In a triangle ABC, BD is a median. If l(BD)=√34l(AB) and ∠DBC=π2. Determine the ∠ABC
The correct Answer is:120∘
Step by step video, text & image solution for In a triangle ABC, BD is a median. If l(BD) = (sqrt3)/4 l(AB) and /_DBC = pi/2. Determine the /_ABC by Maths experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 12 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Topper's Solved these Questions
- SOLUTION OF TRIANGLEBook:MOTIONChapter:SOLUTION OF TRIANGLEExercise:EXERCISE - 4( LEVEL I)
Explore 4 Videos
- SOLUTION OF TRIANGLEBook:MOTIONChapter:SOLUTION OF TRIANGLEExercise:EXERCISE - 4( LEVEL II)
Explore 10 Videos
- SOLUTION OF TRIANGLEBook:MOTIONChapter:SOLUTION OF TRIANGLEExercise:EXERCISE - 2 (LEVEL II)
Explore 6 Videos
- SEQUENCE & SERIES Book:MOTIONChapter:SEQUENCE & SERIES Exercise:Exercise -4 Level -II Previous Year /JEE Advanced
Explore 22 Videos
- STRAIGHT LINE Book:MOTIONChapter:STRAIGHT LINE Exercise:Exercise 4 Lelvel -II
Explore 7 Videos
Similar Questions
For a regular polygon, let r and R be the radii of the inscribed and the circumscribed circles. A false statement among the following is There is a regular polygon with rR=1√2 (17) There is a regular polygon with rR=23 (30) There is a regular polygon with rR=√32 (47) There is a regular polygon with rR=12 (60)
View SolutionLet ABC and ABC' be two non-congruent triangles with sides AB=4,AC=AC'=2√2 and angle B=30∘. The absolute value of the differnce between the area of these triangle is _______
View Solution(i)Find the length of Angle Bisector
View SolutionLet Vr denote the sum of first r terms of an arithmetic progression (A.P.) whose first term is r and the common difference is (2r – 1).
Let Tr=Vr+1−Vr−2andQr+1−Tr for r=1,2…….
1. The sum V1+V2+….+Vn is
A. 112n(n+1)(3n2−n+1)
B. 112n(n+1)(3n2+n+2)
C. 12n(2n2−n+1)
D. 12(2n3−2n+3).
2. Let Tr=Vr+1−Vr−2 and Qr=Tr+1−Tr for r=1,2 Tr is always
(A) an odd number
(B) an even number
(C) a prime number
(D) a composite number
View SolutionLet O(0, 0), P(3, 4), Q(6, 0) be the vertices of the triangle OPQ. The point R inside the triangle OPQ is such that the triangles OPR, PQR are of equal area. The coordinates of R are
View SolutionIn the figure given,/_ABC, is a right isosceles triangle with right angle at C.CD is a parallel to AB and BD = BA.The degree measure of /_DBC equals
View SolutionIn a triangle ABC, BD is a median.If l(BD)=(sqrt(3))/(4)l(AB) and /_DBC=(pi)/(2) Determine the /_ABC
View SolutionIn Figure, ABC is an isosceles triangle with AB=AC, BD and CE are two medians of the triangle. Prove that BD=CE
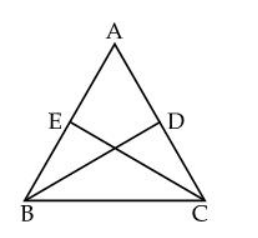
View SolutionABC is an isosceles triangle with AB =AC and BD,CE are its two medians. Show that BD=CE .
