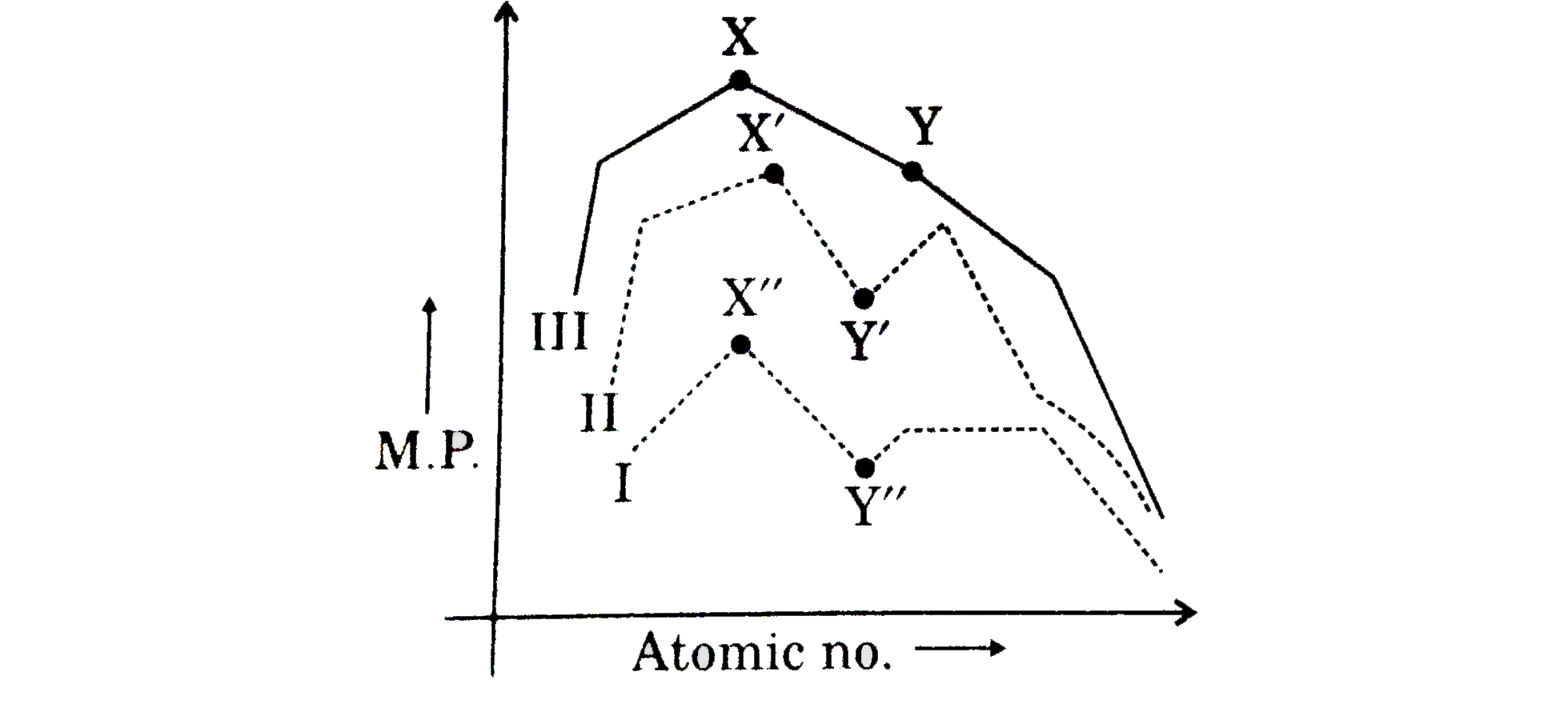
Refer to the graph for trends in M.P. of transition elements of 3d,4d and 5d series.
Q. What does maxima at point 'X' indicate?
One unpaired electron per d-orbital is particularly favourable for strong inteeratomic interaction.
Strong metallic bonding.
Both a and b
None of the above.
