An engine whistling at a constant frequency n0 and moving with a constant velocity goes past a stationery observer. As the engine crosses him, the frequency of the sound heard by him changes by a factor f. The actual difference in the frequencies of the sound heard by him before and after the engine crosses him is
12n0(1−f2)
12n0(1−f2f)
n0(1−f1+f)
12n0(1−f1+f)
The correct Answer is:B
Topper's Solved these Questions
- PRACTICE WORKSHEET 3BOOK - D MUKHERJEECHAPTER - PRACTICE WORKSHEET 3EXERCISE - Assertion- Reason Type
3 Videos
- PRACTICE WORKSHEET 3BOOK - D MUKHERJEECHAPTER - PRACTICE WORKSHEET 3EXERCISE - Linked- Comprehension Type
3 Videos
- PRACTICE WORKSHEET 2BOOK - D MUKHERJEECHAPTER - PRACTICE WORKSHEET 2EXERCISE - Linked- Comprehension Type
4 Videos
- PROPERTIES OF MATTER,FLUIDSBOOK - D MUKHERJEECHAPTER - PROPERTIES OF MATTER,FLUIDSEXERCISE - Type 2
35 Videos
Similar Questions
A train whistling at constant frequency is moving towards a station at a constant speed V. The train goes past a stationary observer on the station. The frequency n′ of the sound as heard by the observer is plotted as a function of time t, figure. Identify the expected curve.
View SolutionIf an observer is moving with uniform velocity v to wards a stationary source of frequency n, and if the velocity of sound in the medium is V, then the apparent change in the frequency of the sound, heard by the observer, is -
View Solution
Knowledge Check
A train whistling at constant frequency is moving towards a station at a constant speed v. The train goes past a stationary observer on the station. The frequency v of the sound as heard by the observer is plotted as a function of time t. Identify the expected curve.
A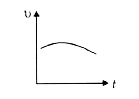 B
B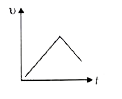 C
C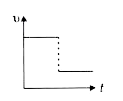 D
D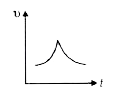
If a source of frequency n moving with velocity v crosses a stationary observer, then the change in the frequency of sound heard by the observer will be (velocity of sound = V)
A2nVvV2+v2B2nVv(V2−v2)C2nVv(V+v)D2nVv(V−v)A railway engine whistling at a constant frequency moves with a constant speed. It goes past a stationary observer standing beside the railway track. The frequency (n) of the sound heard by the observer is plotted agains time (t). Which of the following best represents the resulting curve?
A B
B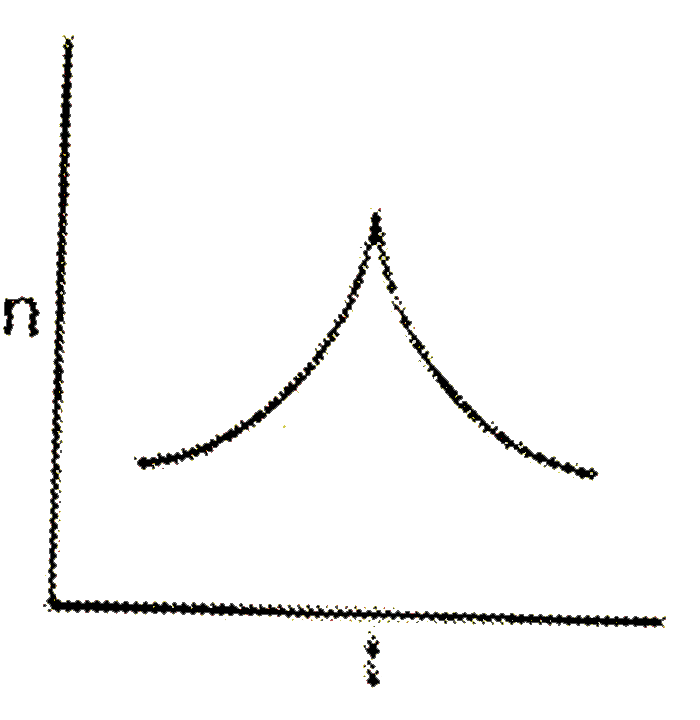 C
C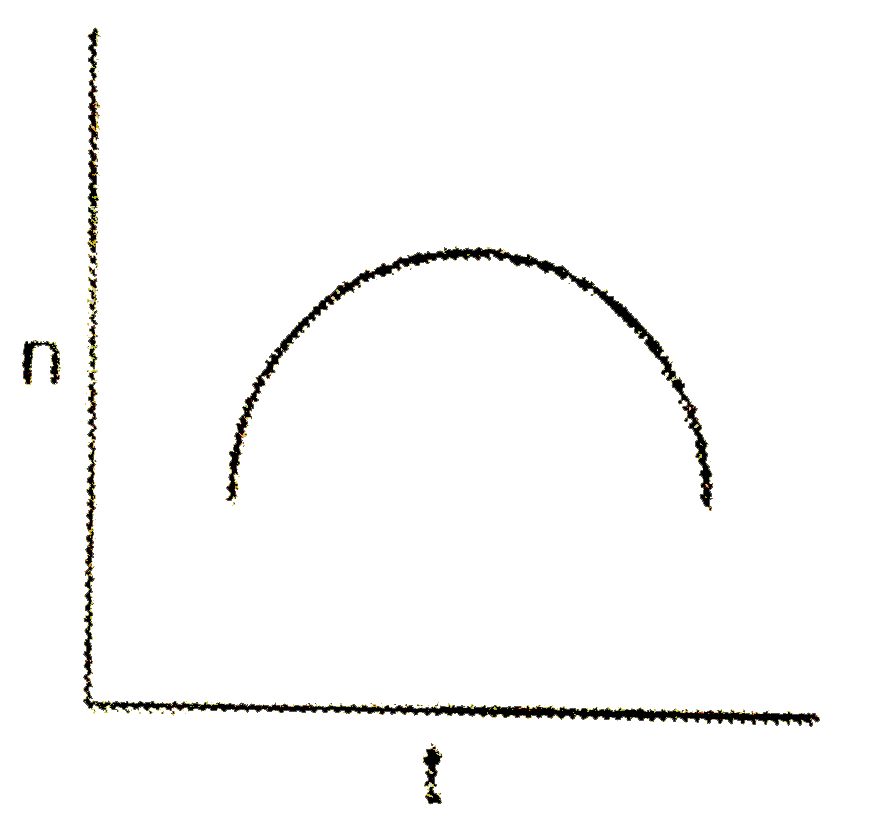 D
D
A source of sound crosses a stationary observer which is moving with uniform velocity v. If the velocity of sound in air is V, then the ratio of the apparent frequencies heard by the observer before and after the source crosses him would be -
View SolutionThe engine of a train sound a whistle at frequency v, the frequency heard by a passenger is
View SolutionIf a stationary observer notes a change of 25% in the frequency of a while of an engine coming towards him then the velocity of the engine is )(velocity of sound =332 m/s )
View SolutionA train is moving with a constant speed along a circular track. The engine of the train emits a sound of frequency f. The frequency heard by the guard at the rear end of the train.
View SolutionA sound source, emitting sound of constant frequency, moves with a constant speed and crosses a stationary observer. The frequency (n) of sound heard by the observer is plotted against time (t). Which of the following graphs represents the correct variation :-
View Solution

