An isolated rail car of mass M is moving alonga straight, frictionless track at an initial speed v0. The car is passing under a bridge when a crate filled with N bowling balls, each of mass m, is dropped from the bridge into the bed of the rail car. the crate splits open and the bowling balls bounce around inside the rail car, but none of them fall out.
(A). Is the momentum of the ratil car+bowling balls system conserved in this collision?
The correct Answer is:A, C
Topper's Solved these Questions
- IMPULSE AND MOMENTUMBook:ANURAG MISHRAChapter:IMPULSE AND MOMENTUMExercise:L-2
Explore 21 Videos
- IMPULSE AND MOMENTUMBook:ANURAG MISHRAChapter:IMPULSE AND MOMENTUMExercise:L-3,(P-1)
Explore 5 Videos
- IMPULSE AND MOMENTUMBook:ANURAG MISHRAChapter:IMPULSE AND MOMENTUMExercise:Example
Explore 50 Videos
- FORCE ANALYSISBook:ANURAG MISHRAChapter:FORCE ANALYSISExercise:Matching type
Explore 13 Videos
- RIGID BODY MOTIONBook:ANURAG MISHRAChapter:RIGID BODY MOTIONExercise:MATCH THE COLUMN
Explore 12 Videos
Similar Questions
A uniform chain of mass M and length L is held vertically in such a way that its lower end just touches the horizontal floor. The chain is released from rest in this position. Any portion that strikes the floor comes to rest. Assuming that the chain does not form a heap on the floor, calculate the force exerted by it on the floor when a length x has reached the floor.
