In a double acting steam engine, the average pressure in 90Ncm−2, the area of the piston is 7.46cm2, the length of the strokes is 1 meter and the number of revolution per second is 5. find the horse power of the engine.
The correct Answer is:9 h.p.
Similar Questions
In A double -acting steam engine, the avearge pressure of steam is 8×104Nm−2. The length of the stroke is 0.8 m and area of cross-section of the piston is 0.18m2. If the piston makes 6 revolution per second, calculate the horse power of the engine.
View SolutionIn a reciprocating steam engine, the avearge pressure of steam is 50Nm−2. The length of half stroke is 50 cm and area of cross section of the piston is 400cm2. If the engine is making 300 strokes per minute, calculate power of the engine in k W.
View Solution
Knowledge Check
Two elastic waves move along the same direction in the same medium. The pressure amplitudes of both the waves are equal, but the wavelength of the first wave is three times that of the second. If the average power transmitted through unit area by the first wave is W1 and that by the second is W2, then
AW1=W2BW1=3W2CW2=3W1DW1=9W2A monochromatic beam of light (λ=4900A) incident normally upon a surface produces a pressure of 5×10−7Nm−2 on it. Assume that 25% of the light incident in reflected and the rest absorbed. Find the number of photons falling per second on a unit area of thin surface
A1×1023B2×1024C3×1020DNone of the aboveTo move an airplane through the air, thrust is generated by some kind of propulsion system. Beginning with the Wright brothers' first flight, many airplanes have used internal combustion engines to turn propellers to generate thrust. Today, most general aviation or private airplanes are powered by internal combustion (IC) engines, much like the engine in your family automobile. When discussing engines, we must consider both the mechanical- operation of the machine and the thermodynamic processes that enable the machine to produce useful work. We consider the thermodynamics of a four-stroke IC engine.
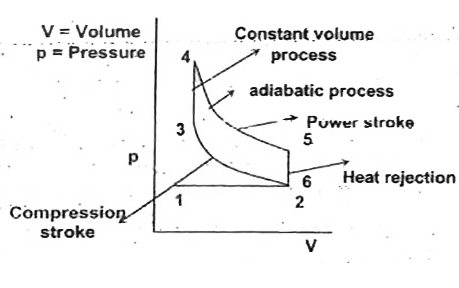
Figure shown represents such a cycle which is used in all Internal combustion engines. The figure shows a p-V diagram of the cycle. Using the engine stage numbering system, we begin at the lower left with Stage 1 being the beginning of the intake stroke of the engine. The pressure is near atmospheric pressure and the gas volume is at a minimum. Between Stage 1 and Stage 2 the piston is pulled out of the cylinder with the intake valve open. The pressure remains constant, and the gas volume increases as fuel/air mixture is drawn into the cylinder through the-intake valve. Stage 2 begins the compression stroke of the engine with the closing of the intake valve. Between Stage 2 and Stage 3, the piston moves back into the cylinder, the gas volume.decreases, and the pressure increases because work is done on the gas by the piston. Stage 3 is the beginning of the combustion of the fuel/air mixture. The combustion occurs very quickly and the volume remains constant. Heat is released during combustion which increases both the temperature and the pressure, according to the equation of slate. Slage 4 begins the power stroke of the engine. Between Stage 4 and Stage 5, the piston is driiven towards the crankshaft, the volume in increased, and the pressure falls as work is done by the gas on the píston. At Stage 5 the exhaust valve is opened and the residual heat in the gas is exchanged with the surroundings. The volume remains constant and the pressure adjusts back to atmospheric conditions. Stage 6 begins the exhaust stroke of the engine during which the piston. moves back into the cylinder, the volume decreases and the pressure remains constant. At the end of the exhaust stroke, conditions have returned to Stage 1 and the process repeats itself. During the cycle, work is done on the gas by the plston between stages 2 and 3. Work is done by the gas on the piston between stages 4 and 5. The difference between the work done by the gas and the work done on the gas is the area enclosed by the cycle curve and is the work produced by the cycle. The work times the rate of the cycle (cycles per second) is equal to the power produced by the engine.
Consider that the above diagram represents an ideal such cycle then choose the incorrect statement fora corresponding real cycle.AThe area of the p-V diagram for the real cycle will be lesser than that for ideal cycle.BThe shape of the p-V diagram for the real cycle will be similar to the corresponding ideal cycle.CThe power produced by the engine for an ideal cycle will be greater than that produced by corresponding real cycle.DThe shape of the p-V diagram for the real cycle will not be similar to the ideal cycle.