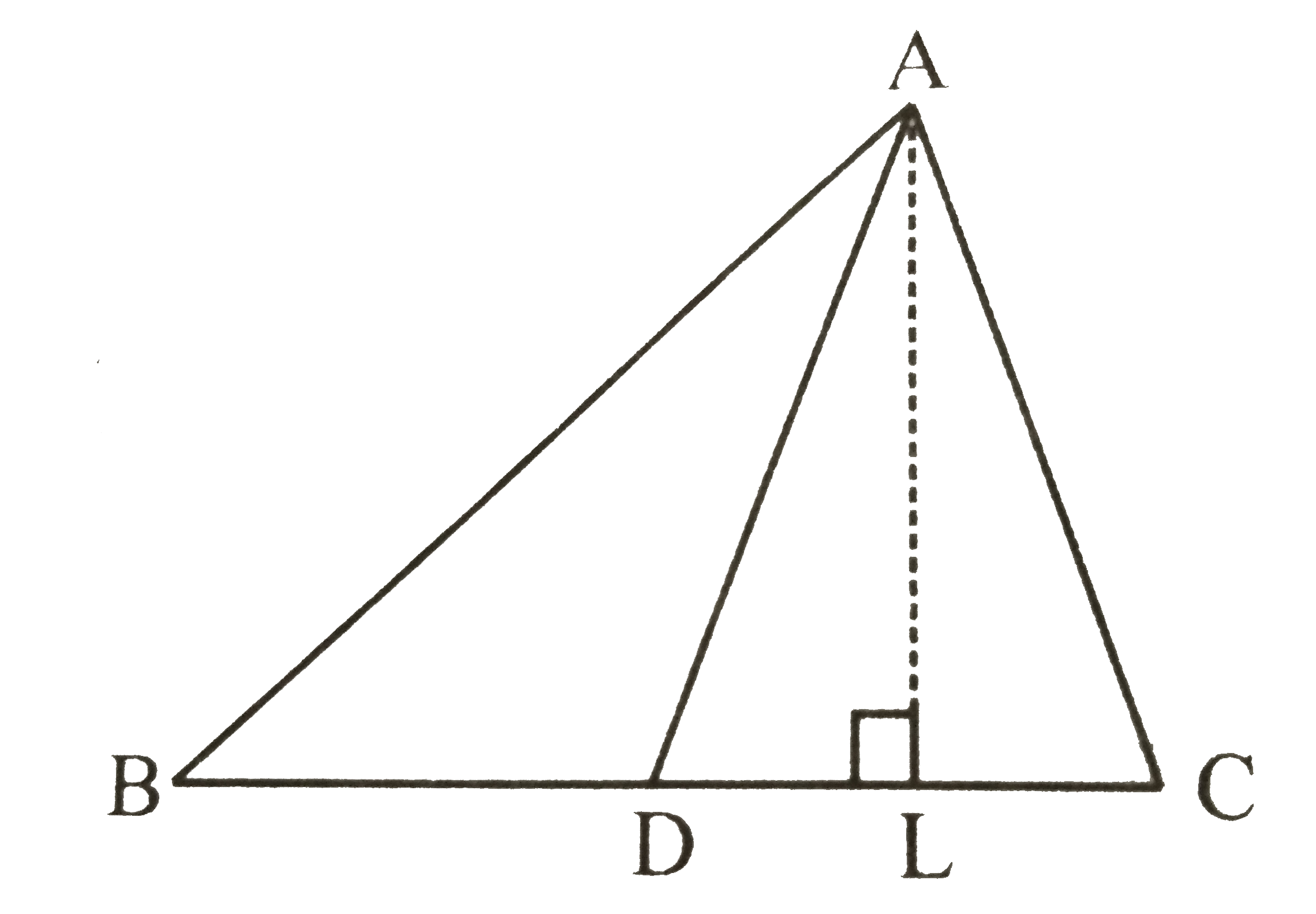
View Solutionत्रिभुज ABC में यदि AD एक माध्यिका है , तो दिखाइए कि
AB2+AC2=2(AD2+BD2).