View SolutionWhile dealing with collision between particles, you must have deal from and Inertial reference frame Often we choose that frame to be fixed in the Laboratary in which the collision is observed. So it is called the Laboratary reference frame or Lab frame From Lab frame we define an elastic collision as a collision in which KE before and after collision is conserved and a perfectly inelastic collision as a collision in which after collision the two colliding bodies have same velocity vector along the line of action of impulse during collision.
If we discusss the head-on collsion between two particles from center of mass reference frame, then the velocity of center of mass (CM) will be taken to be zero in any type of collision i.e. velocity of CM before and after collision will both be zero. Since before collsion velocity of CM was zero (as our frame is fixed to CM) and no external impulse acts, it will remain zero forever
From CM frame, after a head-on elastic collision:
View SolutionIn the figure shown the spring is compressed by 'x0' and released . Two block 'A' and 'B' of masses 'm' and '2m' respectively are attached at the ends of the spring. Blocks are kept on a smooth horizontal surface and released. Find the work done by the spring on 'A' by the time compression of the spring reduced to x02.

View SolutionA motorcycle moves around a vertical circle with a constants speed under the influence of the force of gravity →W, friction between wheel and track →f and normal reaction between wheel track →N :
Column-1Column-2(A)Constant magnitude(P)→N(B)Directed towards centre when value in non-zero(Q)→N+→f(C)Total reaction force by track(R)→f+→w(D)When motion is along vertical the value is zero(S)→N+→w+→f
View SolutionMatch the statements, situations in Column I with that in Column II. One or more matching is possible.
