A rod of mass m and length 2R can rotate about an axis passing through O invertical plane.A disc of mass m and radius R/2 is hinged to the other end P ofthe rod and can freely rotate about P. When disc is at lowest point both rod and disc has angular velocity ω. If rod rotates by maximum angleθ=60∘ with downward vertical, then ω interms of R and g will be(all hinges are smooth)
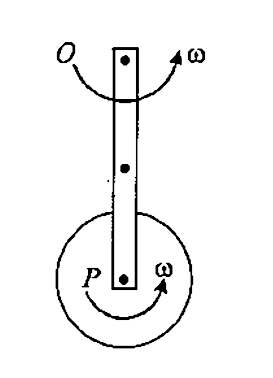
√9g16R
√3g23R
13√gR
None of these
The correct Answer is:A
Step by step video, text & image solution for A rod of mass m and length 2R can rotate about an axis passing through O invertical plane.A disc of mass m and radius R//2 is hinged to the other end P ofthe rod and can freely rotate about P. When disc is at lowest point both rod and disc has angular velocity omega. If rod rotates by maximum angletheta=60^(@) with downward vertical, then omega interms of R and g will be(all hinges are smooth) by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 11 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Similar Questions
A rod of mass m and length L is pivoted at the bottommost point O and can freely rotate about the point O. The rod is disturbed from the vertical position so that it starts rotating about O. When it makes an angle θ with the vertical
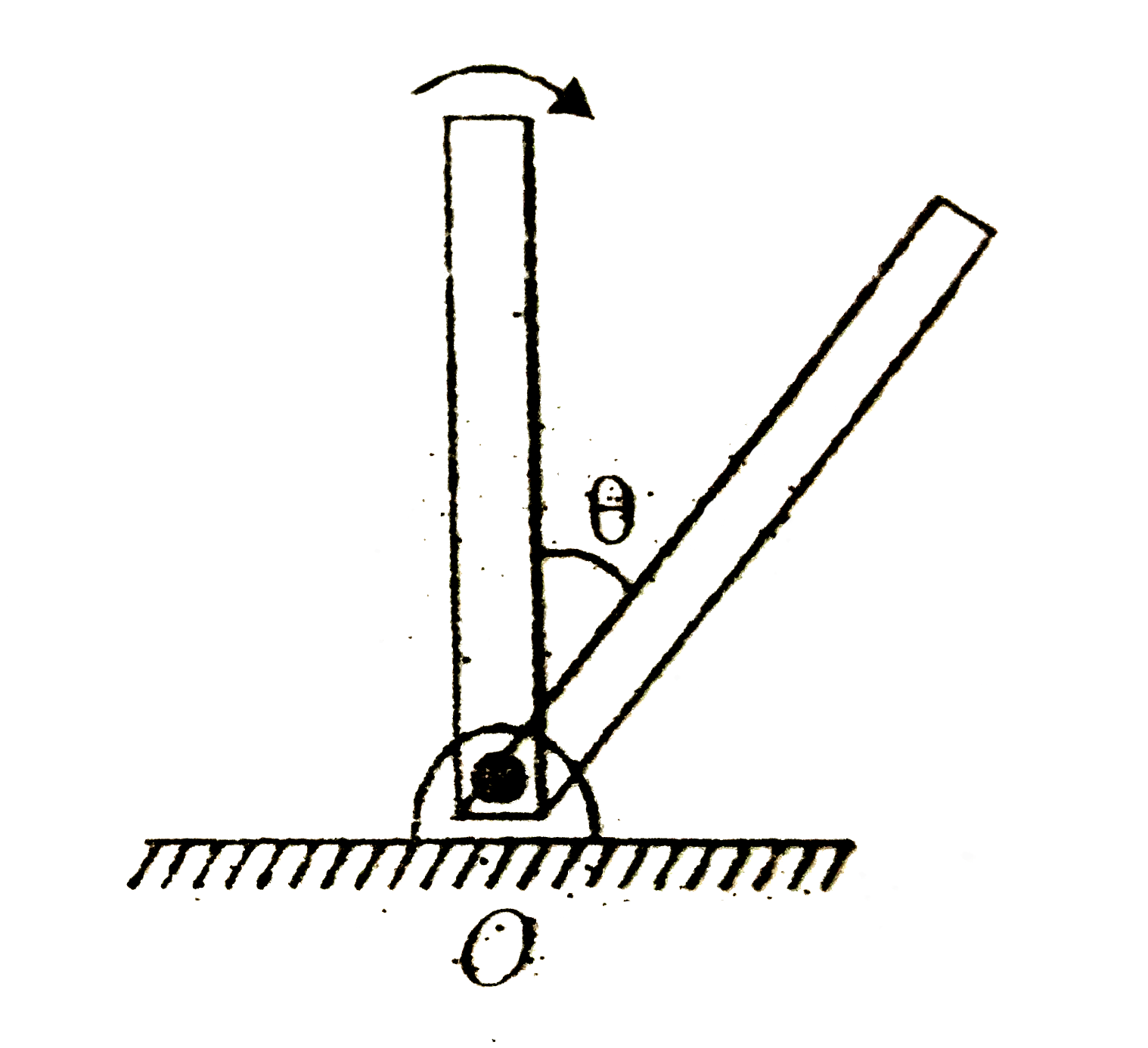
View Solution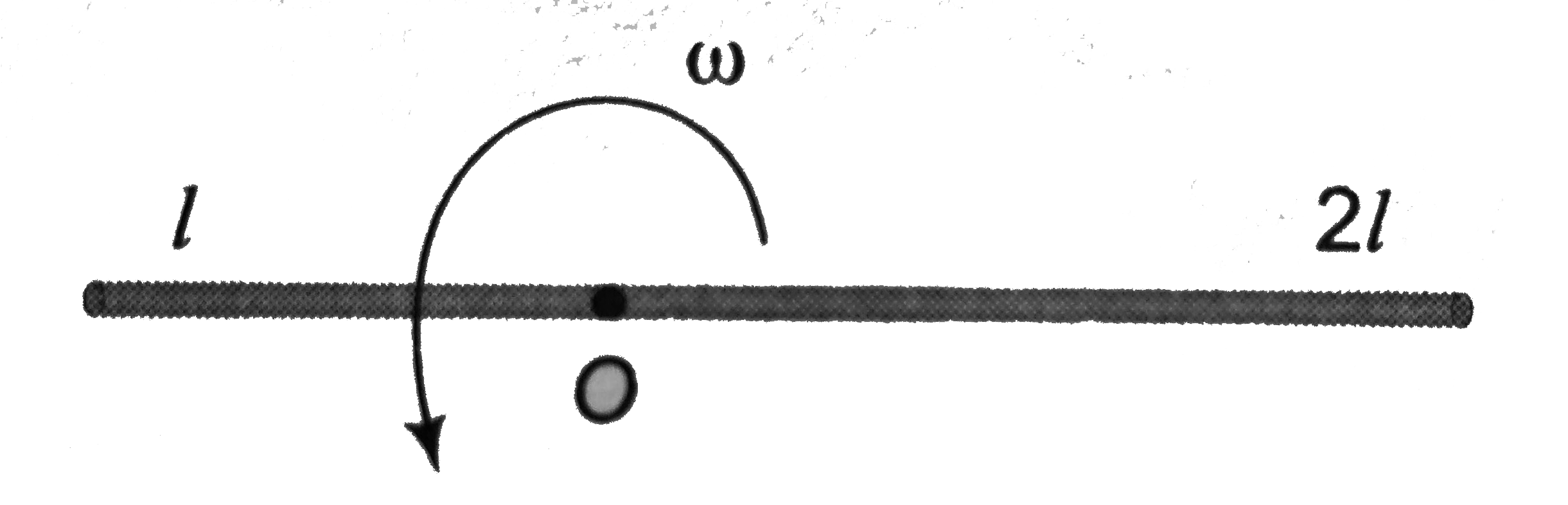
A uniform rod of mass m is rotated about an axis passing through point O as shown. Find angular momentum of the rod about rotational law.
View Solution
Knowledge Check
A thin rod of mass m and length 2L is made to rotate about an axis passing through its center and perpendicular to it. If its angular velocity changes from O to ω in time t, the torque acting on it is
