Which of the following compound can show geometrical isomerism ?
None of the above
The correct Answer is:c
To determine which of the given compounds can show geometrical isomerism, we need to analyze each compound based on the presence of a double bond or a cyclic structure with different substituents.
1. Identify the Compounds: Let's denote the compounds as A, B, and C. We will analyze each one to check for geometrical isomerism.
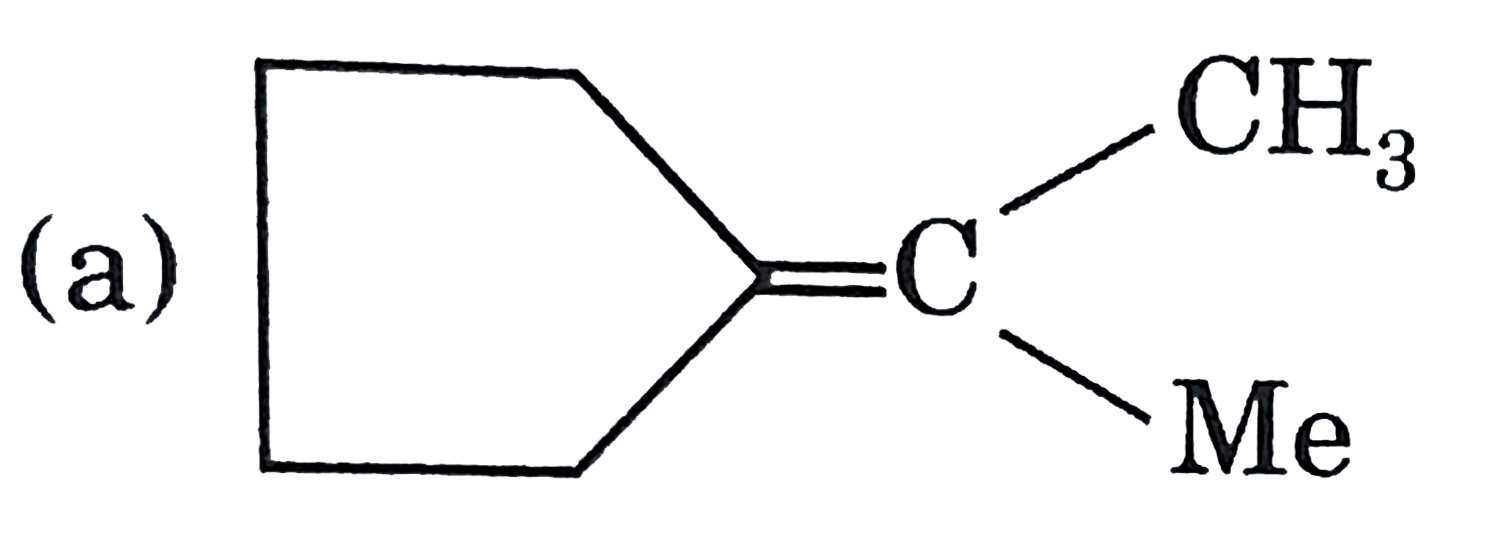
2. Analyze Compound A:
- Compound A has a cyclic structure with substituents.
- Check the substituents: If both substituents attached to the double bond or the ring are the same, geometrical isomerism cannot occur.
- In this case, both substituents on the relevant positions are the same (e.g., CH3 and CH3), so Compound A cannot show geometrical isomerism.