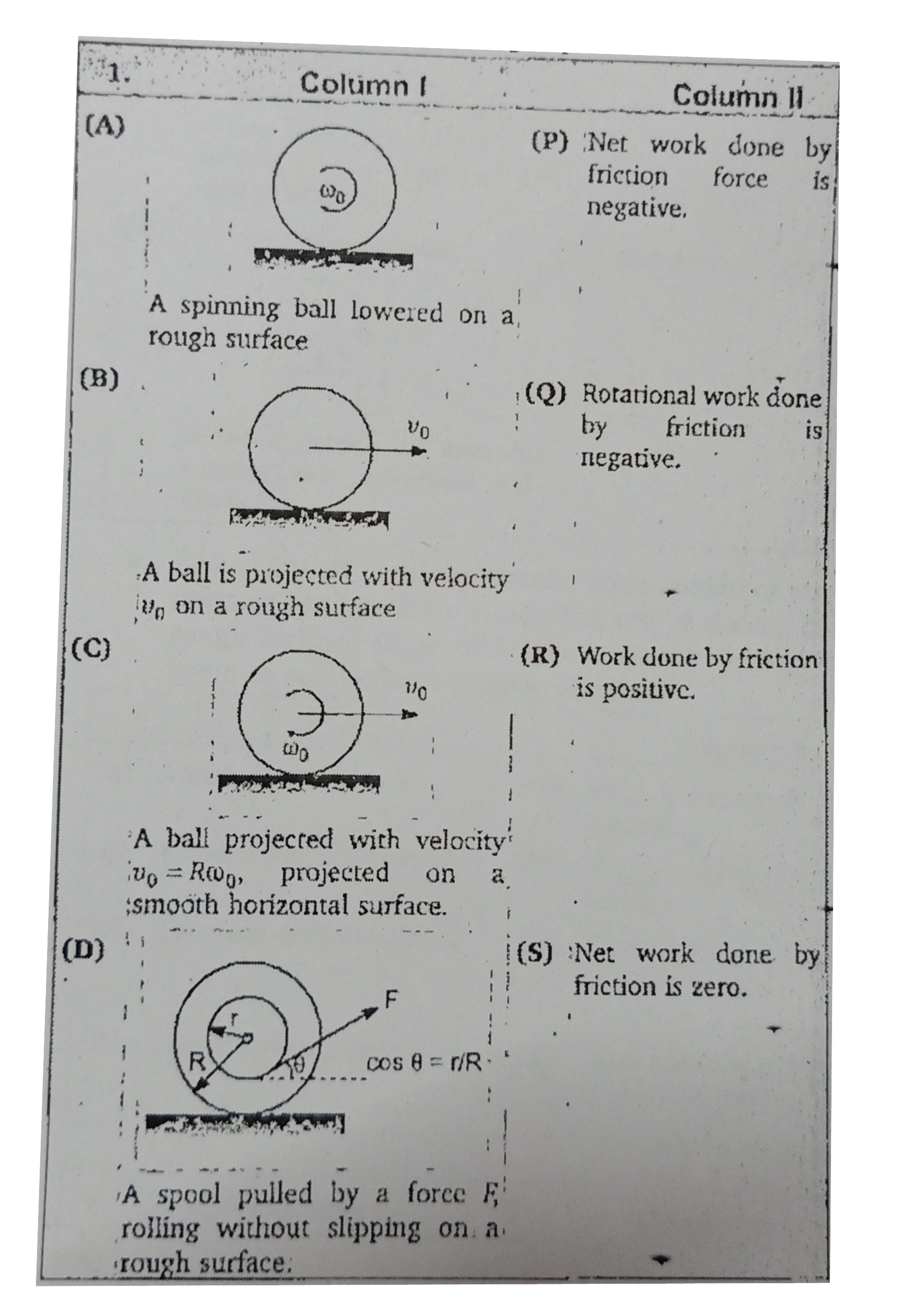
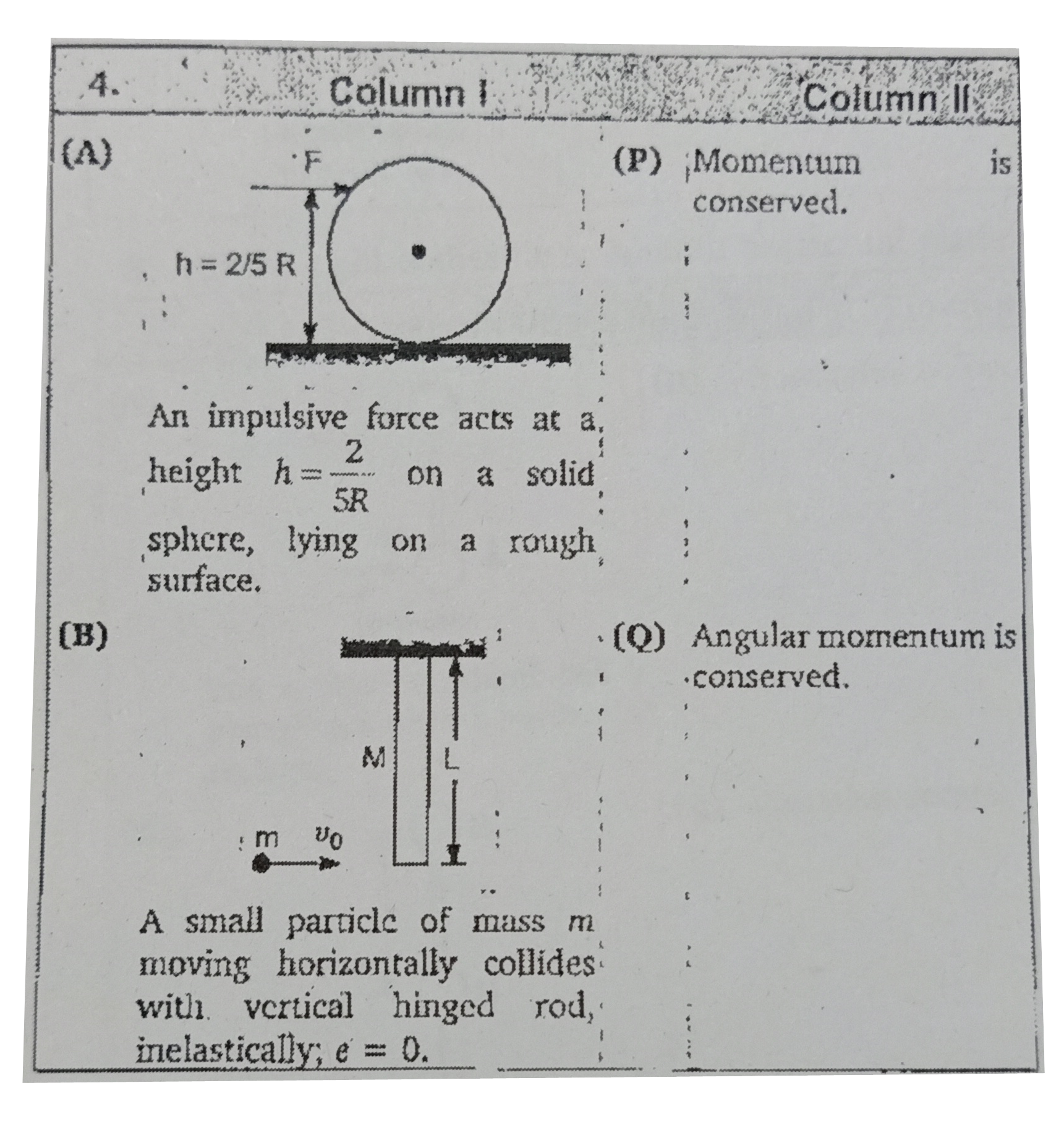
View SolutionA railroad car of mass M is at rest on frictionless rails when a man of mass m strts moving on the car towards the engine. If the car recoils with a speed v backward on the rails, with what velocity is the man aproaching the engine?
View SolutionA man of mass m is standing on a stationary flat car of mass M. The car can move without friction along horizontal rails. The man starts walking with velocity v relative to the car. Work done by him
View SolutionA man standing on a long rail road car throws a ball vertically upward with speed 20 m//s . The car starts from rest and moves with acceleration 2 m//s^(2) . How far behind the man will the ball fall on the car ?
View SolutionConsider a car moving on a horizontal road, convex bridge and concave bridge of same radius R. The speed of the car in each situation is same and equal to v, the mass of the car is m, then
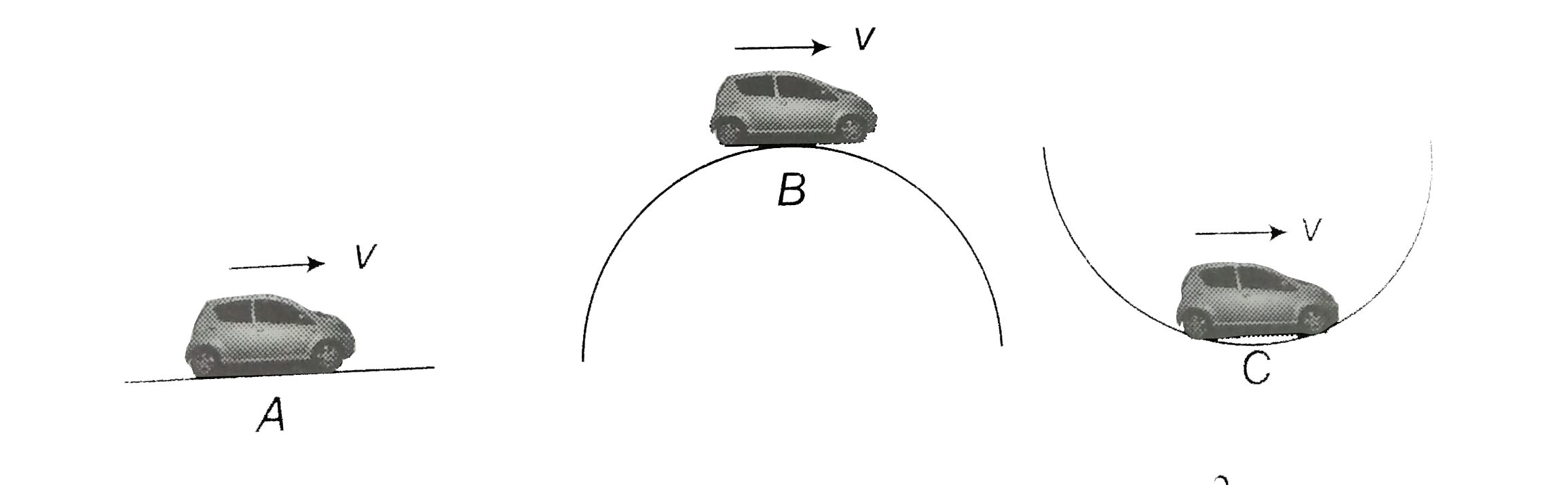



View SolutionA motor car of m travels with a uniform speed v on a convex bridge of radius r. When the car is at the middle point of the bridge, then the force exterted by the car on the bridge is
View SolutionA block of mass m sits at rest on a frictionless table in a rail car that is moving with speed v_(c) along a straight horizontal track (fig.) A person riding in the car pushes on the block with a net horizontal force F for a time t in the direction of the car's motion. What is the final speed of the block according to a person in the car ?
