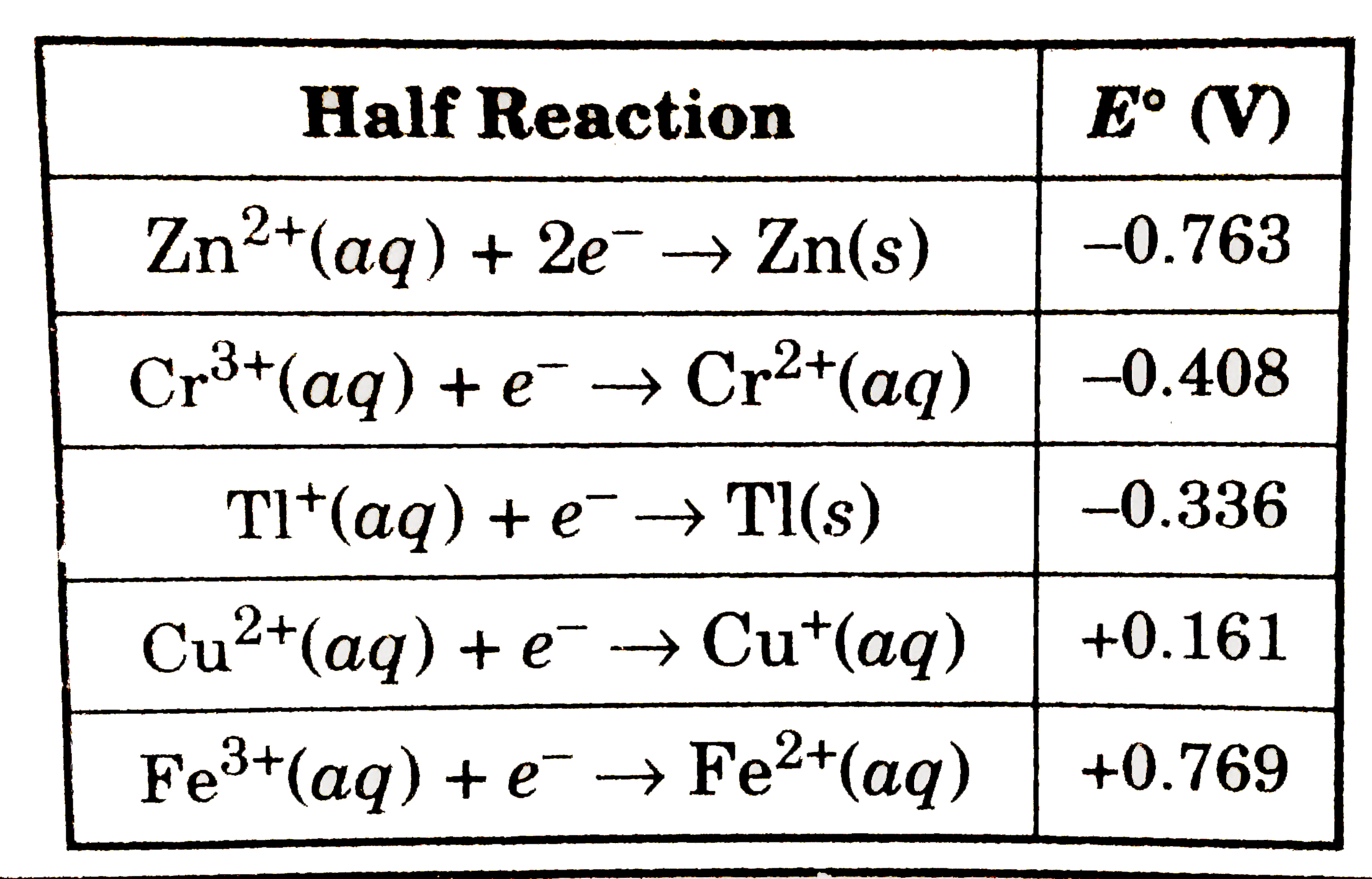
Based on the standard reduction potentials above, which reaction(s) is (are) spontaneous?
