A solid conducting sphere of radius r is having a charge Q and point charges +q and -q are kept at distance d from the centre of sphere as shown in the figure. The electric potential at the centre of solid sphere
(assume potential to be 0 at infinity)
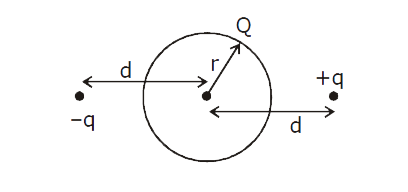
14πε_(0)Qr
Similar Questions
A conducting sphere of radius R is given a charge Q. The electric potential and the electric field at the centre of the sphere respectively are
View SolutionA point charge Q is placed at a distance d from the centre of an uncharged conducting sphere of radius R. The potential of the sphere is (d>R): (Assume potential at infinity to be zero)
View SolutionA point charge +Q is located at a distance of r from the centre of an uncharged conducting sphere of radjus R. Find the electric potential of that sphere Find the electric field and electric potential at the centre of the sphere due to induced charges on the sphere?
View SolutionA non-conducting sphere of radius R is given a charge Q. Charge is uniformly distributed in its volume. The electric potential at centre and at the surface of sphere respectively are
View SolutionPotential at a point x-distance from the centre inside the conducting sphere of radius R and charged with charge Q is
View SolutionA conducting sphere of radius R is given a charge Q . The electric potential and the electric field at the centre of the sphere respectively are
View SolutionA conducting sphere of radius R is given a charge Q . The electric potential and the electric field at the centre of the sphere respectively are
View SolutionThe region between two concentric spheres of radii 'a' and 'b', respectively(see figure), has volume charge density ρ=Ar , where A is a constant and r is the distance from the centre. At the centre of the spheres is a point charge Q. The value of A such that the electric field in the region between the spheres will be constant, is :
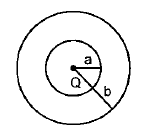
View Solution