AmL2ω12tBmL2ω3tCmL2ωtD4mL2ω6tA rod is rotating with angular velocity ω about axis AB. Find cosθ.
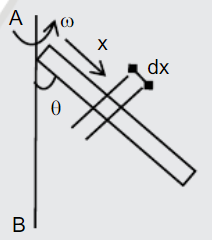 Ag2lω2Bglω2C2g(lω)2D3g2lω2
Ag2lω2Bglω2C2g(lω)2D3g2lω2A thin uniform rod of mass 'M' and ength 'L' is rotating about a perpendicular axis passing through its centre with a constant angular velocity 'ω'. Two objects each of mass M3 are attached gently to the two ends of the rod. The rod will now rotate with an angular velocity of
A13ωB17ωC16ωD12ω
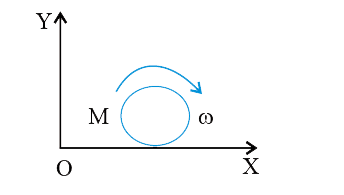
A disc of mass M and radius R is rolling with angular speed w on horizontal plane as shown. The magnitude of angular momentum of the disc about the origin O is :
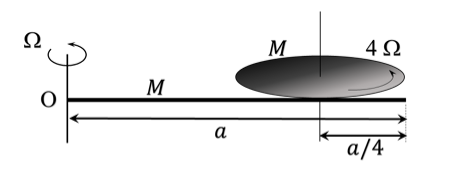
View SolutionA thin rod of mass M and length a is free to rotate in horizontal plane about a fixed vertical axis passing through point O. A thin circular disc of mass M and of radius a/4 is pivoted on this rod with its center at a distance a/4 from the free end so that it can rotate freely about its vertical axis. Assume that both rod and disc have uniform density and they remain horizontal during motion. An outside stationary observer finds the rod rotating with an angular velocity Ω and the disc rotating about its vertical axis with angular velocity 4Ω. Total angular momentum of system about point O is (Ma2Ω48)n. The value of n is
View SolutionA rod of mass 12 m and length l lying on a smooth horizontal plane can rotate freely about a stationary, vertical axis passing through the rod's end. A particle of mass m moving along the plane with speed v0 hits the rod's end perpendicularly and gets stuck there. Find the angular velocity of the system.