View SolutionAn isolated rail car of mass M is moving alonga straight, frictionless track at an initial speed v0. The car is passing under a bridge when a crate filled with N bowling balls, each of mass m, is dropped from the bridge into the bed of the rail car. the crate splits open and the bowling balls bounce around inside the rail car, but none of them fall out.
(B).What is the average speed of the rail car + bowling balls system some time after the collision?
View SolutionA car of mass =m=1000 kg is moving with constant speed v=100 m//s on a parabolic shaped bridge AFOE of span force applied by the bridge on the car when he car is at point E, is:
View SolutionM द्रव्यमान की एक लंबी रेल कार घर्षणरहित रेलपथ पर स्थिर खड़ी है। रेल कार में m द्रव्यमान का एक व्यक्ति इंजन की ओर चलना प्रारंभ करता है। इसके कारण रेल कार रेलपथ पर पीछे की ओर v चाल से चलने लगती है। व्यक्ति तथा इंजन के पास आने का वेग निकालें।
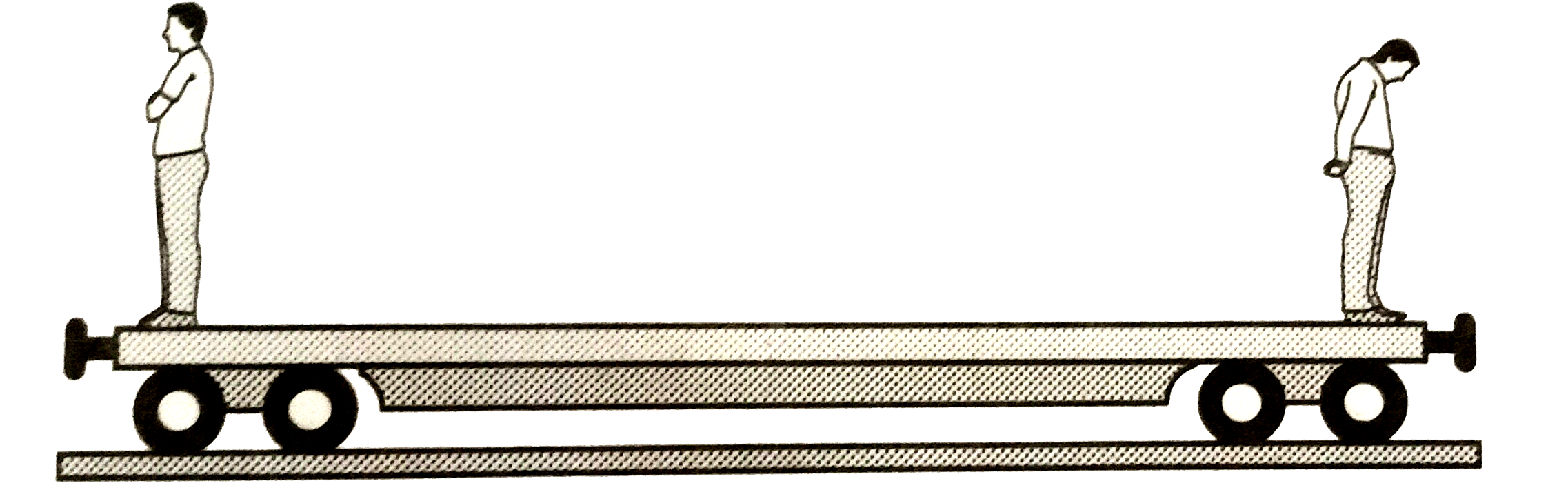
View Solutionएक चिकने रेलपथ पर स्थिर खड़ी हुई M द्रव्यमान की एक रेल कार के दोनों किनारों पर m द्रव्यमान के दो व्यक्ति खड़े हैं (चित्र 15.E)। बायीं ओर खड़ा व्यक्ति बायीं ओर, इस स्थिर रेल कार के सापेक्ष क्षैतिज चाल u से कूद जाता है। इस कारण कार दाहिनी ओर चलने लगती है। इसके पश्चात दूसरा व्यक्ति दाहिनी ओर, पुनः इस चलती रेल कार के सापेक्ष u चाल से कूद जाता है। दोनों व्यक्तियों के बाहर कूदने के पश्चात रेल कार का बेग ज्ञात करें।

View Solution

