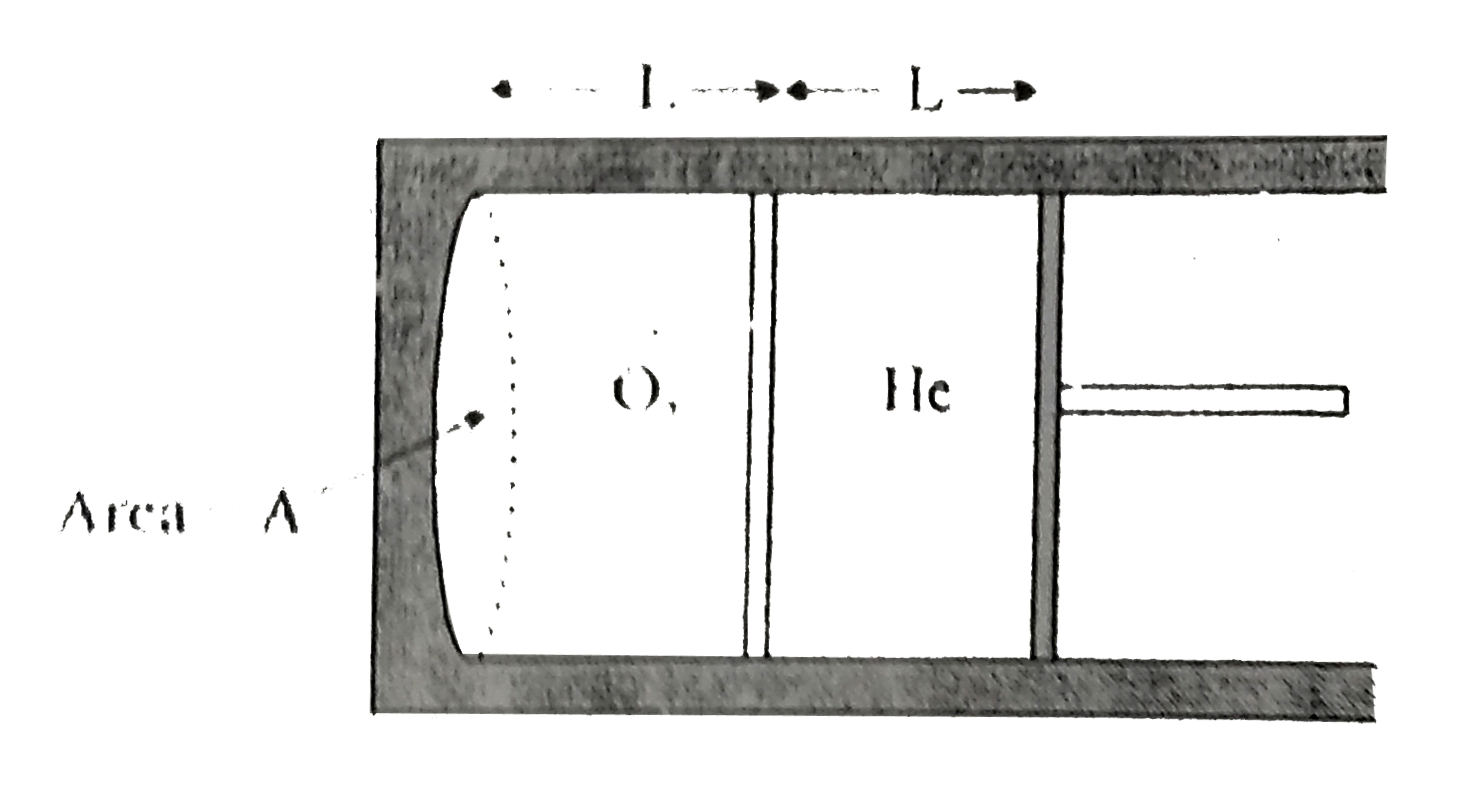
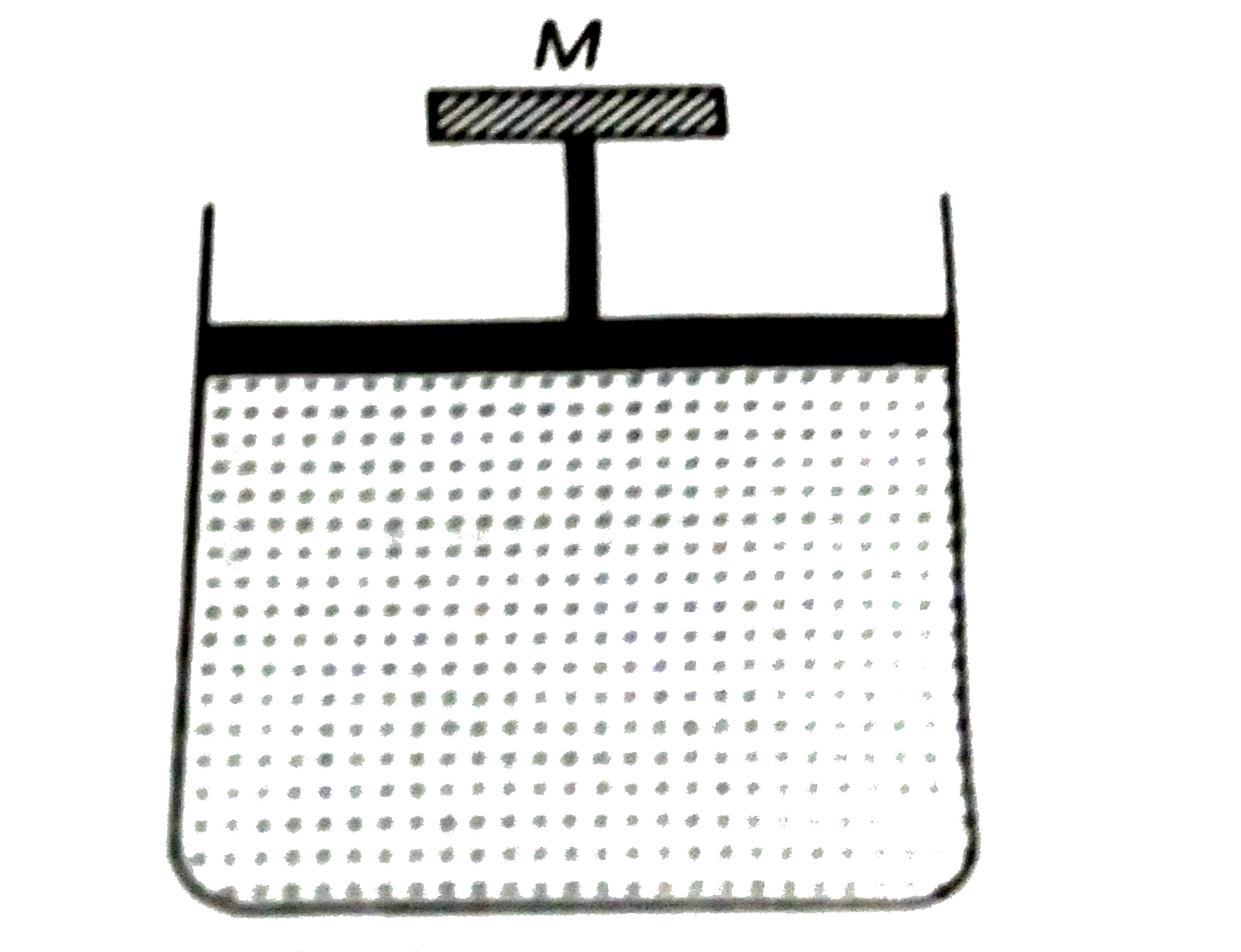
View SolutionA cylinder containing an ideal gas is in vertical position and has a piston of mass M that is able to move up or down without friction (figure). If the temperature is increased
View SolutionA cylindrical vessel made of thermally insulating material is divided into two equal parts by an insulating and. Movable piston. Both parts contain ideal monoatomic gas . The gas in the left part is supplied heat such that the volume of right part becomes one-eight of its initial volume . Work done by the gas in the right part is
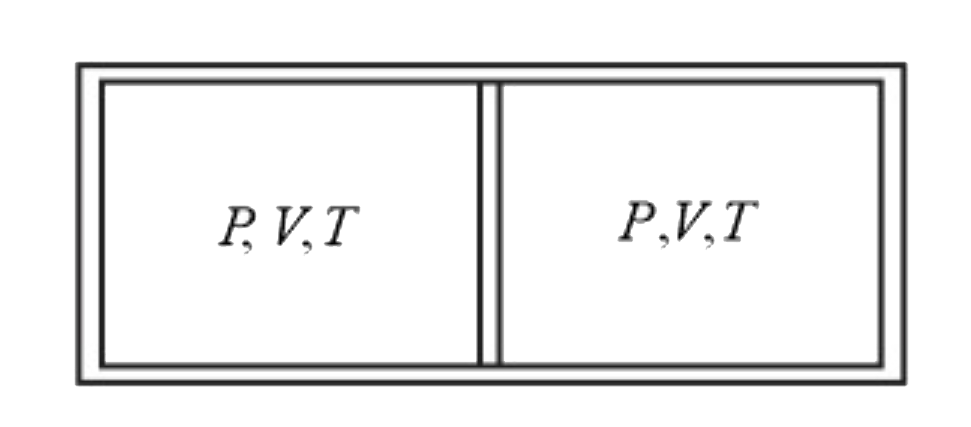
View SolutionFigure shows an insulated cylinder of volume V containing monatomic gas in both the compartments. The piston is diathermic. Initially the piston is kept fixed and the system is allowed to acquire a state of thermal equilibrium. The initial pressures and temperatures are as shown in the figure. Calculate

Final volume of the left compartment.
View SolutionFigure shows an insulated cylinder of volume V containing monatomic gas in both the compartments. The piston is diathermic. Initially the piston is kept fixed and the system is allowed to acquire a state of thermal equilibrium. The initial pressures and temperatures are as shown in the figure. Calculate

The final pressures of left and right compartment respectively are
View Solution

