Following titration method is taken to compute stepwise ionisation constant of a weak dibasic acid 
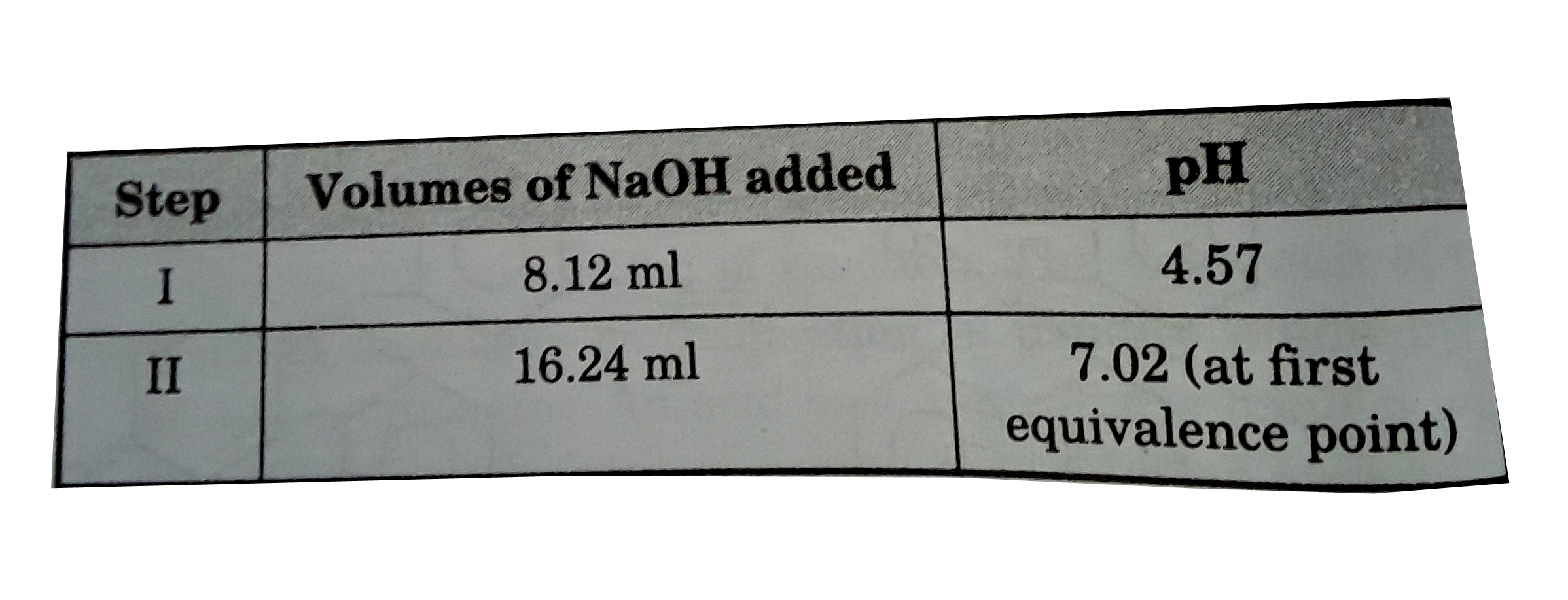
has two ionisable protons and there can be stepwise neutralisation by NaOH.
Which H+ removed in step I?
pKa2(=−logKa2) of p-hydroxybexzonic acid is nearly:
4.5
7
9.5
5
The correct Answer is:c
Step by step video, text & image solution for Following titration method is taken to compute stepwise ionisation constant of a weak dibasic acid has two ionisable protons and there can be stepwise neutralisation by NaOH. Which H^(+) removed in step I? pK_(a_2)(=-logK_(a_2)) of p-hydroxybexzonic acid is nearly: by Chemistry experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 12 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
For every diprotic acid of the type H2X, how would you relate ionisation constant Ka1 and Ka2
View SolutionThe dissociation of weak electrolyte (a weak base or weak acid) id expressed in terms of Ostwald dilution law. An acid is a substance which furnishes a proton or accepts an electron pair whereas a base is proton acceptor or electron pair donor. Storonger is the acid weaker is its conjugate base. The dissociation constants of an acid (Ka) and its conjugate base are related by (Kw=Ka×Kb, where Kw is ionic prodcut of water equal to 10-14 at 25∘C. The numerical value of Kw however increases with temperature. In a solution of an acid or base [H+][OH−]=1014.Thus, the [H+] in a solution is expressed as : [H+]=10−pHand pH+pOH=14. Buffer solutions are the solutions which do not show appreciable change in the pH on addition of small amount of acid or base.