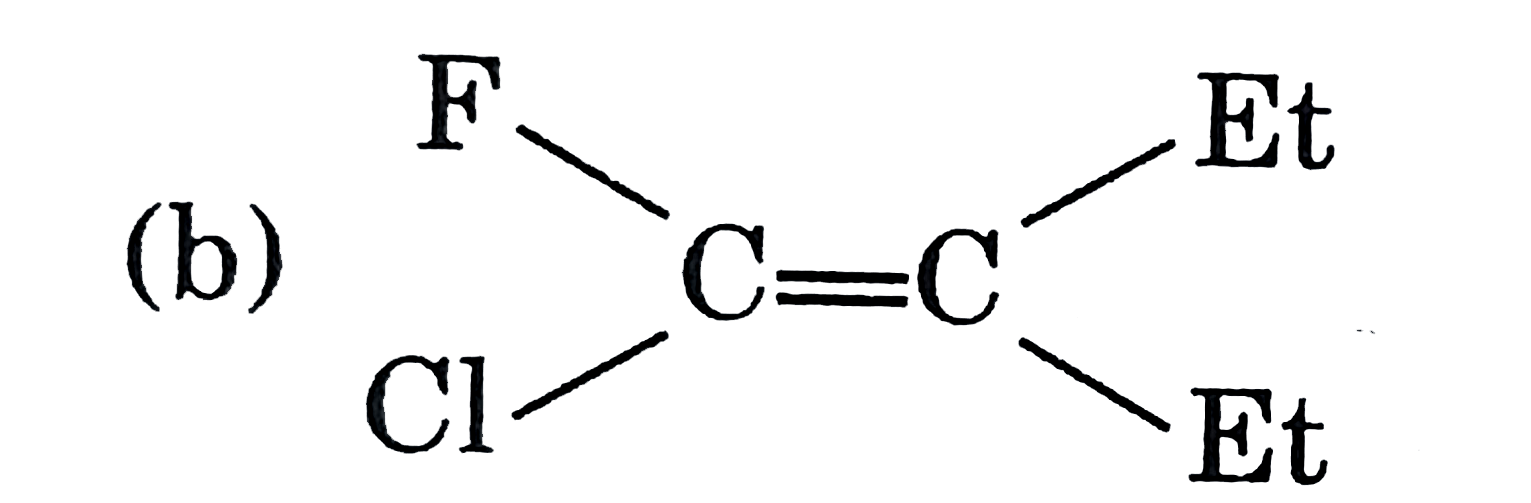
3. Analyze Compound B:
- Compound B also has a double bond.
- Check the substituents on the double bond: If both substituents are the same, geometrical isomerism cannot occur.
- Here, we find that both substituents are the same (e.g., CH3 and CH3), so Compound B cannot show geometrical isomerism.
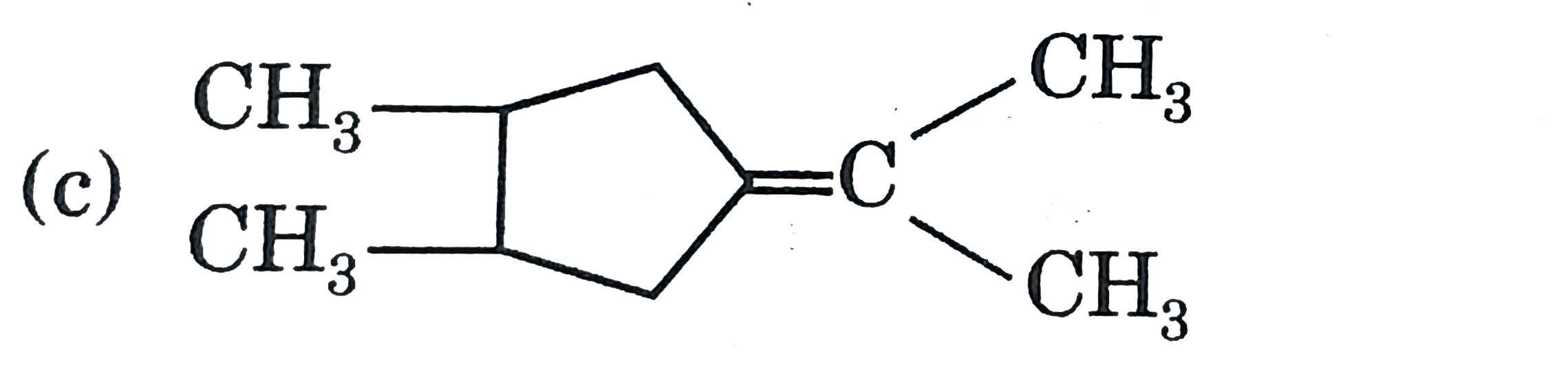
4. Analyze Compound C:
- Compound C has a double bond with different substituents.
- Check the substituents: If there are two different groups attached to each carbon of the double bond, geometrical isomerism can occur.
- In this case, we have CH3 and H on one carbon, and CH3 and H on the other carbon. Since these groups are different, geometrical isomerism is possible.