The correct Answer is:C
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
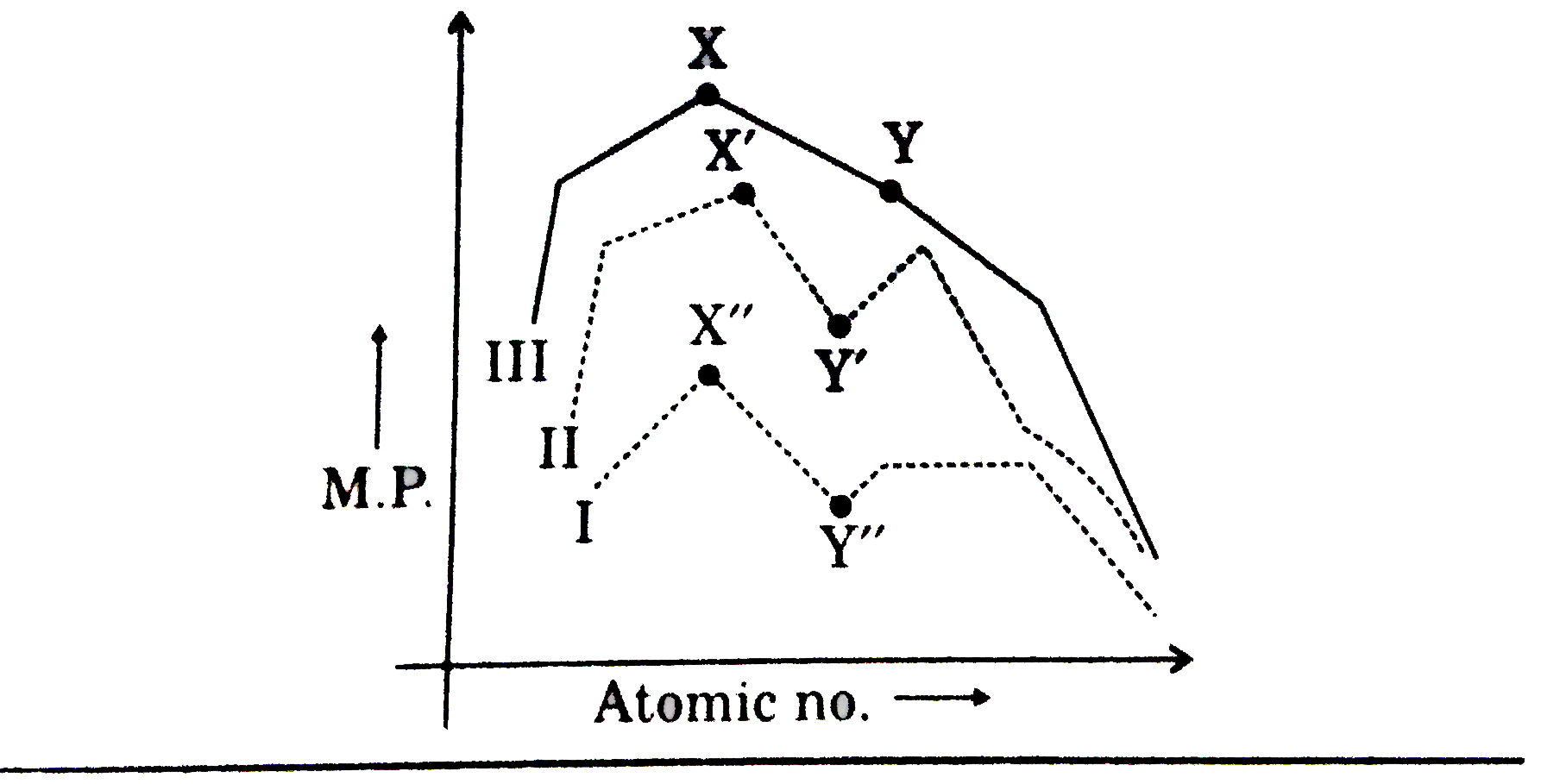
Refer to the graph for trends in M.P. of transition elements of 3d,4d and 5d series.
Q. A metal having high boiling point:Ahas high enthalpy of atomizationBtends to be noble in their reactionsChas strong metallic bondingDall of the above.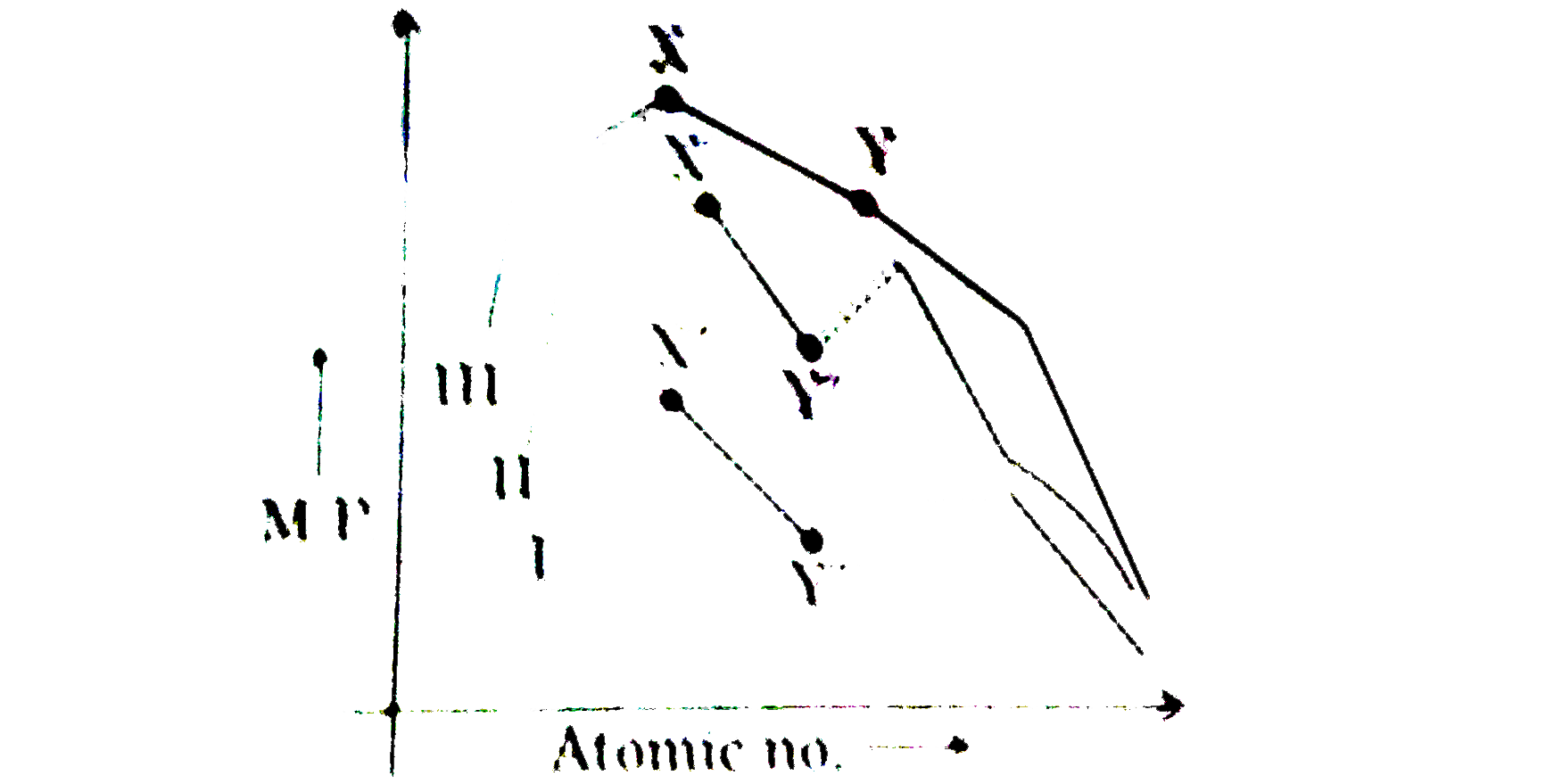
Refer to the graph for trends in M.P. of transition elements of 3d,4d and 5d series.
Q. Choose the correct statement(s).AIII refers to 3rd transition series of periodic table.BX corresponds to tungstenCY" corresponds to manganese.Dall of the above.In the above graph, point D indicates
ALimiting PoointBYield pointCBreaking pointDElastic limit
Read the given passage and answer the questions number 1 to 5 that follow :
The d-block of the periodic table contains the elements of the groups 3 - 12 and are known as transition elements. In general, the electronic configuration of these elements is (n - 1) d1−10ns1−2. The d-orbitals of the penultimate energy level in their atoms receive electrons giving rise to the three rows of the transition metals i.e., 3d, 4d and 5d series. However, Zn Cd and Hg are not regarded as transition elements. Transition elements exhibit certain characteristic properties like variable oxidation states, complex formation, formation of coloured ions and alloys, catalytic activity, etc. Transition metals are hard (except Zn, Cd and Hg) and have a high melting point.
Which transition metal of 3d series does not show variable oxidation states ?
View SolutionRead the given passage and answer the questions number 1 to 5 that follow :
