 ltBrgt A block is attached to the end of a linear spring, the other end of which is anchored to a wall. The block is oscillating between extreme positions X and Y on a frictionless table, and when the block is at Point O, the spring is at its natural length. the value of the spring's force constant, k, is known, but the mass of the block, m, is unknown
ltBrgt A block is attached to the end of a linear spring, the other end of which is anchored to a wall. The block is oscillating between extreme positions X and Y on a frictionless table, and when the block is at Point O, the spring is at its natural length. the value of the spring's force constant, k, is known, but the mass of the block, m, is unknown
Q. If ω=√km, and the distance between O and Y is d, what is the speed of the block at point O?
dω2
dω
2dω
d2ω
The correct Answer is:B
When the block is at point Y, all its energy is due to the potential energy of the stretched spring, which is 12kd2. At the moment the block passes through the equilibrium position, O, this energy has been converted entirely to kinetic. By setting 12mv2 equal to 12kd2, we find that
12mv2=12kd2⇒v=d√k/m=dω.
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
A person standing on a horizontal floor feels two forces : the downward pull of gravity and the upward supporting force from the floor. These two forces
View SolutionA block of mass m slides with constant speed down a ramp whose incline angle is θ. If F1 is the magnitude of the gravitational force acting parallel to the ramp and F2 is the magnitude of the normal force acting on the block, what is the value of F1/F2?
View SolutionA block of mass m is attached to one end of a mass less spring of spring constant k. the other end of spring is fixed to a wall the block can move on a horizontal rough surface. The coefficient of friction between the block and the surface is mu then the compession of the spring for which maximum extension of the spring becomes half of maximum compression is .
View SolutionIn the figure shown, a spring of spring constant K is fixed at on end and the other end is attached to the mass 'm' . The coefficient of friction between block and the inclined plane is mu . The block is released when the spring is in tis natural length. Assuming that the theta gt mu , the maximum speed of the block during the motion is.
View SolutionA block of mass 'm' is attached to a spring in natural length of spring constant 'k'. The other end A of the spring is moved with a constat velocity v away from the block . Find the maximum extension in the spring.
