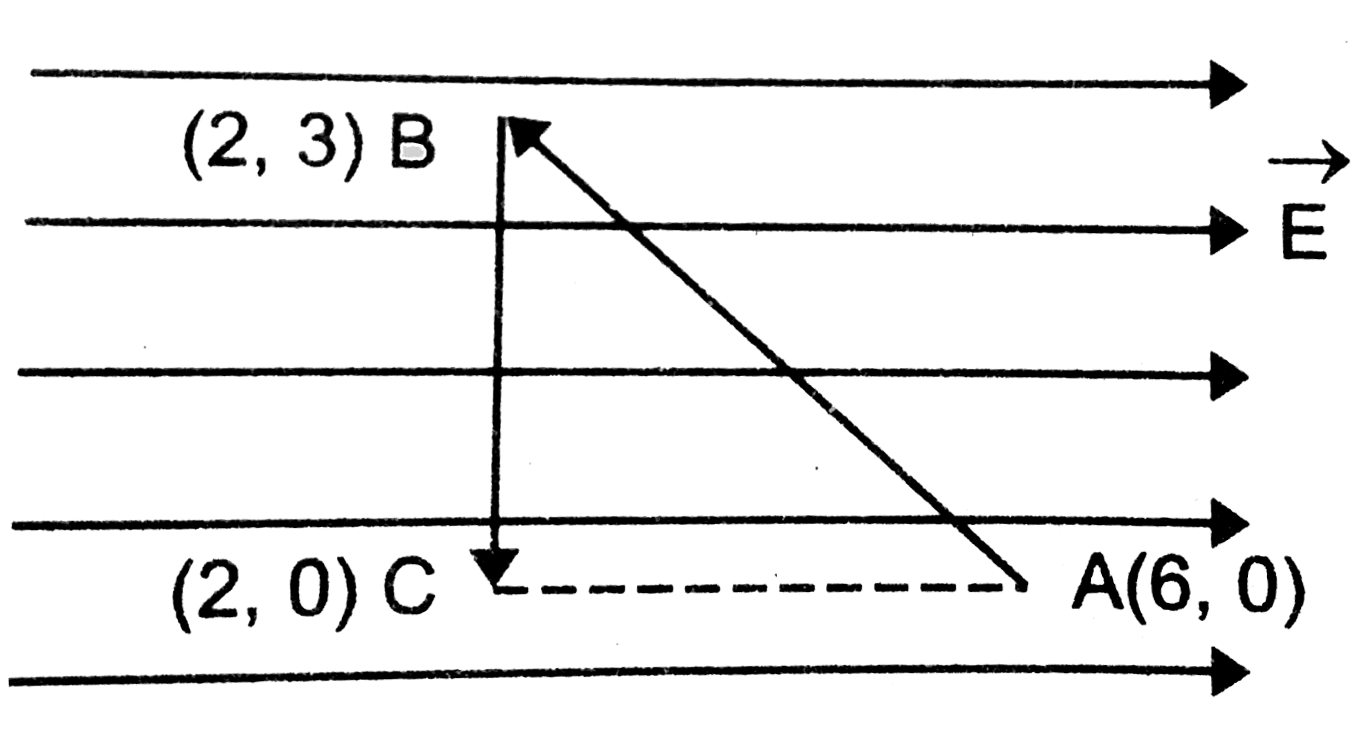
A test charge q is moved without acceleration along the path from A to B from B to C in electric field E as shown in fig.

(i) Calculate the potential difference between A and C.
VA−VC=−∫62→E⋅d→x=−∫62Edxcos0∘=−∫62Edx
=−E∫62dx=−4E
∴VC−VA=4E.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- ELECTRIC POTENTIAL BOOK - CHHAYA PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - ELECTRIC POTENTIAL EXERCISE - Examination Archive with solutions (NEET)
1 Video
- ELECTRIC FIELDBOOK - CHHAYA PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - ELECTRIC FIELDEXERCISE - CBSE SCANNER
31 Videos
- ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION & ALTERNATING CURRENTBOOK - CHHAYA PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION & ALTERNATING CURRENTEXERCISE - CBSE SCANNER
28 Videos
Similar Questions
A molecule of a substance has permanent dipole moment p. A mole of this substance is polarised by applying a strong electrostatic field E. The direction of the field is suddenly changed by an angle of 60∘. If N is the Avogadro's number the amount of work done by the field is
View SolutionA charge q is placed at the centre of a cube of side l. What is the electric flux passing through each face of the cube?