Which of the following statements are correct?
(P) At 25∘C,pHof10−10MNaOH is nearly 7.
(Q) The degree of dissociation of a weak acid is given by 11+10(pka−pH).
(R) For weak electrolytes of polyprotic acid nature having no other electrolyte, the anion concentration produced in II step of dissocitation is always equal to K2 at reasonable concentration of acid.
(S) The concentraion of amide ions produced during self ionisation of NH3 is equal to concentration of ammonium ions.
Ostwld dilution law is valid for strong electrolytes.
View Solution
Knowledge Check
Following titration method is taken to compute stepwise ionisation constant of a weak dibasic acid

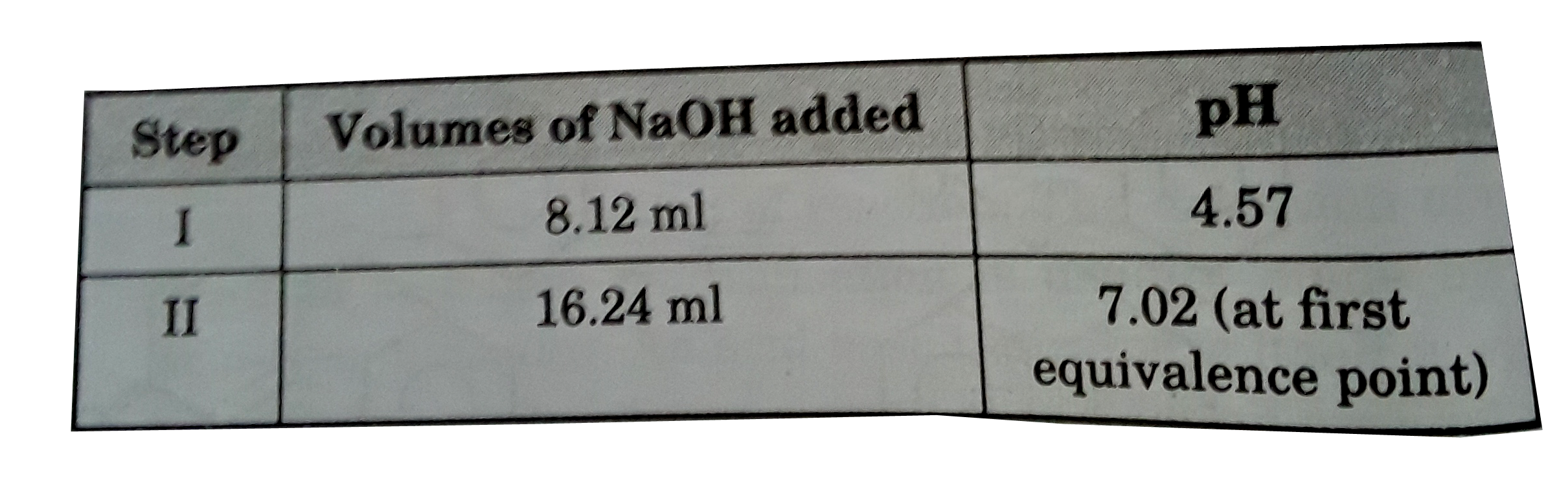
has two ionisable protons and there can be stepwise neutralisation by NaOH.
Which H+ removed in step I?
pKa1(=−logKa1) of p-hydroxybenzonic acid is :A4.57B9.47C4.9D7Assertion : H3PO3andH2SO4 are known as dibasic acids .
Reason : They have two ionisable protons per moleculae of the acid .AIf both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion .BIf both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion .CIf assertion is true but reason is false .DIf both assertion and reason are false .Statement-1 : The ionisation constants of weak diprotic acid are in the order of Ka1>Ka.
Statement-2 : Removal of H+ from anion is difficult as compared to neutral atom.AIf both the statements are true and statement -2 is the correct explanation of statement-IBIf both the statements are true but statement-2 is not the correct explanation of statement-ICIf statement-I is true and statement-2 is falseDIf statement-I is false and statement-2 is true.
Consider a weak acid HX that is partially ionised in the aqueous solution.
HX+H2O(l)⇔H3O+(aq)+X−(aq)
I. The equilibrium constant of the above reaction is
Ka=C2α2C(1−α)=Cα21−α
where, C = initial concentration of the undissociated acid.
