A number N0 of atoms of a radio active element are placed inside a closed volume. The radioactive decay constant for the nucleus of this element is λ1. The daughter nucleus that form as a result of the decay process are assumed to be radioactive too with a radioactive decay constant λ2. Determine the time variation of the number of such nucleus. Consider two limiting cases λ1>>λ2 and λ1<<λ2.
The correct Answer is:[N0e−λ2t.λ1N0λ2(t−e−λ2t)]
Similar Questions
A radioactive substance A having N0 active nuclei at t=0, decays to another radioactive substance B with decay constant λ1. B further decays to a stable substance C with decay constant λ2. (a) Find the number of nuclei of A,B and C time t. (b) What should be the answer of part (a) if λ1>>λ2 and λ1<<λ2
View SolutionA radioactive substance A having N0 active nuclei at t=0, decays to another radioactive substance B with decay constant λ1. B further decays to a stable substance C with decay constant λ2. (a) Find the number of nuclei of A,B and C time t. (b) What should be the answer of part (a) if λ1>>λ2 and λ1<<λ2
View Solution
Knowledge Check
In the β decay of a radioactive nucleus
AThe atomic number is decreased by oneBa neutron is changed into a protonCa proton is changed into a neutronDthe mass number is unchangedIn the β decay of a radioactive nucleus
