A section of an electrical circuit XY is shown in figure-5.100 which carries a current of 5A which is decreasing at the rate of 10A/s. Find the potential difference Vy−Vx'
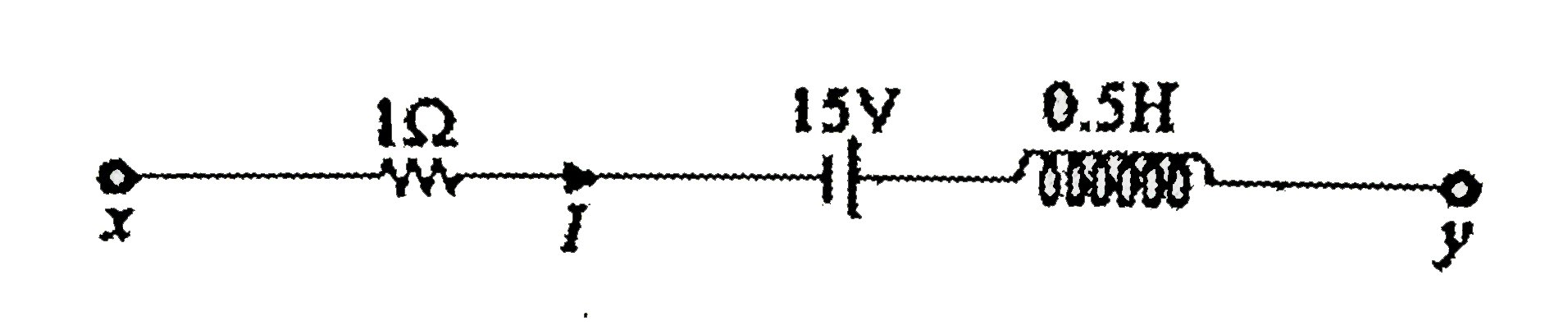
Step by step video & image solution for A section of an electrical circuit XY is shown in figure-5.100 which carries a current of 5A which is decreasing at the rate of 10 A//s. Find the potential difference V_(y)-V_(x') by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 12 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
When the current in the portion of the circuit shown in the figure is 2A and increasing at the rate of 1A/s,the measured potential difference Va−Vb=8V.However when the current is 2A and decreasing at the rate of 1A/s, the measured potential difference Va−Vb=4V.The values of R and L are:
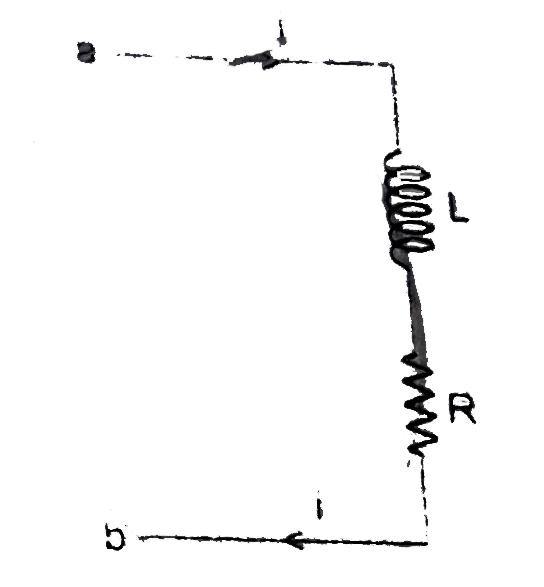 A3ohm and 2 Henry respectivelyB2ohm and 3 Henry respectivelyC10ohm and 6 Henry respectivelyD6ohm and 1 Henry respectively
A3ohm and 2 Henry respectivelyB2ohm and 3 Henry respectivelyC10ohm and 6 Henry respectivelyD6ohm and 1 Henry respectivelyIf I=5A and decreasing at a rate of 102(A/sec) , then VB−VA
 A5VB10VC15VD20V
A5VB10VC15VD20VWhen the current in a certain inductor coil is 5.0A and is increasing at the rate of 10.0A/s,the magnitude of potential difference across the coil is 140V.When the current is 5.0A and decreasing at the rate of 10.0A/s,the potential difference is 60V.The self inductance of the coil is :
A2HB4HC10HD12H
A part of a complete circuit is shown in the figure . At some instant the value of current I is 1 A and it is decreasing at a rate of 102As−1 . The value of the potential difference VP−VQ, (in volts) at that instant , is ____________.
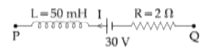
View SolutionIf the instantaneous change on the capacitor is 100μC and current through the circuit is decreasing at the rate of 2×103 As then potential difference VA−VB is equal to
_PHY_E06_046_Q01.png)
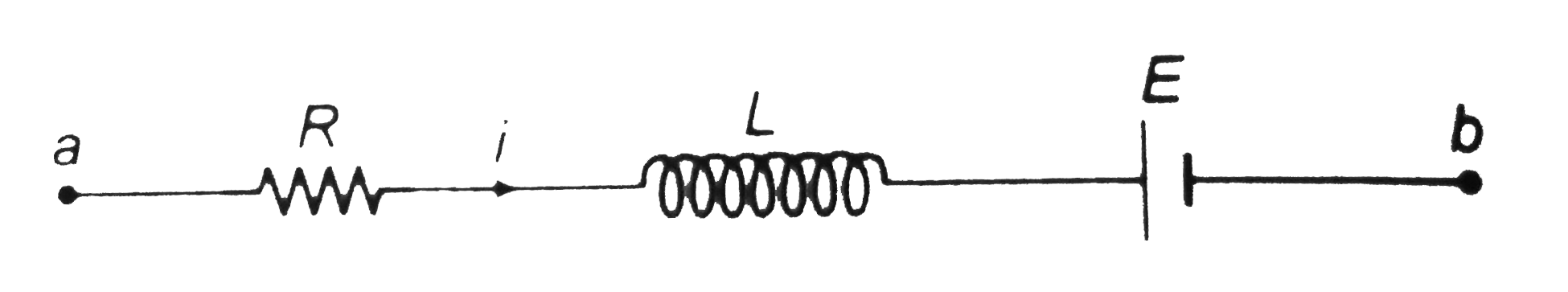
View SolutionIn the circuit diagram shown in Figure, R=10Ω,L=l5H,E=20v,i=2A. This current is decreasing at a rate of −1.0A/s. Find Vab at this instant.
View SolutionWhat is the potential difference VB−VA when the current i is 5A and is decreasing at a rate of 103A /s
View SolutionWhen the current in the portion of the circuit shown in the figure is 2 A and increasing at the rate of 1As−1, then the measured potential difference Vab=8V.
However, when the current is 2 A and decreasing at the rate of 1As−1, then the measured potential difference Vab=4V.
The values of R and L are

View Solution