A block of mass m is at rest on a frictionless, horizontal table placed in a laboratory on the surface of Earth. An identical block is at rest on a frictionless, horizontal table placed on the surface of the moon. Let F be the net force necessary to give the earthbound block an acceleration of a across the table. Given that gmoon is one sixth of gEarth, the force necessary to give the moon-bound block the same acceleration a across the table is
F12
F6
F3
F
The correct Answer is:D
The horizontal motion across the frictionless tables is unafflected by (vertical) gravitational acceleration. It would take as much force to accelerate the block across the table on Earth as it would on the moon. (If friction were taken into account, then the smaller weight of the block on the moon would imply a smaller normal force by the table and hence a smaller frictional force. Less force would be needed on the moon in this case).
Similar Questions
A block of mass M placed on a frictionless horizontal table is pulled by another block of mass m hanging vertically by a massless string passing over a frictionless pulley. The tension in the string is :
View SolutionA block of mass 2 kg placed on a long frictionless horizontal table is pulled horizontally by a constant foerce F. It is found to move 10 m in the first two seconds. Find the magnitude of F.
View SolutionA block of mass 1 kg is placed on a horizontal surface . The reaction force to the weight of the block is
View SolutionA block of mass 3kg is at rest on a rough inclined plan as shown in the Figure. The magnitude of net force exerted by the surface on the block will be

View SolutionA wooden block of mass m resting on a rough horizontal table is pulled by a force F as shown in the figure. If μ is the coefficient of friction between block and table, its acceleration will be
View SolutionA block of mass m is placed at rest on a smooth wedge of mass M placed at rest on a smooth horizontal surface. As the system is released

View SolutionA block of mass m is kept on a horizontal table. If the static friction coefficient is μ., find the frictional force acting on the block.
View SolutionA wooden block of mass M resting on a rough horizontal surface is pulled with a force T at an angle q to the horizontal. If m is coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface, the acceleration of the block is
View SolutionA block of mass m1 rests on a horizontal table. A string tied to the block is passed on a frictionless pulley fixed at the end of the table and to the other end of string is hung another block of mass m2. The acceleration of the system is
View SolutionBlocks are in contact on a frictionless table. A horizontal force F=3N is applied to one block as shown. The force exerted by the smaller block m2 on block m1 is :
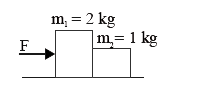
View Solution