AThe atomic number is decreased by oneBa neutron is changed into a protonCa proton is changed into a neutronDthe mass number is unchangedThe graph between number of decayed atoms N' of a radioactive element and time t is.
A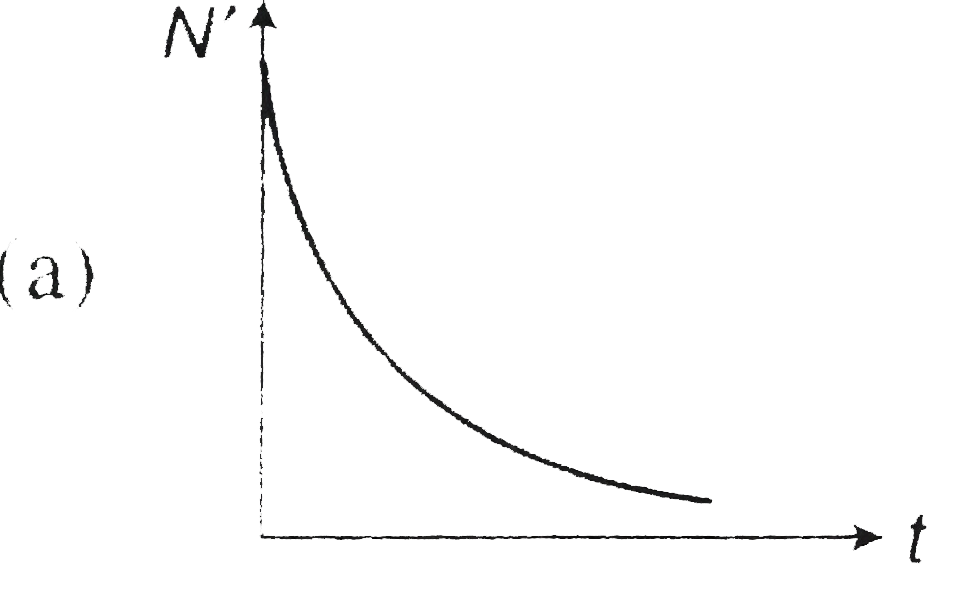 .B
.B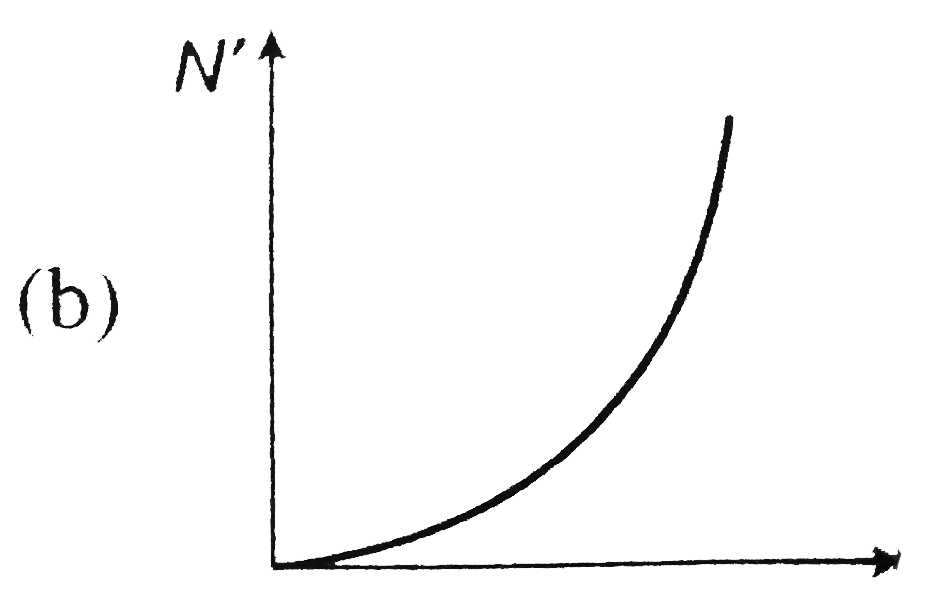 .C
.C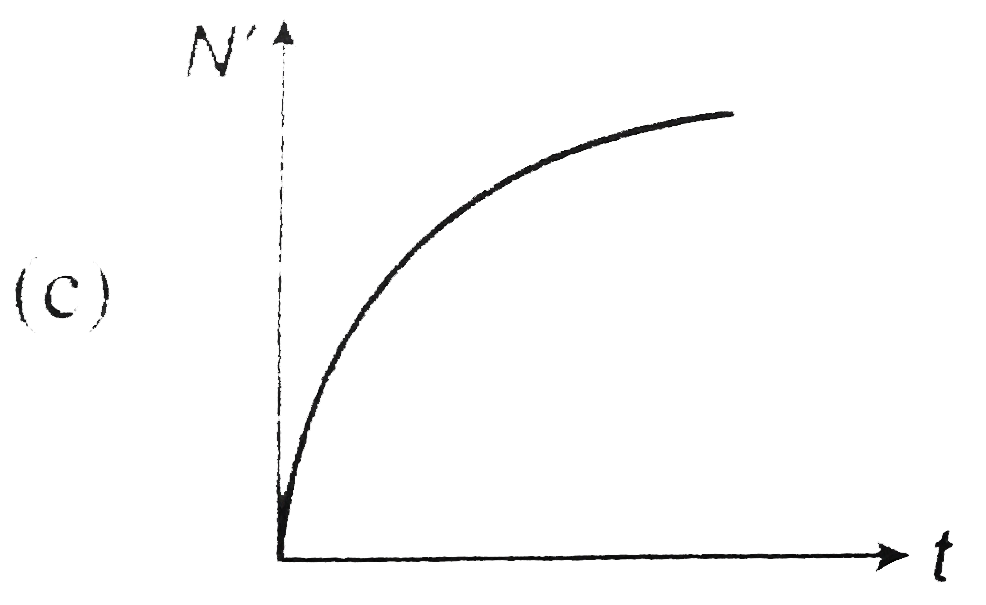 .D
.D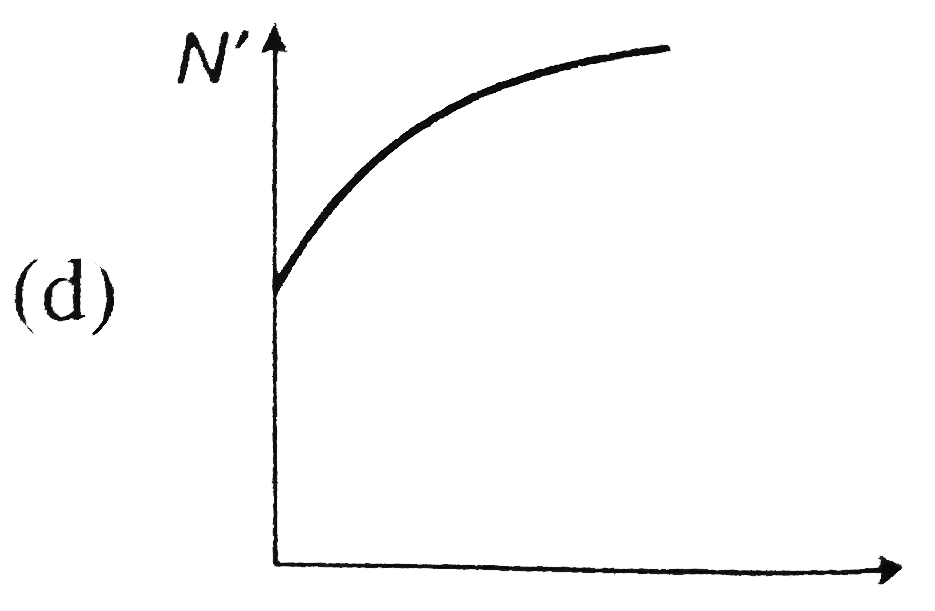 .
.
The decay constant (λ) for radioactive decay is independent of
View SolutionThe decay constant (λ) for radioactive decay is independent of
View SolutionThe decay constant λ of a radioactive sample:
View SolutionNuclei of a radioactive element A are being produced at a constant rate α. The element has a decay constant λ . At time t=0, there are N0 nuclei of the element . The number N of nuclei of A at time t is
View SolutionNuclei of a radioactive element A are being produced at a constant rate α. The element has a decay constant λ. At time t=0, there are N0 nuclei of the element.
(a) Calculate the number N of nuclei of A at time t.
(b) If α=2N0λ, calculate the number of nuclei of A after one half-life of A, and also the limiting value of N as t→∞.
View Solution