α = extent up to which HX is ionised into ions, Ka is called the dissociation or ionisation constant of acid HX.
II. It can represented alternatively in terms of molar concentration as follows,
Ka=[H+]X−HX
III. At a given temperature T,Ka is a measure of the strength of the acid HX, i.e. larger the value of Ka, the stronger is the acid.
Which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
View SolutionThe dissociation of weak electrolyte (a weak base or weak acid) is expressed in terms of Ostwald's dilution law. An acid is substance which furnishes a proton or accepts an electron pair, where a base is proton acceptor or electron pair donor. Stronger is acid, weaker is its conjugate base. The dissociation constants of an acid (Ka) and its conjugate base (Kb) are related by Kw=Ka×Kb, where Kw is ionic product of water equal to 10−14at25∘C. The numerical value of Kw however increase with temperature. In a solution of an acid or base [H+][OH−]=10−14. Thus the [H+] in a solution is expressed as: [H+]=10−pH and pH+pOH=14. Buffer solution are the solutions which do not show appreciable change in the pH on addition of small amount of acid or base.
Which of the following statements are correct ?
(1) pH of 10−10 M NaOH is nearly 7.
(2) The degree of dissociation of a weak acid is given by 11+10(pKaq−pH)
(3) For weak electrolytes of polyprotic acid nature having no other electrotrolype, the anion concentration produced in II step of dissociation is always equal to K2 at reasonable concentration of acid.
(4) The concentration of amide ions produced during self ionisation of NH3 is equal concentration of ammonium ions.
(5) Ostwald's dilution law is valid for strong electrolytes.
View SolutionThe dissociation of weak electrolyte (a weak base or weak acid) is expressed in terms of Ostwald's dilution law. An acid is substance which furnishes a proton or accepts an electron pair, where a base is proton acceptor or electron pair donor. Stronger is acid, weaker is its conjugate base. The dissociation constants of an acid (Ka) and its conjugate base (Kb) are related by Kw=Ka×Kb, where Kw is ionic product of water equal to 10−14at25∘C. The numerical value of Kw however increase with temperature. In a solution of an acid or base [H+][OH−]=10−14. Thus the [H+] in a solution is expressed as: [H+]=10−pH and pH+pOH=14. Buffer solution are the solutions which do not show appreciable change in the pH on addition of small amount of acid or base.
Which of the following statements are true ?
(1) CIO−4 is weak base than CIO−3
(2) The degree of dissociation of weak is 1.8×10−9
(3) The equilibrium constant for dissociation of H2O is 1.78×10−16
(4) PO3−4 is conjugate acid of HPO2−4
View SolutionThe dissociation of weak electrolyte (a weak base or weak acid) is expressed in terms of Ostwald's dilution law. An acid is substance which furnishes a proton or accepts an electron pair, where a base is proton acceptor or electron pair donor. Stronger is acid, weaker is its conjugate base. The dissociation constants of an acid (Ka) and its conjugate base (Kb) are related by Kw=Ka×Kb, where Kw is ionic product of water equal to 10−14at25∘C. The numerical value of Kw however increase with temperature. In a solution of an acid or base [H+][OH−]=10−14. Thus the [H+] in a solution is expressed as: [H+]=10−pH and pH+pOH=14. Buffer solution are the solutions which do not show appreciable change in the pH on addition of small amount of acid or base.
The protonation constant for NH3 from water is 6×105 . The deprotonation from NH+4 to H2O has rate constant 5.6×10−10. The rate constant for NH+4 and OH− reaction to give NH3 and H2O would be:
View SolutionThe dissociation of weak electrolyte (a weak base or weak acid) is expressed in terms of Ostwald's dilution law. An acid is substance which furnishes a proton or accepts an electron pair, where a base is proton acceptor or electron pair donor. Stronger is acid, weaker is its conjugate base. The dissociation constants of an acid (Ka) and its conjugate base (Kb) are related by Kw=Ka×Kb, where Kw is ionic product of water equal to 10−14at25∘C. The numerical value of Kw however increase with temperature. In a solution of an acid or base [H+][OH−]=10−14. Thus the [H+] in a solution is expressed as: [H+]=10−pH and pH+pOH=14. Buffer solution are the solutions which do not show appreciable change in the pH on addition of small amount of acid or base.
SO2 contents in the atmosphere is 10 ppm and the solubility of SO2 in water is 1.36 mol litre−1. If pKa of H2SO3 is 1.92, the pH of rainwater is:
View Solution