View SolutionA bar magnet is moved in the direction indicated by the arrow between two coils PQ and CD. Predict the directions of induced current in each coil.

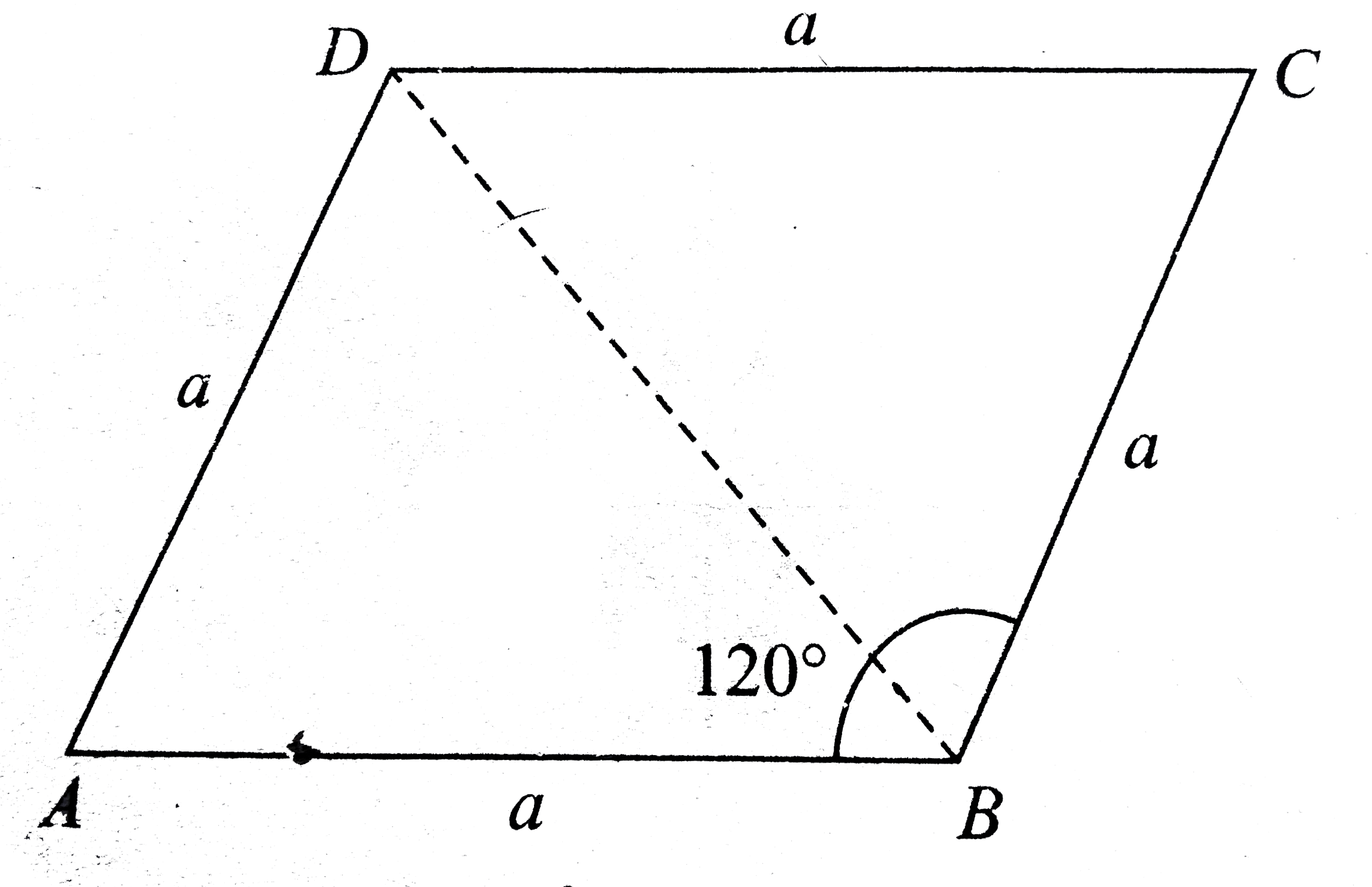
View SolutionA charge +Q at A (see Fig. 3.140) produces electric field E and electric potential V at D. If we now put charges −3Q and +Q at B and C, respectively, then the electric field and potential at D will be
 .
