A steel ball of mass m=50g falls from the height h=1.0m on the horizontal surface of a massive slab. Find the cumulative momentum that the ball imparts to the slab after numerous bounces, if every impact decreases the velocity of the ball η=1.25 times.
The correct Answer is:[m√2gh(1+η1−η)]
Step by step video, text & image solution for A steel ball of mass m=50g falls from the height h=1.0m on the horizontal surface of a massive slab. Find the cumulative momentum that the ball imparts to the slab after numerous bounces, if every impact decreases the velocity of the ball eta=1.25 times. by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 11 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
In which o the following cases the centre of mass of a rod is certainly not at its centre?
View SolutionA steel ball is dropped on a hard surface from a height of 1m and rebounds to a height of 64cm . The maximum height attained by the ball after n^(th) bounce is (in m)
View SolutionA steel ball of mass m=50g falls from the height h=1.0m on the horizontal surface of a massive slab. Find the cumulative momentum that the ball imparts to the slab after numerous bounces, if every impact decreases the velocity of the ball η=1.25 times.
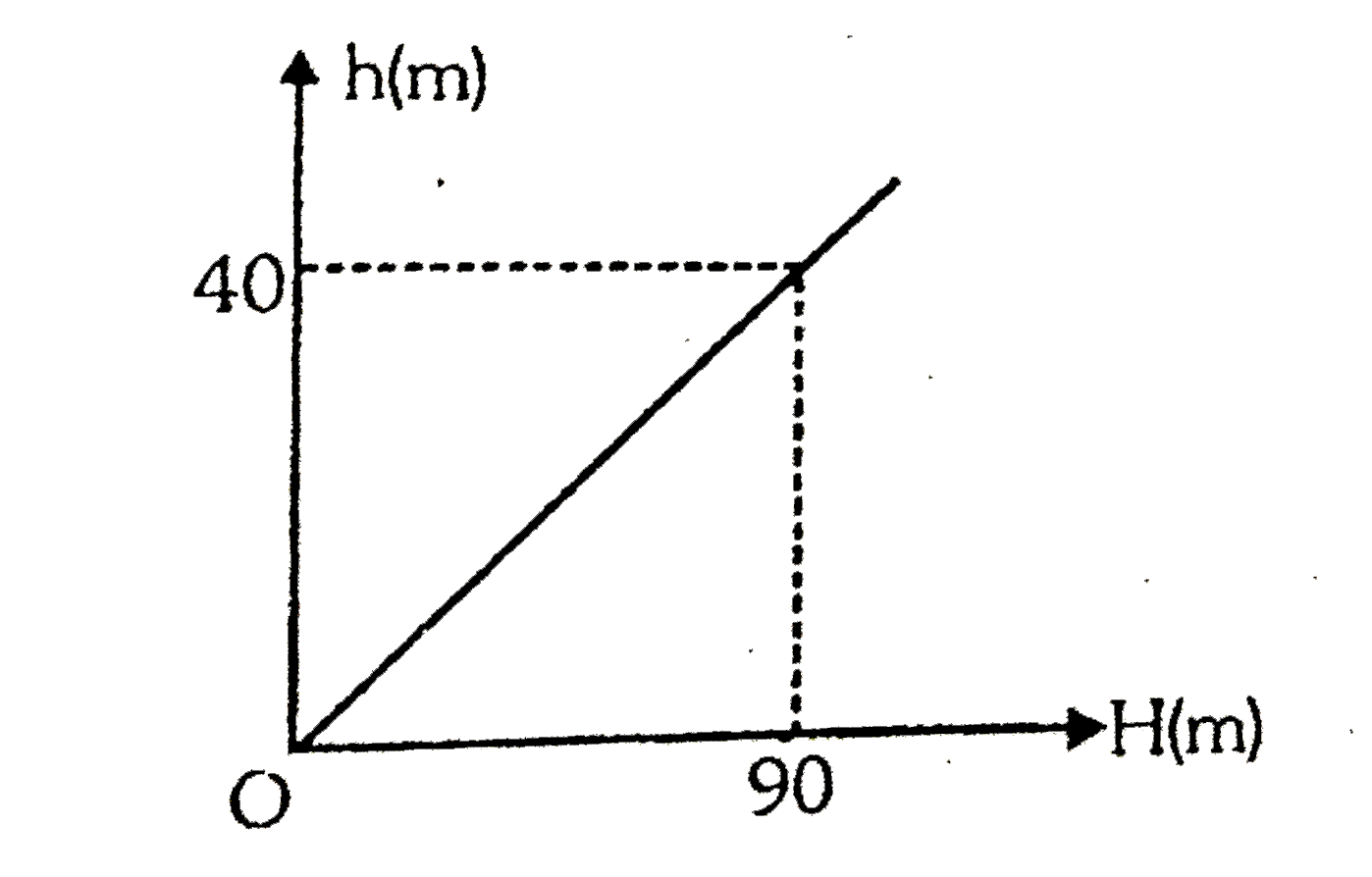
View SolutionA ball of mass 2kg dropped from a height H above a horizontal surface rebounds to a height h after one bounce. The graph that relates H to h is shown in figure. If the ball was dropped from an initial height of 81 m and made ten bounces, the kinetic energy of the ball immediately after the second impact with the surface was
View SolutionA tennis ball is lying on a rigid floor. A steel ball is dropped on it from some height. The steel ball bounces vertically after hitting the ball on the floor. It possible that the tennis ball with also bounce ?
View SolutionA metal ball falls from a height of 32 metre on a steel plate. If the coefficient of restitution is 0.5, to what height will the ball rise after second bounce