View Solution△ABC में, यदि AD माध्यिका है तो सिद्ध कीजिए कि AB2+AC2=2(AD2+BD2)
View Solutionसमद्विबाहु त्रिभुज ABC में AB=AC तथा BD⊥AC हो, तो सिद्ध कीजिए कि BD2−CD2=2CD.AD
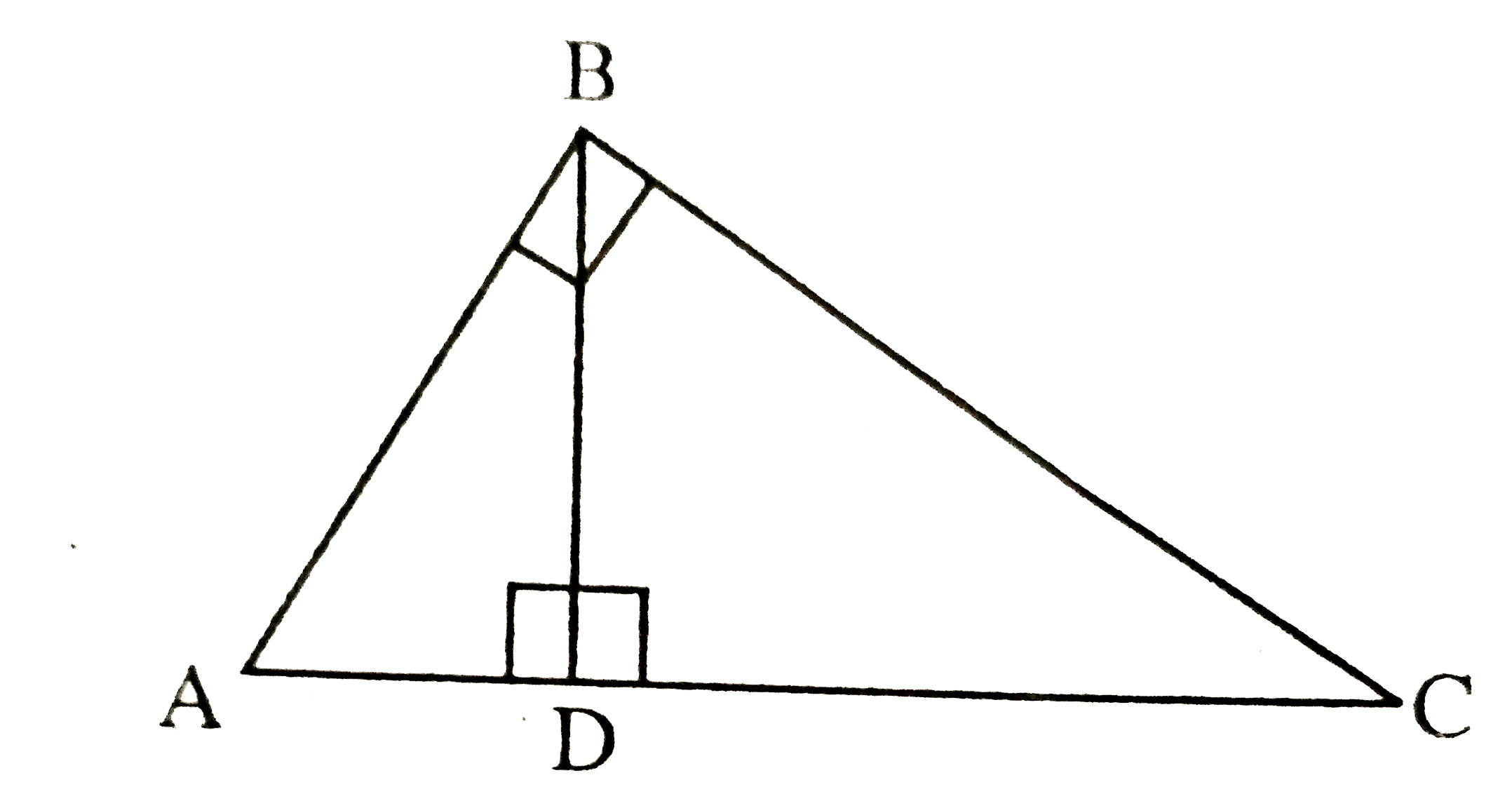
View SolutionIn a right-angled triangle ABC,∠ABC=90∘,AB=3cm,BC=4cm and the perpendicular BD on the side AC from the point B which meets the side AC at the point D. Determine the length of BD.
View SolutionABC সমকোণী ত্রিভুজ ∠B=90∘ , AB র উপর D এমন একটি বিন্দু যে AB : BC : BD = √3 : 1 : 1 , ∠ACD -এর মান নির্ণয় করো ।
View SolutionABC is an isosceles triangle with AB =AC and BD,CE are its two medians. Show that BD=CE .
View Solutionएक त्रिभुज ABC में BD एक माध्यिका है। यदि l(BD)=√34⋅(AB) एवं ∠DBC=π2 हो, तो ∠ABC का मान ज्ञात कीजिए।
View Solution