View SolutionA uniform rod of mass m and length l rotates in a horizontal plane with an angular velocity ω about a vertical axis passing through one end. The tension in the rod at a distance x from the axis is
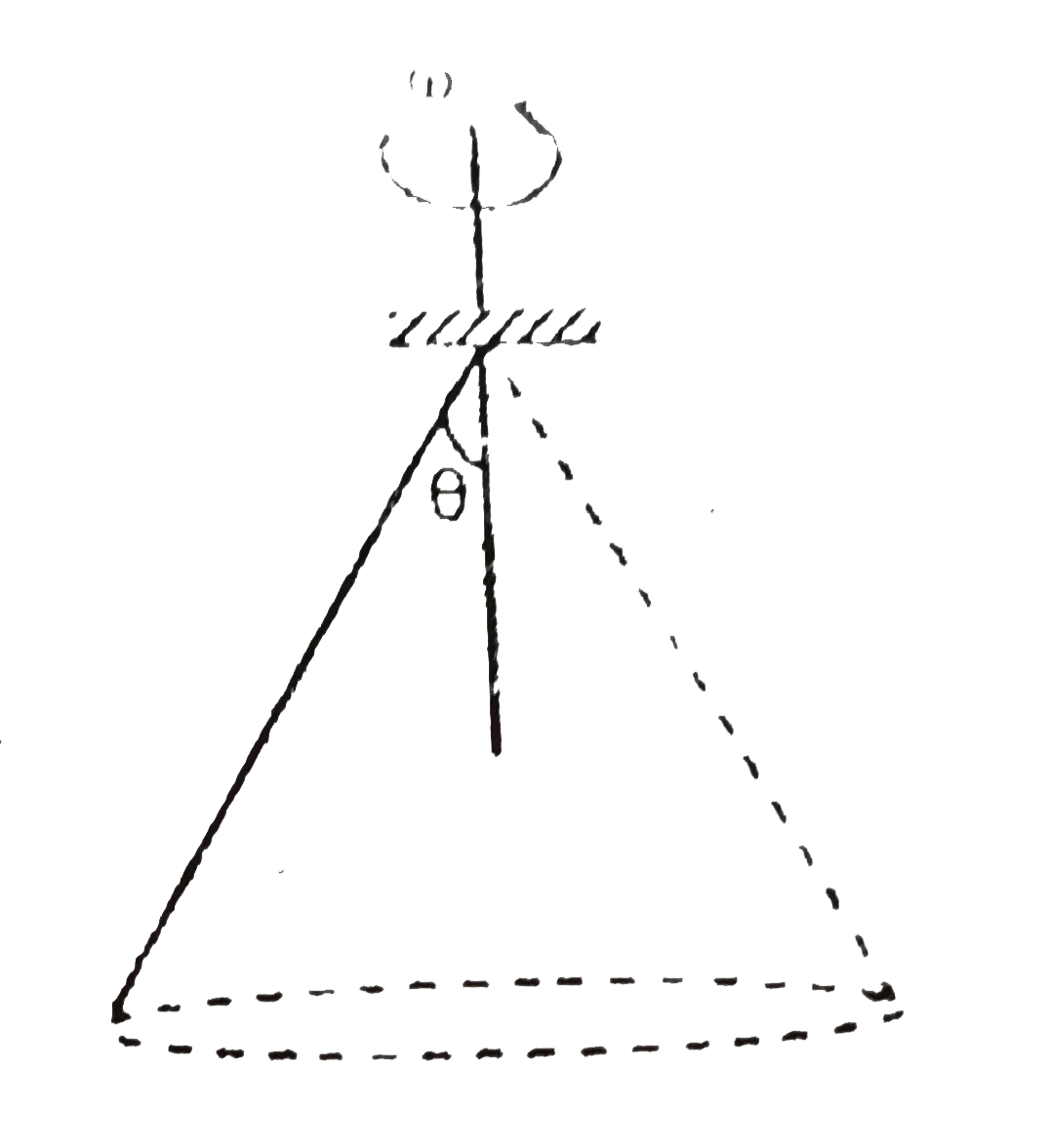
View SolutionA rod of mass m and length l is rotating about a fixed point in the ceiling with an angular velocity ω as shown in the figure. The rod maintains a constant angle θ with the vertical.
What is the rate of change of angular momentum of the rod ?
View Solution