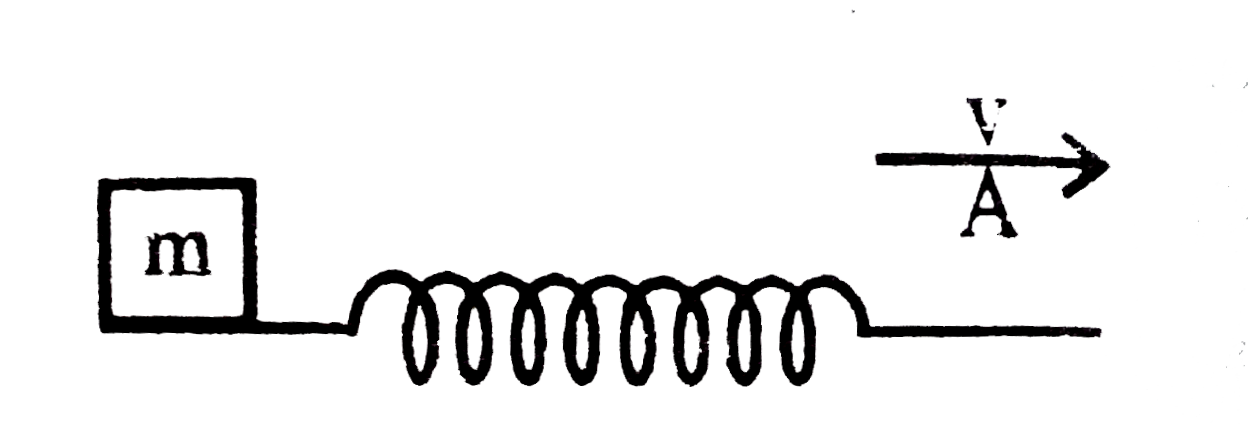
View SolutionA block of mass m is attached to a spring of force constant k whose other end is fixed to a horizontal surface. Initially the spring is in its natural length and the block is released from rest. The average force acting on the surface by the spring till the instant when the block has zero acceleration for the first time is
View SolutionA block Q of mass 2m is placed on a horizontal frictionless plane. A second block of mass m is placed on it and is connected to a spring of spring constant K, the two block are pulled by distance A. Block Q oscillates without slipping. The work done by the friction force on block Q when the spring regains its natural length is:
View SolutionA block of mass m, attacted to a string of spring constant k, oscillates on a smooth horizontal table. The other end of the spring is fixed to a wall. The block has a speed v when the spring is at its natural length. Before coming to an instantaneous rest. If the block moves a distance x from the mean position, then
View SolutionA block of mass m, lying on a smooth horizontal surface, is attached to a spring (of negligible mass) of spring constant k. The other end of the spring is fixed, as shown in the figure. The block is initally at rest in its equilibrium position. If now the block is pulled withe a constant force F, the maximum speed of the block is :

View SolutionA block of mass m, lying on a smooth horizontal surface, is attached to a spring (of negligible mass) of spring constant k. The other end of the spring is fixed, as shown in the figure. The block is initally at rest in its equilibrium position. If now the block is pulled withe a constant force F, the maximum speed of the block is :
View Solutionm द्रव्यमान के एक गुटके से एक स्प्रिंग को दबाकर रखा जाता हैं । इस स्प्रिंग का स्प्रिंग स्थिरांक k हैं तथा स्प्रिंग का दूसरा सिरा दीवार में बँधा हैं । गुटका घर्षणरहित टेबुल पर फिसल सकता हैं । स्प्रिंग की स्वाभाविक लंबाई l0 हैं तथा उसे स्वाभाविक लंबाई के आधे तक दबाकर छोड़ा जाता हैं । दीवार से गुटके की दूरी के फलन के रुप में वेग का व्यंजक निकालें ।
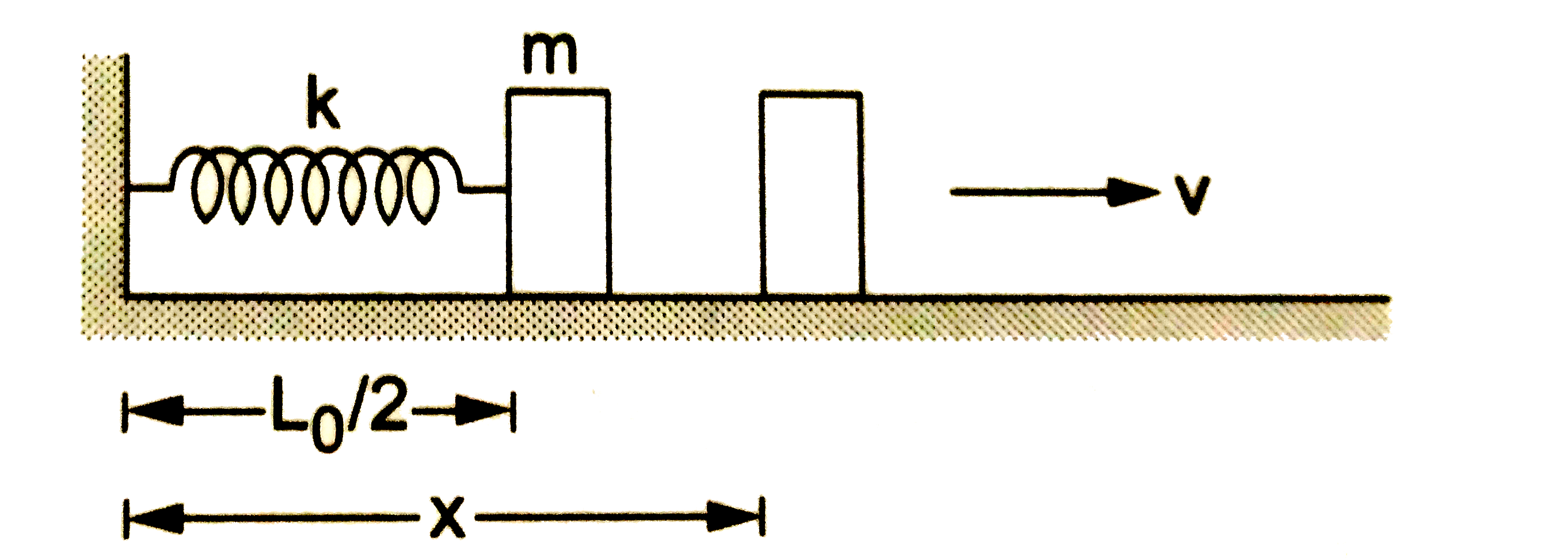
View Solutionएक चिकनी क्षैतिज सतह वाली टेबुल पर एक ब्लॉक एक स्प्रिंग से बाँधकर आगे - पीछे दोलन करता हैं । स्प्रिंग का दूसरा किनारा टेबुल के एक बिंदु पर बाँधकर रखा गया हैं । स्प्रिंग का स्प्रिंग - नियतांक k हैं । जिस समय स्प्रिंग अपनी स्वाभाविक लंबाई में होता हैं , ब्लॉक की चाल v हैं । ब्लॉक टेबुल पर रुकने के पहले इस स्थिति से अधिकतम कितनी दूरी तक चलेगा ?