.
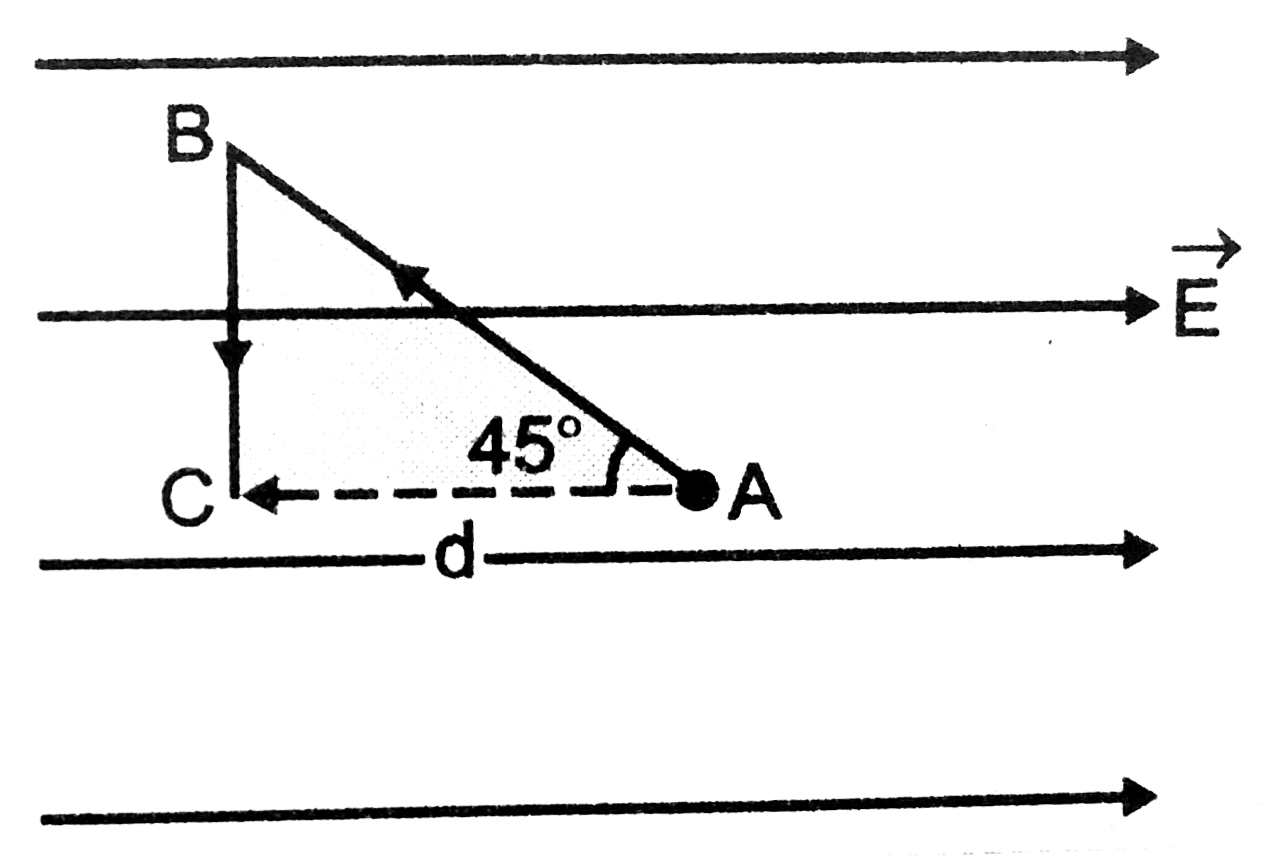
View SolutionThree points A,B,C lie in a uniform electric field E of 5xx10^(3) N//C as shown in Fig. Find the potential difference between A and C.