(P) Cr2+(aq)+Fe3+(aq)→Cr2+(aq)+Fe2+(aq)
(Q) Cu2+(aq)+Fe2+(aq)→Cu2+(aq)+Fe3+(aq)
P only
Q only
Both P and Q
Neither P nor Q
The correct Answer is:A
Step by step video, text & image solution for Based on the standard reduction potentials above, which reaction(s) is (are) spontaneous? (P) Cr^(2+)(aq)+Fe^(3+)(aq)rarrCr^(2+)(aq)+Fe^(2+)(aq) (Q) Cu^(2+)(aq)+Fe^(2+)(aq)rarrCu^(2+)(aq)+Fe^(3+)(aq) by Chemistry experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 12 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Similar Questions
Write balanced ionoic half equation (oxidation and reduction) for each of the following reactions:
(a) Mn3+(aq)→MnO2(s)+Mn2+(aq)
(b) Mn(s)+NOӨ3(aq)→Mn2+(aq)+NO2(g)
(c ) H2O2(aq)+Fe2+(aq)→Fe3+(aq)+H2O(l)
(d) Te(s)+NOӨ3(aq)→TeO2(s)+NO(g)
View SolutionCalculate the standard cell potentails of the galvanic cells in which the following reactions take place.
(a) 2Cr(s)+3Cd2+→2Cr3+(aq)+3Cd(s)
Given E∘Cr3+/Cr=−0.74 V,E∘Cd2+/Cd=−0.40 V
(b) Fe2+(aq)+Ag+(aq)→Fe3+(aq)+Ag(s)
Gievn E∘Ag+/Ag=0.80 V,E∘Fe3+/Fe2+=0.77 V
Also calculate ΔG∘ and equilibrium constant for the reaction.
View Solution
Knowledge Check
The standard reduction potentials at 298 K for the following half reactions are given against eath
Zn2+(aq)+2e−→Zn(s),−0.762V
Cr3+(aq)+3e−→Cr(s),−0.740v
2H+(Aq)+2e−→H2(g),0.00V
Fe3+(aq)+e−→Fe2+(aq),0.770V
Which is the strongest reducing agentAZn(s)BCs(s)CH2(g)DFe3+(aq)Fe2+(aq.)+Cr2O2−7+H+→Fe3+(aq.)+Cr3+
AFor disproportionation reaction.BFor comproportionation reaction.CFor either intermolecular redox reaction or displacement reactionDFor either thermal combination redox reaction or thermal decomposition redox reaction.
Calculate the standard cell potentials of galvanic cell in whiCHM the following reactions take place :
a.Cr(s)+3Cd2+(aq)→2Cr3+(aq)+3Cd
b.Fe2+(aq)+Ag⊕(aq)→Fe3+(aq)+Ag(s)
Calculate the ΔrGc− and equilibrium constant of the reactions .
View SolutionCalculate the standard cell potentials of galvanic cell in which the following reactions take place:
(i) 2Cr(s)+3Cd2+(aq)→2Cr3+(aq)+3Cd
(ii) Fe2+(aq)+Ag+(aq)→Fe3+(aq)+Ag(s)
Given: ECr3+,Cr=−0.74V,E∘Cd2+,Cd=−0.04V,EAg+,Ag=0.80V,E∘Fe3+,Fe2+=0.77V.
Calculate the ΔrG∘ and equilibrium constant of the reactions.
View SolutionComplete the following chemical reaction equations :
(i) MnO−4(aq)+C2O2−4(aq)+H+(aq)→
(ii) Cr2O2−7(aq)+Fe2+(aq)+H+(aq)→
View SolutionUsing the standard electrode potentials given in Table, predict if the reaction between the following is feasible:
a.Fe3+(aq) and Ic−(aq)
b. Ag⊕(aq) and Cu(s)
c. Fe3+(aq) and Brc−(aq)
d. Ag(s) and Fe3+(aq)
e.Br2(aq) and Fe2+(aq).
View SolutionUsing the standard electrode potentials given in Table, predict if the reaction between the following is feasible:
a.Fe3+(aq) and Ic−(aq)
b. Ag⊕(aq) and Cu(s)
c. Fe3+(aq) and Brc−(aq)
d. Ag(s) and Fe3+(aq)
e.Br2(aq) and Fe2+(aq).
View SolutionUsing the standard electrode potentials, predict if the reaction between the following is feasible :
(a) Fe3+(aq) and I−(aq), (b) Ag+(aq) and Cu(s)
(iii) Fe3+(aq) and Br− (aq), (d) Ag (s) and Fe3+ (aq)
( c) Br2(aq) and Fe2+ (aq).
Given standard electrode potentials:
E∘1/2,I2=0.541V,E∘Cu2+,Cu=0.34V
E∘1/2,Br2,Br−=1.09V,E∘Ag+/Ag=0.80V
E∘Fe3+,Fe2+=0.77V
View Solution