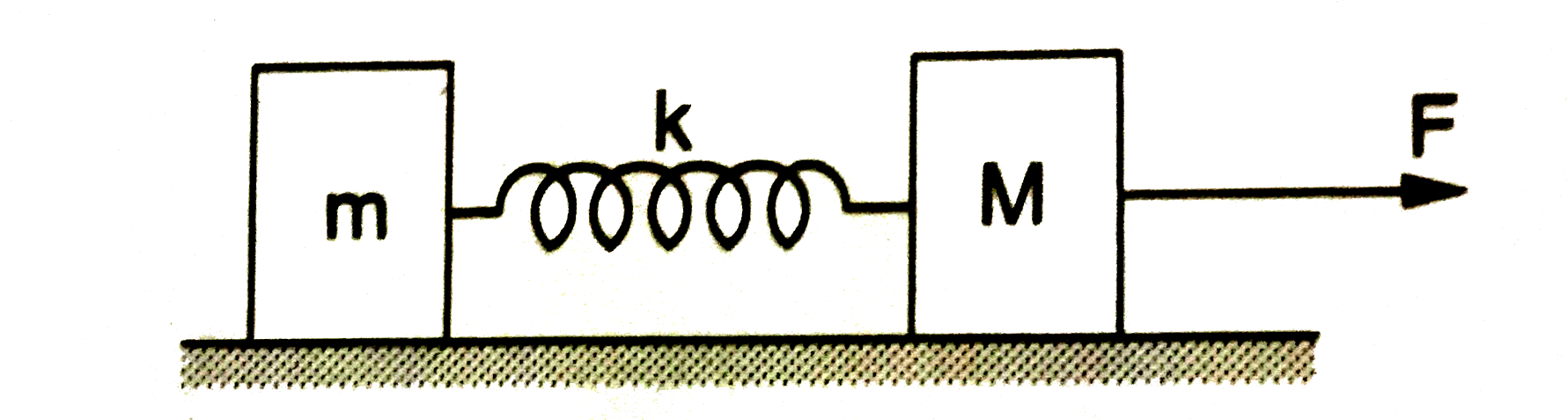
View Solutionचित्र में दो गुटके दिखाए गए हैं जिनके द्रव्यमान m तथा M है। ये गुटके एक घर्षणरहित क्षैतिज सतह पर रखे हैं तथा k स्प्रिंग नियतांक वाले एक स्प्रिंग से जुड़े हैं। प्रारंभ में स्प्रिंग अपनी स्वाभाविक लंबाई में है तथा गुटके स्थिर हैं। अब एक अचर बल F, द्रव्यमान M वाले गुटके पर लगना प्रारंभ करता है। स्प्रिंग की लंबाई में अधिकतम वृद्धि निकालें।
View Solutionस्प्रिंग नियतांक K की स्प्रिंग से जुड़ा द्रव्यमान m का एक गुटका चिकनी क्षैतिज मेज पर दोलन कर रहा हैं | स्प्रिंग का दूसरा सिरा दीवार से जुड़ा हैं | स्प्रिंग की सामान्य लम्बाई पर गुटके की चाल v हैं | विराम में आने से पूर्व यदि गुटका साम्य स्थिति से दूरी x तक चलता हैं, तो :
View SolutionA block Q of mass 2m is placed on a horizontal frictionless plane. A second block of mass m is placed on it and is connected to a spring of spring constant K, the two block are pulled by distance A. Block Q oscillates without slipping. The work done by the friction force on block Q when the spring regains its natural length is
View SolutionA block of mass m, lying on a smooth horizontal surface, is attached to a spring (of negligible mass) of spring constant k. The other end of the spring is fixed, as shown in the figure. The block is initally at rest in its equilibrium position. If now the block is pulled withe a constant force F, the maximum speed of the block is :

View Solution