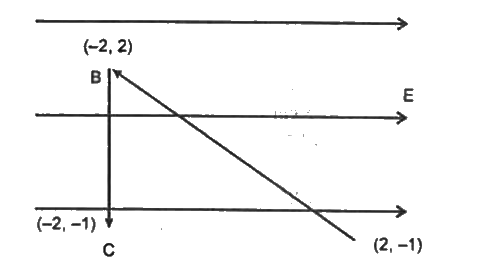
View SolutionA test charge q is moved without acceleration from A to C along the path from A to B and then from B to C in electric field E as shown in Fig. (i) Calculate the potential difference between A and C (ii) At what point [of A and C] is the electric potential more and why?
View SolutionA test charge q0 is moved without acceleration from A to C over the path ABC as shown in Fig.
Calcualate potential difference beetween A and C.
View Solutionएक परिक्ष्ण आवेश q को बिना त्वरण के A से B के अनुदिश त्तपश्चता B से C के अनुदिश चित्र में दर्शाए अनुसार विधुत क्षेत्र →E में Aसे C तक चलाया जाता है |

(i) A और C के बीच विभवांतर ज्ञात कीजिए |
(ii) किसी बिन्दु (दोनों में से ) पर विधुत विभव अधिक होगा और क्यों है |
View SolutionIn the electric field of a point charge ( + q) , placed at the centre of a circle , a certain test charge is carried from point A to B, C,D and E Least amount of work is done along the path
View Solutionआरेख (चित्र) में दिखाए अनुसार, किसी विद्युत् क्षेत्र E में, एक परीक्षण आवेश 'q' को बिना त्वरण के, पहले A से B तक और फिर B से C तक विस्थापित
किया जाता है। इस प्रकार आवेश 'q' के A से C तक जाने पर (i) A तथा C के बीच विभवान्तर के मान का परिकलन कीजिए। (ii) इन दो बिन्दुओं में से किस बिन्दु पर विद्युत विभव अधिक है ? अपने उत्तर के लिए कारण लिखिए।
View SolutionA test charge q is moved without acceleration from A to C along the path form A to B and then from B to C in electric field E as shown in the figure.
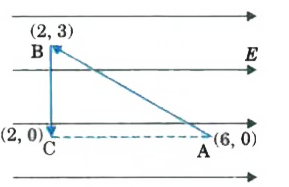
(i) Calculate the potential difference between A and C.
(ii) At which point (of the two) is the electric potential more and why?
View SolutionA charge + Q at A as shown in fig. produces electric field E and electric potential V at D. if we now put charges -2 Q and + Q at B and C respectively , then the electric field and potential at D will be :
View Solution(a) Figure 24-10a shows two points i and fin a uniform electric field →E. The points lie on the same electric field line (not shown) and are separated by a distanced. Find the potential difference Vf−Vi by moving a positive test charge q0 from i to f along the path shown, which is parallel to the field direction.
(b) Now find the potential difference Vf−Vi by moving the positive test charge q0 from i to f along the path icf shown in Fig. 24-10b.
View SolutionA test charge 'q' is moved without acceleration from A to C along the path from A to B and then from B to C in electric field E as shows in the figure. (i) Calculate the potential difference between A and C. (ii) At which point (of the two) is the electric potential more and why ?

View SolutionA test charge q_(0) A The path from C to C goes without acceleration as shown by ABC. The difference between A and C is
View SolutionA test charge q is moved without acceleration from A to C along the path from A to B and then from B to C in electric field E as shown in Fig. (i) Calculate the potential difference between A and C (ii) At what point [of A and C] is the electric potential more and why?

View Solution