The d-block of the periodic table contains the elements of the groups 3 - 12 and are known as transition elements. In general, the electronic configuration of these elements is (n - 1) d1−10ns1−2. The d-orbitals of the penultimate energy level in their atoms receive electrons giving rise to the three rows of the transition metals i.e., 3d, 4d and 5d series. However, Zn Cd and Hg are not regarded as transition elements. Transition elements exhibit certain characteristic properties like variable oxidation states, complex formation, formation of coloured ions and alloys, catalytic activity, etc. Transition metals are hard (except Zn, Cd and Hg) and have a high melting point.
Why are melting points of transition metals high ?
View SolutionRead the given passage and answer the questions number 1 to 5 that follow :
The d-block of the periodic table contains the elements of the groups 3 - 12 and are known as transition elements. In general, the electronic configuration of these elements is (n - 1) d1−10ns1−2. The d-orbitals of the penultimate energy level in their atoms receive electrons giving rise to the three rows of the transition metals i.e., 3d, 4d and 5d series. However, Zn Cd and Hg are not regarded as transition elements. Transition elements exhibit certain characteristic properties like variable oxidation states, complex formation, formation of coloured ions and alloys, catalytic activity, etc. Transition metals are hard (except Zn, Cd and Hg) and have a high melting point.
Why are Zn, Cd and Hg non-transition elements ?
View SolutionWhich of the following transition metals of 4d series has the lowest melting point?
View SolutionWhich one belongs to 3d-transition series
View Solution