- The possible isomers are:
- Cis Isomer: Both CH3 groups are on the same side.
- Trans Isomer: The CH3 groups are on opposite sides.
- Therefore, Compound C can show geometrical isomerism.
5. Conclusion: Based on the analysis, the compound that can show geometrical isomerism is Compound C.
Final Answer:
The compound that can show geometrical isomerism is C.
- Compound A has a cyclic structure with substituents.
- Check the substituents: If both substituents attached to the double bond or the ring are the same, geometrical isomerism cannot occur.
- In this case, both substituents on the relevant positions are the same (e.g., CH3 and CH3), so Compound A cannot show geometrical isomerism.
- Compound B also has a double bond.
- Check the substituents on the double bond: If both substituents are the same, geometrical isomerism cannot occur.
- Here, we find that both substituents are the same (e.g., CH3 and CH3), so Compound B cannot show geometrical isomerism.
- Compound C has a double bond with different substituents.
- Check the substituents: If there are two different groups attached to each carbon of the double bond, geometrical isomerism can occur.
- In this case, we have CH3 and H on one carbon, and CH3 and H on the other carbon. Since these groups are different, geometrical isomerism is possible.
- The possible isomers are:
- Cis Isomer: Both CH3 groups are on the same side.
- Trans Isomer: The CH3 groups are on opposite sides.
- Therefore, Compound C can show geometrical isomerism.
The compound that can show geometrical isomerism is C.
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
Which of the following compounds can show geometrical isomerism.
A B
B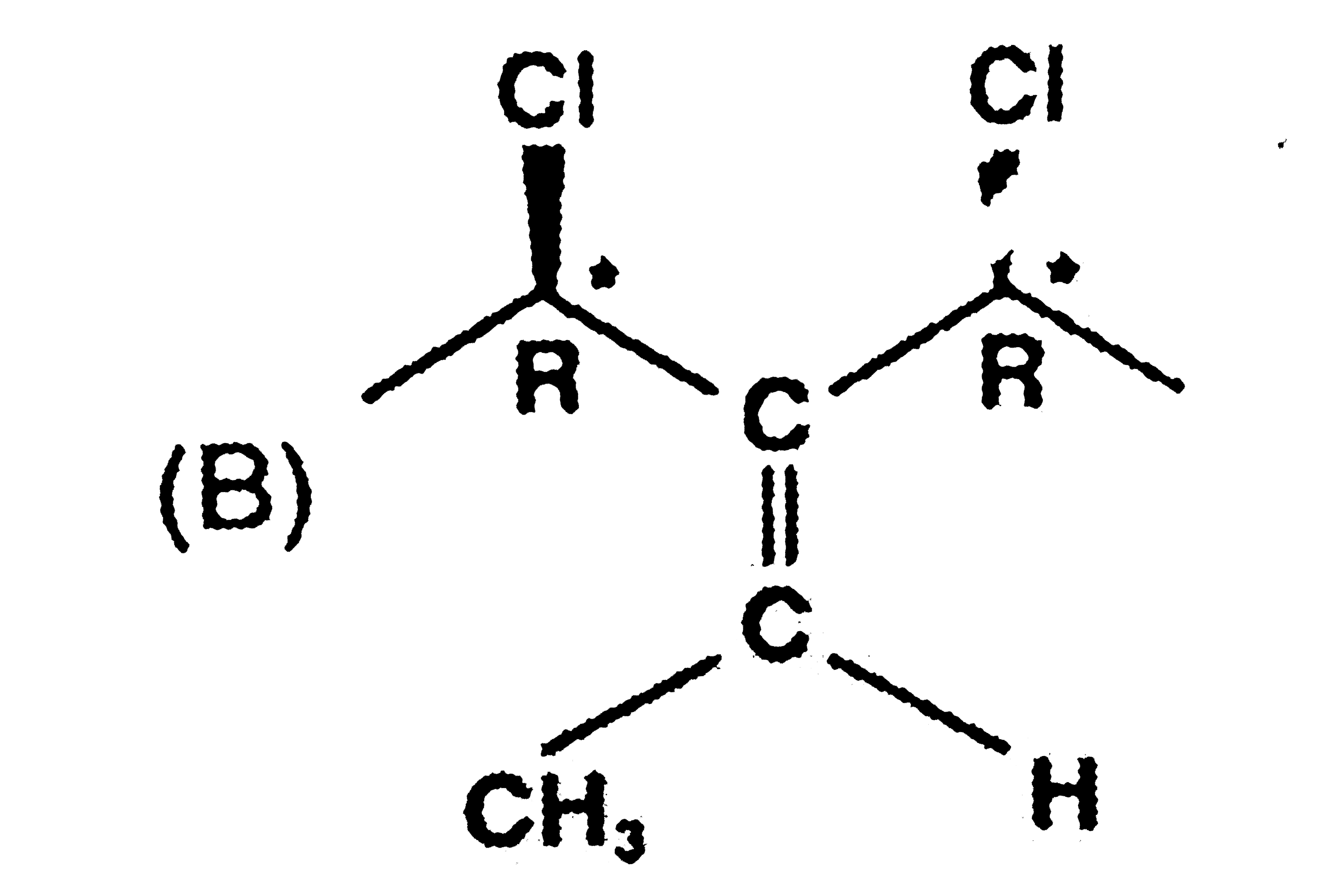 C
C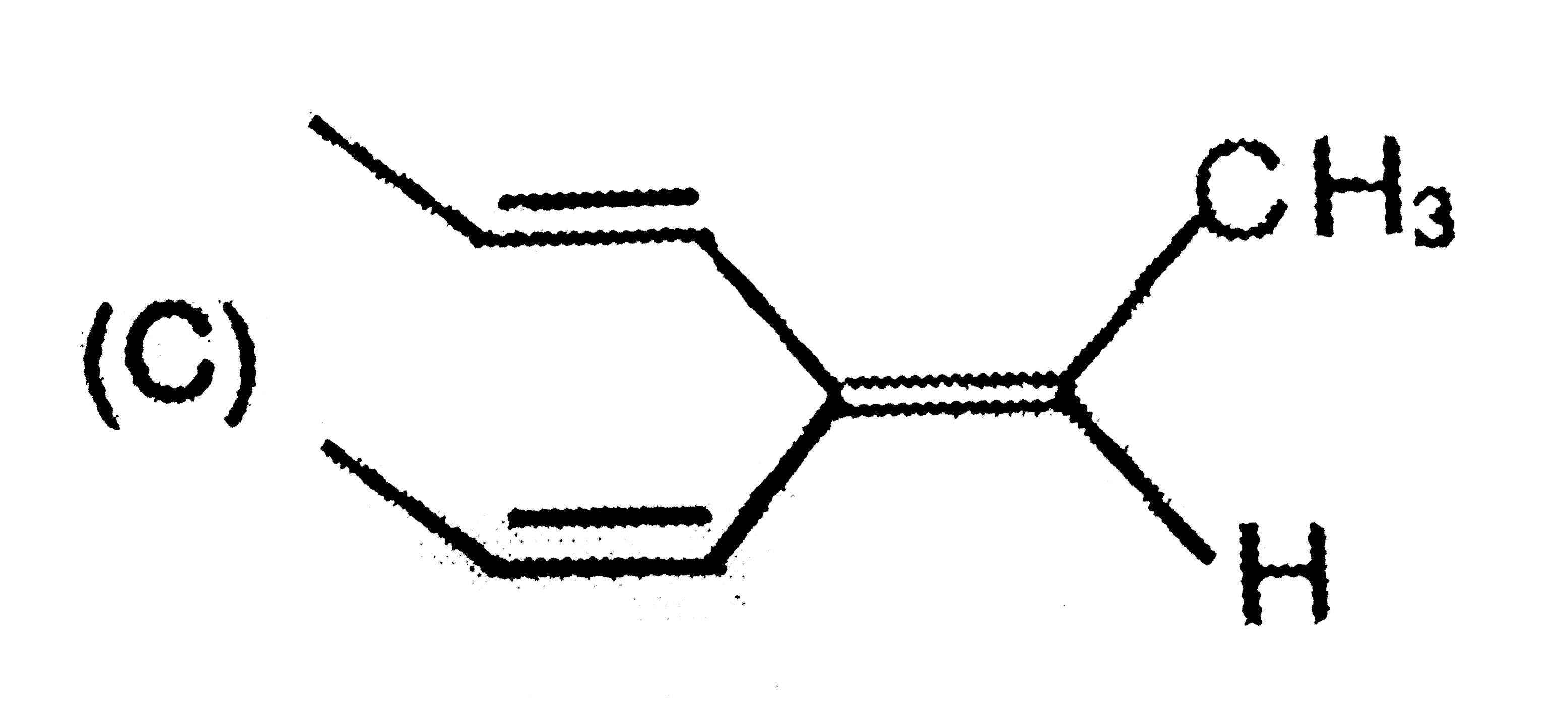 D
D
Which of the following compound can not show geometrical isomerism ?