The area of a rectangle is 45516cm2. If its length is 714 cm, then find its breadth.
View SolutionOne end of a steel rod (K=46Js−1m−1^(@)C^(-1)of≤n>h1.0m is kept in ice at 0∘C and the other end is kept in boiling water at 100^(@)C.Theareaofcrosssectionoftherodis0.04cm^(2).As∑∈gnoheatloss→theatmosphere,f∈dthemassoftheiceme<∈gpersecond.Latentheatoffusionofice=3.36xx10^(5)Jkg^(-1) .
View SolutionConsider a vertical tube open at both ends. The tube consistss of two parts, each of different cross sections and each part having a piston which can move smoothly in respective tubes. The two piston which can move smoothly in respective tube wire. The piston are joined together by an inextensible wire. The combined mass of the two piston is 5kgand area of cross section of the upper piston is 10cm2 greater than that of the lower piston. Amount of gas enclosed by the pistons is 1mol. When the gas is heated slowly, pistons move by 50cm. Find the rise in the temperature of the gas in the form X/RK, where R is universal gas constant. Use g=10m/s2 and outside pressure =105N/m2).

View SolutionIn a petrol engine,the rate of production of heat due to the combustion of petrol is 7.46×105calh−1 . The efficiency of the engine is 30%. Calculate the horse power of the engine, if J is 4.2×107 erg cal−1
View SolutionTo move an airplane through the air, thrust is generated by some kind of propulsion system. Beginning with the Wright brothers' first flight, many airplanes have used internal combustion engines to turn propellers to generate thrust. Today, most general aviation or private airplanes are powered by internal combustion (IC) engines, much like the engine in your family automobile. When discussing engines, we must consider both the mechanical- operation of the machine and the thermodynamic processes that enable the machine to produce useful work. We consider the thermodynamics of a four-stroke IC engine.
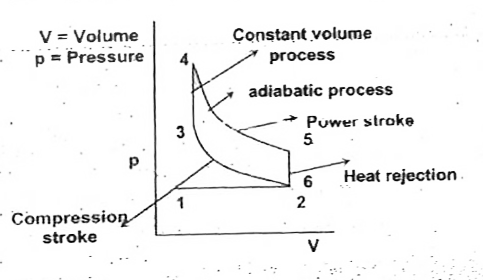
Figure shown represents such a cycle which is used in all Internal combustion engines. The figure shows a p-V diagram of the cycle. Using the engine stage numbering system, we begin at the lower left with Stage 1 being the beginning of the intake stroke of the engine. The pressure is near atmospheric pressure and the gas volume is at a minimum. Between Stage 1 and Stage 2 the piston is pulled out of the cylinder with the intake valve open. The pressure remains constant, and the gas volume increases as fuel/air mixture is drawn into the cylinder through the-intake valve. Stage 2 begins the compression stroke of the engine with the closing of the intake valve. Between Stage 2 and Stage 3, the piston moves back into the cylinder, the gas volume.decreases, and the pressure increases because work is done on the gas by the piston. Stage 3 is the beginning of the combustion of the fuel/air mixture. The combustion occurs very quickly and the volume remains constant. Heat is released during combustion which increases both the temperature and the pressure, according to the equation of slate. Slage 4 begins the power stroke of the engine. Between Stage 4 and Stage 5, the piston is driiven towards the crankshaft, the volume in increased, and the pressure falls as work is done by the gas on the píston. At Stage 5 the exhaust valve is opened and the residual heat in the gas is exchanged with the surroundings. The volume remains constant and the pressure adjusts back to atmospheric conditions. Stage 6 begins the exhaust stroke of the engine during which the piston. moves back into the cylinder, the volume decreases and the pressure remains constant. At the end of the exhaust stroke, conditions have returned to Stage 1 and the process repeats itself. During the cycle, work is done on the gas by the plston between stages 2 and 3. Work is done by the gas on the piston between stages 4 and 5. The difference between the work done by the gas and the work done on the gas is the area enclosed by the cycle curve and is the work produced by the cycle. The work times the rate of the cycle (cycles per second) is equal to the power produced by the engine.
Choose.the correct statement.
View Solution