View SolutionA steel ball of mass w=50gm falls from height h=1 m on the horizontal surface of a massive slab. Find the cumulative momentum imparted to the slab by the ball after numerous bounces, if the coefficient of restitution between the ball and the slab is e = 0.8.
View Solutionएक गेंद h ऊँचाई से पृथ्वी तल पर अभिलंबवत टकराती है। यदि संघट्ट का प्रत्वस्थान गुणक e हो तो संघट्ट के बाद गेंद किस ऊँचाई तक ऊपर उठेगी ?
View SolutionA steel ball of mass 0.5 kg is dropped from a height of 4 m on to a horizontal heavy steel slab. The collision is elastic and the ball rebounds to its original height. Calculate the impulse delivered to the ball during impact.
View SolutionA steel ball of mass 0.5 kg is dropped from a height of 4 m on to a horizontal heavy steel slab. The collision is elastic and the ball rebounds to its original height. If the ball is in contact with the slab for 0.002 s, find the average reaction force on the ball during impact.
View SolutionA bouncing ball of mass 200 g falls from the height of 5m on a horizontal ground. After every impact with the ground, the velocity of the ball decreases by (1)/(2) times. The total momentum the ball imparts on to the ground after 3 impacts is (Let g=10m//s^(2) )
View SolutionA ball falls vertically with a momentum 'p' and then bounces for large number of times before coming to rest. The total momentum imparted by ball to floor is (e = coff. of restitution):
View SolutionM द्रव्यमान की एक गेंद h ऊँचाई से फर्श पर गिरती है जिसका प्रत्यावस्थान गुणांक है। दो उछाल के बाद गेंद के द्वारा हासिल की गई ऊँचाई होती है
View SolutionWhen a steel ball of 0.1 mass falls from a height of 10 m, it collides with the earth and bounces up to 5.4 m. If the energy released in this process is absorbed by the ball, how much will the temperature of the ball increase?
View Solutionएक गेंद को 10 m ऊँचाई से गिराया जाता है। यदि भूमि तल से टकराने के बाद गेंद की ऊर्जा 40% कम हो जाती है, तो गेंद वापस कितनी ऊँचाई तक उछलेगी?
View SolutionA ball is dropped on a plane horizontal surface from height H. The ball bounces and reaches height h. Show that cofficient of restitution is e = sqrtfrac(h)(H)
View Solution