A B
B C
C D
D
Which of the following compound can not show geometrical isomerism?1
A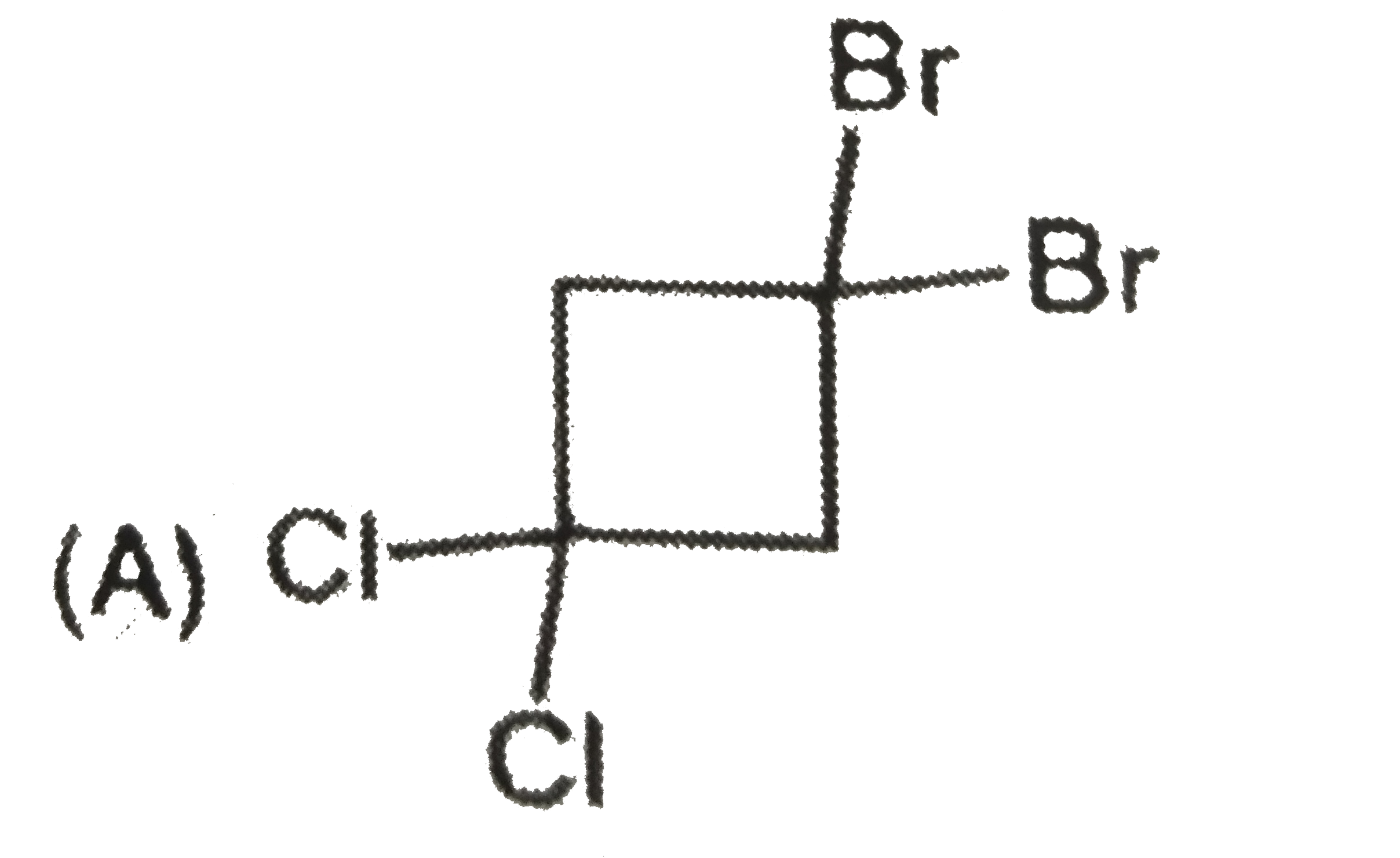 B
B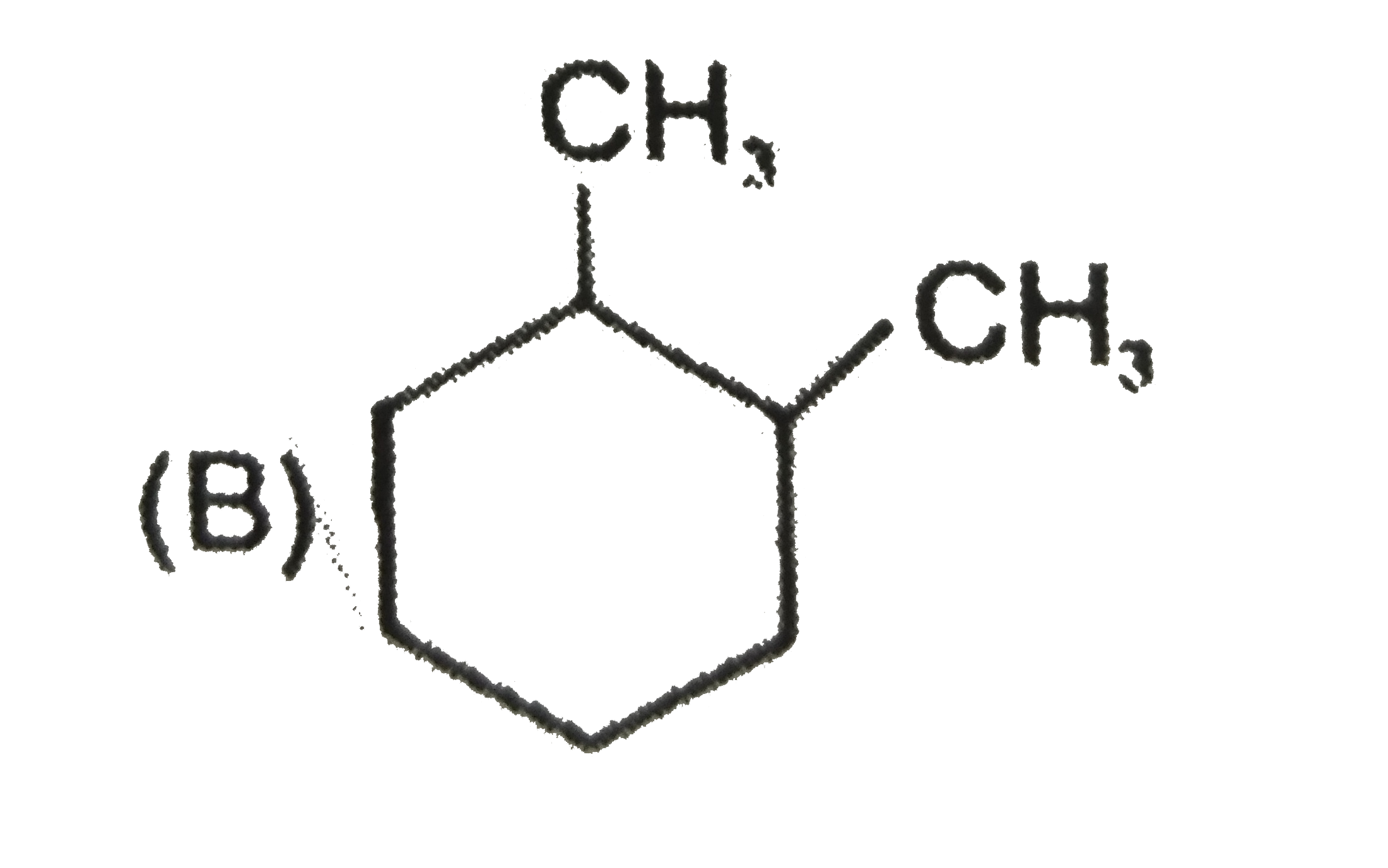 C
C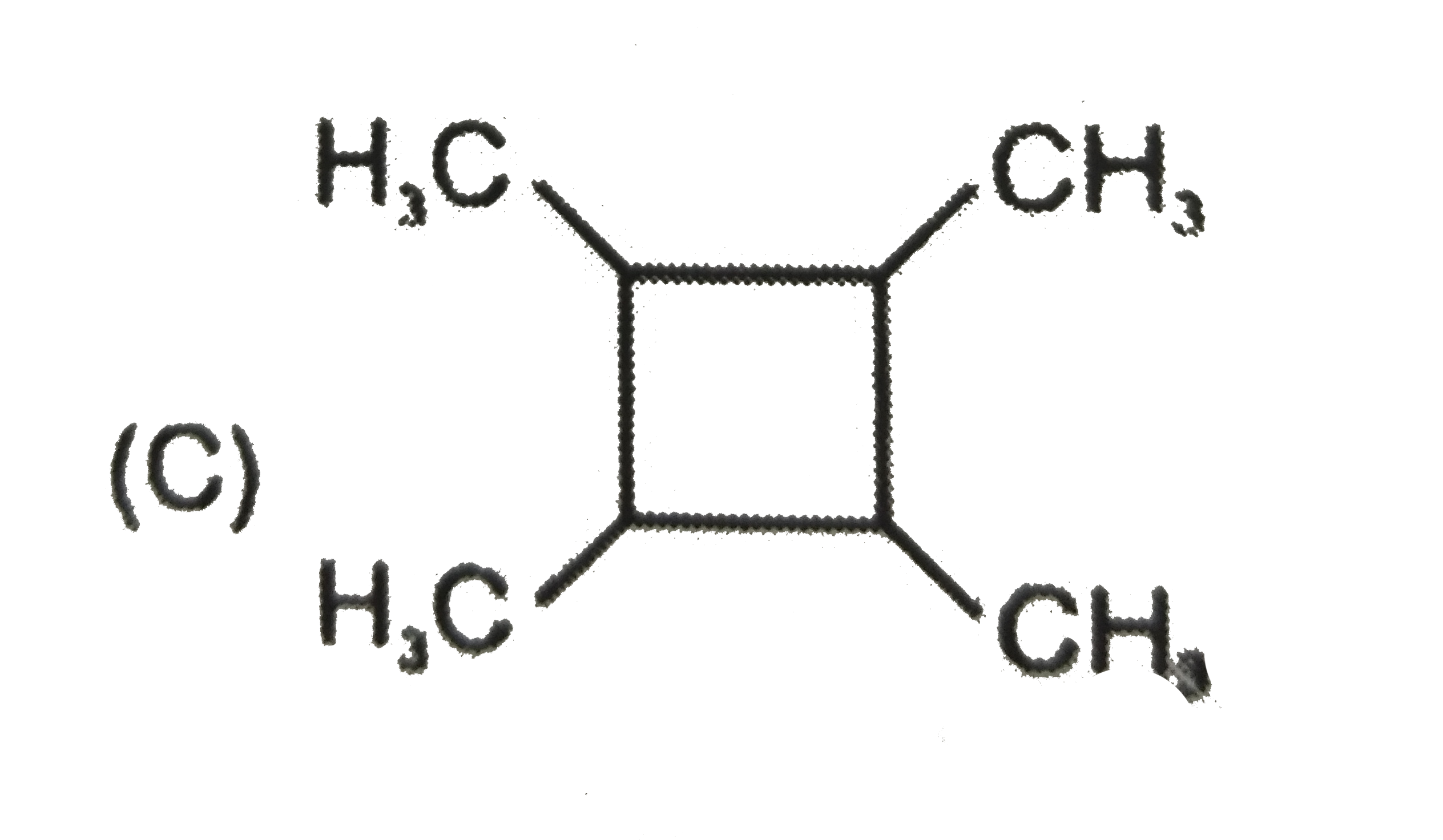 D
D
Which of the following compounds shows geometrical isomerism ?
View SolutionWhich of the following compound will show geometrical isomerism?
View SolutionWhich of the following compound(s) show geometrical isomerism?
View SolutionWhich of the following compounds will show geometrical isomerism ?
View SolutionWhich of the following compounds will show geometrical isomerism
View Solution